|
Vaimos
Vaimos (Voilier Autonome Instrumenté pour Mesures Océanographiques de Surface) is an autonomous sailing boat with embedded instrumentation for ocean surface measurements. Its goal is to collect measurements at the surface of the ocean. This robot is the result of a collaboration between ENSTA Bretagne and IFREMER. ENSTA-Bretagne (OSM Team) develops control algorithms and the software architecture, IFREMER (LPO+RDT) builds the mechanics, the embedded instrumentation. Brest-Douarnenez. One of the longest trips the robot has done is Brest-Douarnenez where Vaimos has done more than 100 km in an autonomous mode. Since Vaimos has made trips more than 350 km long. In 2013, Vaimos participated in the World Robotic Sailing Championship (WRSC) 2013 in Brest, France . Control The robot follows a desired trajectory which is a sequence of lines. When following a line, the robot has two modes. # the ''direct mode'': the direction to be followed is consistent with the directi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotics
Robotics is an interdisciplinarity, interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrates fields of mechanical engineering, electrical engineering, Information engineering (field), information engineering, mechatronics, electronics, bioengineering, computer engineering, control engineering, software engineering, mathematics, etc. Robotics develops machines that can substitute for humans and replicate human actions. Robots can be used in many situations for many purposes, but today many are used in dangerous environments (including inspection of radioactive materials, bomb detection and bomb disposal, deactivation), manufacturing processes, or where humans cannot survive (e.g. in space, underwater, in high heat, and clean up and containment of hazardous materials and radiation). Robots can take any form, b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World Robotic Sailing Championship
WRSC (World Robotic Sailing Championship) is an autonomous sailboat competition that aims at stimulating the development of autonomous marine robotics. It is a spinoff competition from the Microtransat challenge, a trans Atlantic race for autonomous sailing robots. The WRSC is intended to promote the development of autonomous wind propelled sailing robots, through a series of short distance races, navigation and autonomy challenges. Many teams who take part in the Microtransat (or who plan to) also attend the WRSC. The accompanying IRSC (International Robotic Sailing Conference) provides researchers working on problems related to autonomous sailing the chance to exchange ideas during a scientific conference. History The first World Robotic Sailing Championships (WRSC) was organised by INNOC (The Austrian Association for Innovative Computer Science) and took place in Austria in 2008; it has taken place annually in different country every year since. ''First edition'' (2008) F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autonomous Sailing Ship
A sailing ship is a sea-going vessel that uses sails mounted on masts to harness the power of wind and propel the vessel. There is a variety of sail plans that propel sailing ships, employing square-rigged or fore-and-aft sails. Some ships carry square sails on each mast—the brig and full-rigged ship, said to be "ship-rigged" when there are three or more masts. Others carry only fore-and-aft sails on each mast, for instance some schooners. Still others employ a combination of square and fore-and-aft sails, including the barque, barquentine, and brigantine. Early sailing ships were used for river and coastal waters in Ancient Egypt and the Mediterranean. The Austronesian peoples developed maritime technologies that included the fore-and-aft crab-claw sail and with catamaran and outrigger hull configurations, which enabled the Austronesian expansion into the islands of the Indo-Pacific. This expansion originated in Taiwan BC and propagated through Island Southeast A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
