|
Vaccine Schedule
A vaccination schedule is a series of vaccinations, including the timing of all doses, which may be either recommended or compulsory, depending on the country of residence. A vaccine is an antigenic preparation used to produce active immunity to a disease, in order to prevent or reduce the effects of infection by any natural or "wild" pathogen. Vaccines go through multiple phases of trials to ensure safety and effectiveness. Many vaccines require multiple doses for maximum effectiveness, either to produce sufficient initial immune response or to boost response that fades over time. For example, tetanus vaccine boosters are often recommended every 10 years. Vaccine schedules are developed by governmental agencies or physicians groups to achieve maximum effectiveness using required and recommended vaccines for a locality while minimizing the number of health care system interactions. Over the past two decades, the recommended vaccination schedule has grown rapidly and become more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polish Call For Vaccination
Polish may refer to: * Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe * Polish language * Polish people, people from Poland or of Polish descent * Polish chicken * Polish brothers (Mark Polish and Michael Polish, born 1970), American twin screenwriters * Kevin Polish, an American Paralympian archer Polish may refer to: * Polishing, the process of creating a smooth and shiny surface by rubbing or chemical action ** French polishing, polishing wood to a high gloss finish * Nail polish * Shoe polish * Polish (screenwriting), improving a script in smaller ways than in a rewrite See also * * * Polishchuk (surname) * Polonaise (other) A polonaise ()) is a stately dance of Polish origin or a piece of music for this dance. Polonaise may also refer to: * Polonaises (Chopin), compositions by Frédéric Chopin ** Polonaise in A-flat major, Op. 53 (, ''Heroic Polonaise''; ) * Polon ... {{Disambiguation, surname Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the '' hepatitis B virus'' (HBV) that affects the liver; it is a type of viral hepatitis. It can cause both acute and chronic infection. Many people have no symptoms during an initial infection. For others, symptoms may appear 30 to 180 days after becoming infected and can include a rapid onset of sickness with nausea, vomiting, yellowish skin, fatigue, yellow urine, and abdominal pain. Symptoms during acute infection typically last for a few weeks, though some people may feel sick for up to six months. Deaths resulting from acute stage HBV infections are rare. An HBV infection lasting longer than six months is usually considered chronic. The likelihood of developing chronic hepatitis B is higher for those who are infected with HBV at a younger age. About 90% of those infected during or shortly after birth develop chronic hepatitis B, while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five develop chronic cases. Most of those ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
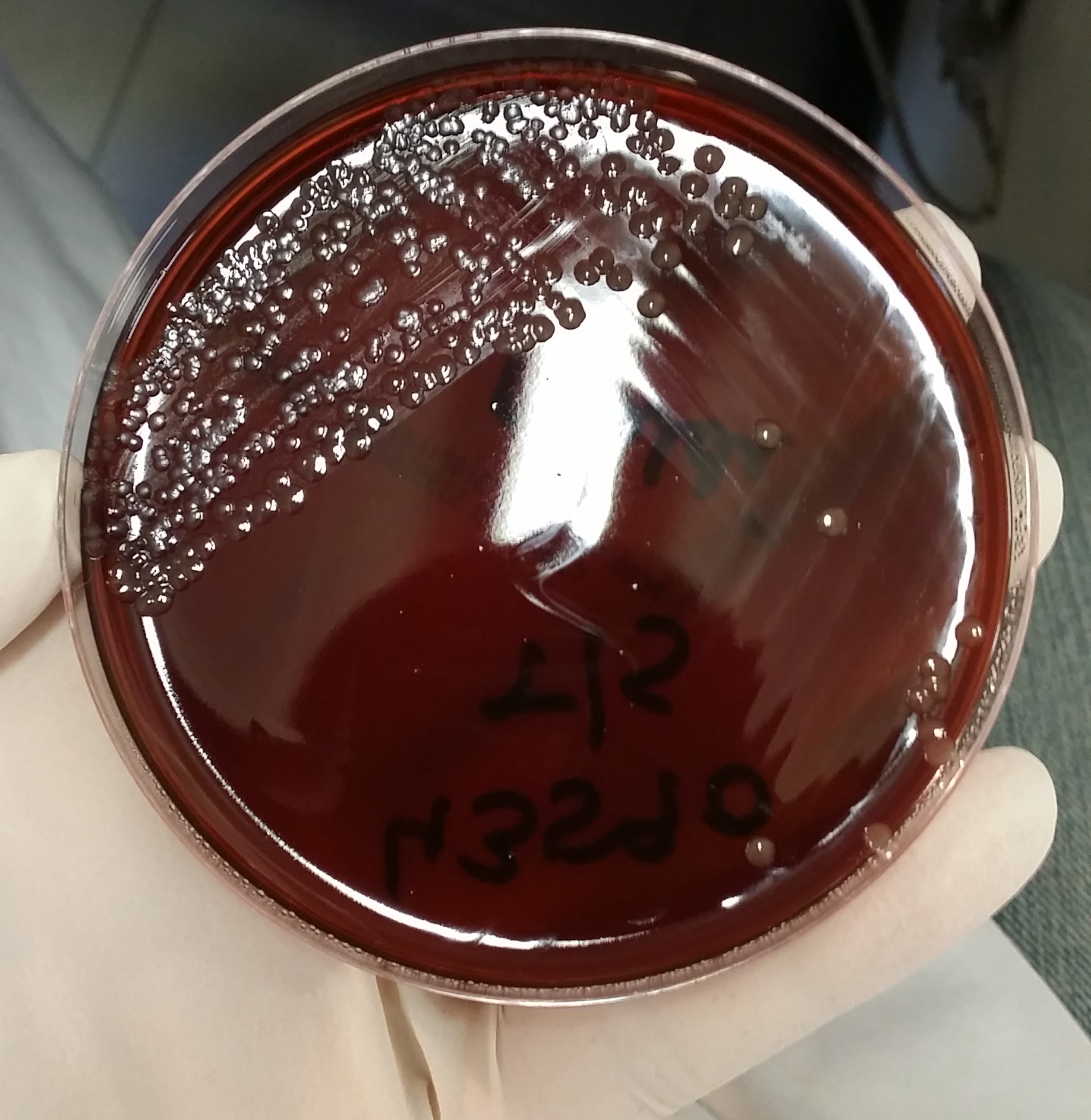
Pneumococcal
''Streptococcus pneumoniae'', or pneumococcus, is a Gram-positive, spherical bacteria, alpha-hemolytic member of the genus ''Streptococcus''. ''S. pneumoniae'' cells are usually found in pairs (diplococci) and do not form spores and are non motile. As a significant human pathogenic bacterium ''S. pneumoniae'' was recognized as a major cause of pneumonia in the late 19th century, and is the subject of many humoral immunity studies. ''Streptococcus pneumoniae'' resides asymptomatically in healthy carriers typically colonizing the respiratory tract, sinuses, and nasal cavity. However, in susceptible individuals with weaker immune systems, such as the elderly and young children, the bacterium may become pathogenic and spread to other locations to cause disease. It spreads by direct person-to-person contact via respiratory droplets and by auto inoculation in persons carrying the bacteria in their upper respiratory tracts. It can be a cause of neonatal infections. ''Streptococcus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These symptoms begin one to four (typically two) days after exposure to the virus and last for about two to eight days. Diarrhea and vomiting can occur, particularly in children. Influenza may progress to pneumonia from the virus or a subsequent bacterial infection. Other complications include acute respiratory distress syndrome, meningitis, encephalitis, and worsening of pre-existing health problems such as asthma and cardiovascular disease. There are four types of influenza virus: types A, B, C, and D. Aquatic birds are the primary source of influenza A virus (IAV), which is also widespread in various mammals, including humans and pigs. Influenza B virus (IBV) and influenza C virus (ICV) primarily infect humans, and influenza D virus (IDV) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meningococcal