École Nationale Supérieure De Techniques Avancées Bretagne
The ''École Nationale Supérieure de Techniques Avancées de Bretagne'' ( en, National Institute of Advanced Technologies of Brittany) often referred as ENSTA Bretagne formerly ENSIETA is one of the 207 French engineering schools accredited on 1 September 2017 to deliver engineering diplomas (French grande école of engineering). The ENSTA Bretagne is a higher education establishment and a research centre run under the supervision of the French Ministry of Armed Forces which governs a total of 4 engineering schools: École Polytechnique, ENSTA ParisTech, ENSTA Bretagne and ISAE-Supaero. It is the most prestigious engineering school in France which deals with marine and naval engineering. Moreover, ENSTA Bretagne is an applied school for the École Polytechnique, because of its excellence in lots of strategic fields. The school gets a specific partnership with IMT Atlantique, the second Institut Mines-Télécom of France while the best one is Telecom Paris. Every year, it tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IFREMER
) , preceding2 = ''Institut Scientifique et Technique des Pêches Maritimes'' ( en, Scientific and technical institute for marine fisheries) , dissolved = , superseding = , jurisdiction = , headquarters = Brest, France , employees = 1,593 , budget = 213 million euros , chief1_name = François Houllier , chief1_position = ''Président directeur général'' (CEO) , chief2_name = , chief2_position = , parent_agency = , child1_agency = , child2_agency = , website www.ifremer.fr, footnotes = IFREMER (Institut Français de Recherche pour l'Exploitation de la Mer; ) is an oceanographic institution in Brest, France. Scope of works Ifremer focuses its research activities in the following areas: * Monitoring, use and enhancement of coastal seas * Monitoring and optimization of aquaculture production * Fishery resources * Exploration and exploitation of the oceans and their biodiversity * Circulation and marine ecosys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Points Of Sail
A point of sail is a sailing craft's direction of travel under sail in relation to the true wind direction over the surface. The principal points of sail roughly correspond to 45° segments of a circle, starting with 0° directly into the wind. For many sailing craft 45° on either side of the wind is a ''no-go'' zone, where a sail is unable to mobilize power from the wind. Sailing on a course as close to the wind as possible—approximately 45°—is termed ''beating'', a point of sail when the sails are ''close-hauled''. At 90° off the wind, a craft is on a ''beam reach''. The point of sail between beating and a beam reach is called a ''close reach''. At 135° off the wind, a craft is on a ''broad reach''. At 180° off the wind (sailing in the same direction as the wind), a craft is ''running downwind''. A given point of sail (beating, close reach, beam reach, broad reach, and running downwind) is defined in reference to the true wind—the wind felt by a stationary observe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval Arithmetic