''Neisseria meningitidis'', often referred to as the meningococcus, is a Gram-negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a coccus because it is round, and more specifically a diplococcus because of its tendency to form pairs. About 10% of adults are carriers of the bacteria in their nasopharynx. As an exclusively human pathogen, it causes developmental impairment and death in about 10% of cases. It causes the only form of bacterial meningitis known to occur epidemically, mainly in Africa and Asia. It occurs worldwide in both epidemic and endemic form. ''N. meningitidis'' is spread through saliva and respiratory secretions during coughing, sneezing, kissing, chewing on toys and through sharing a source of fresh water. It has also been reported to be transmitted through oral sex and cause urethritis in men. It infects its host cells by sticking to them wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shingles
Shingles, also known as herpes zoster or zona, is a viral disease characterized by a painful skin rash with blisters in a localized area. Typically the rash occurs in a single, wide mark either on the left or right side of the body or face. Two to four days before the rash occurs there may be paresthesia, tingling or local pain in the area. Other common symptoms are fever, headache, and tiredness. The rash usually heals within two to four weeks, but some people develop ongoing neuropathy, nerve pain which can last for months or years, a condition called postherpetic neuralgia (PHN). In those with Immunosuppression, poor immune function the #Disseminated shingles, rash may occur widely. If the rash involves the eye, vision loss may occur. Shingles is caused by the varicella zoster virus (VZV) that also causes chickenpox. In the case of chickenpox, also called varicella, the initial infection with the virus typically occurs during childhood or adolescence. Once the chickenpox ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chickenpox
Chickenpox, also known as varicella ( ), is a highly contagious disease caused by varicella zoster virus (VZV), a member of the herpesvirus family. The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the chest, back, and face. It then spreads to the rest of the body. The rash and other symptoms, such as fever, tiredness, and headaches, usually last five to seven days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, and bacterial skin infections. The disease is usually more severe in adults than in children. Chickenpox is an airborne disease which easily spreads via human-to-human transmission, typically through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. The incubation period is 10–21 days, after which the characteristic rash appears. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mumps
MUMPS ("Massachusetts General Hospital Utility Multi-Programming System"), or M, is an imperative, high-level programming language with an integrated transaction processing key–value database. It was originally developed at Massachusetts General Hospital for managing patient medical records and hospital laboratory information systems. MUMPS technology has since expanded as the predominant database for health information systems and electronic health records in the United States. MUMPS-based information systems, such as Epic Systems', provide health information services for over 78% of patients across the U.S. A unique feature of the MUMPS technology is its integrated Query language, database language, allowing direct, high-speed read-write access to permanent disk storage. History 1960s-1970s - Genesis MUMPS was developed by Neil Pappalardo, Robert A. Greenes, and Curt Marble in Dr. Octo Barnett's lab at the Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH) in Boston during 1966 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubella
Rubella, also known as German measles or three-day measles, is an infection caused by the rubella virus. This disease is often mild, with half of people not realizing that they are infected. A rash may start around two weeks after exposure and last for three days. It usually starts on the face and spreads to the rest of the body. The rash is sometimes itchy and