Interval arithmetic (also known as interval mathematics, interval analysis, or interval computation) is a mathematical technique used to put bounds on rounding errors and measurement errors in mathematical computation. Numerical methods using interval arithmetic can guarantee reliable and mathematically correct results. Instead of representing a value as a single number, interval arithmetic represents each value as a range of possibilities. For example, instead of saying the height of someone is approximately 2 meters, one could using interval arithmetic, say that the height of the person is definitely between 1.97 meters and 2.03 meters. Mathematically, using interval arithmetic, instead of working with an uncertain real-valued variable x, one works with an interval ,b/math> that defines the range of values that x can have. In other words, any value of the variable x lies in the closed interval between a and b. A function f, when applied to x, yields an inexact value; f in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
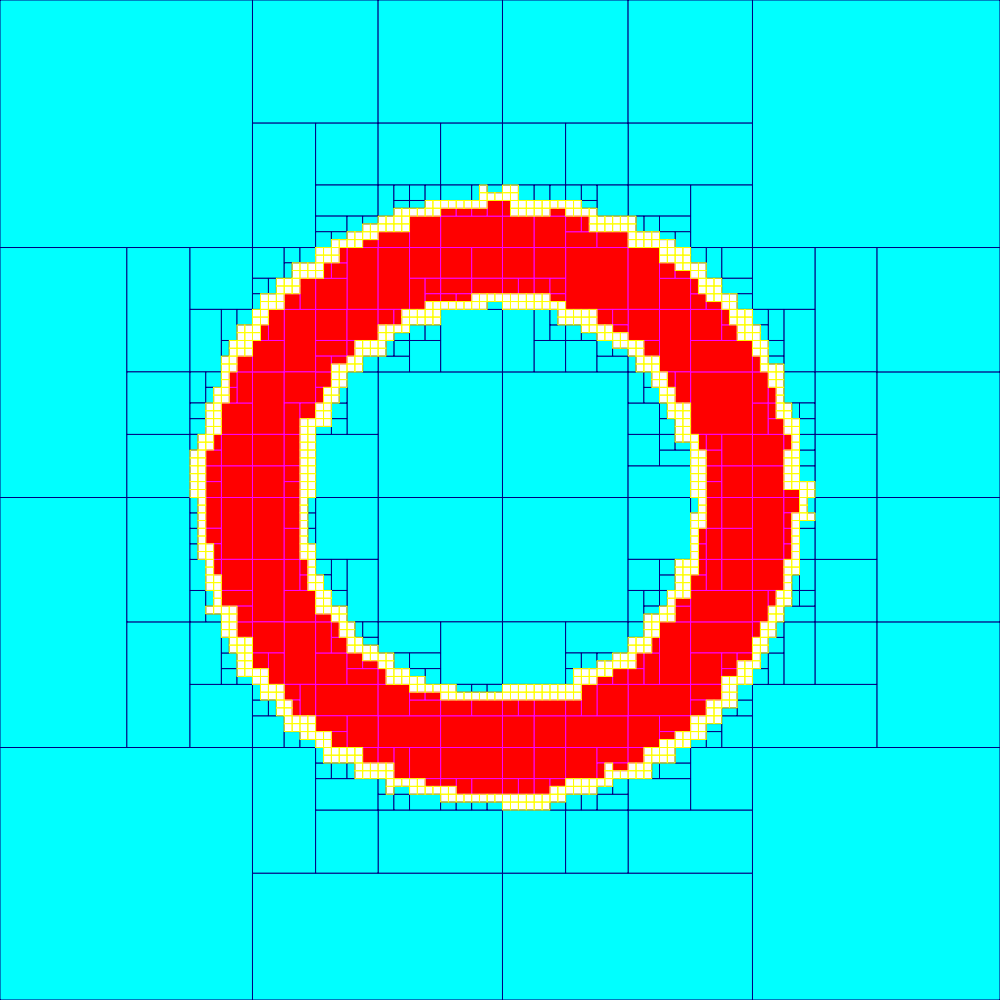
Set Inversion
In mathematics, set inversion is the problem of characterizing the preimage ''X'' of a set ''Y'' by a function ''f'', i.e., ''X'' = ''f'' −1(''Y'' ) = . It can also be viewed as the problem of describing the solution set of the quantified constraint "''Y''(''f'' (''x''))", where ''Y''( ''y'') is a constraint, e.g. an inequality, describing the set ''Y''. In most applications, ''f'' is a function from R''n'' to R''p'' and the set ''Y'' is a box of R''p'' (i.e. a Cartesian product of ''p'' intervals of R). When ''f'' is nonlinear the set inversion problem can be solved using interval analysis combined with a branch-and-bound algorithm. The main idea consists in building a paving of R''p'' made with non-overlapping boxes. For each box 'x'' we perform the following tests: # if ''f'' ( 'x'' ⊂ ''Y'' we conclude that 'x''⊂ ''X''; # if ''f'' ( 'x'' ∩ ''Y'' = ∅ we conclude that 'x''∩ ''X'' = ∅; # Otherwise, the box ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sailboats
A sailboat or sailing boat is a boat propelled partly or entirely by sails and is smaller than a sailing ship. Distinctions in what constitutes a sailing boat and ship vary by region and maritime culture. Types Although sailboat terminology has varied across history, many terms have specific meanings in the context of modern yachting. A great number of sailboat-types may be distinguished by size, hull configuration, keel type, purpose, number and configuration of masts, and sail plan. Popular monohull designs include: Cutter The cutter is similar to a sloop with a single mast and mainsail, but generally carries the mast further aft to allow for a jib and staysail to be attached to the head stay and inner forestay, respectively. Once a common racing configuration, today it gives versatility to cruising boats, especially in allowing a small staysail to be flown from the inner stay in high winds. Catboat A catboat has a single mast mounted far forward and does not carr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robots
"\n\n\n\n\nThe robots exclusion standard, also known as the robots exclusion protocol or simply robots.txt, is a standard used by websites to indicate to visiting web crawlers and other web robots which portions of the site they are allowed to visit.\n\nThis relies on voluntary compliance. Not all robots comply with the standard; email harvesters, spambots, malware and robots that scan for security vulnerabilities may even start with the portions of the website where they have been told to stay out.\n\nThe \"robots.txt\" file can be used in conjunction with sitemaps, another robot inclusion standard for websites.\n History\nThe standard was proposed by Martijn Koster, when working for Nexor in February 1994\n on the ''www-talk'' mailing list, the main communication channel for WWW-related activities at the time. Charles Stross claims to have provoked Koster to suggest robots.txt, after he wrote a badly-behaved web crawler that inadvertently caused a denial-of-service attack on Kos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |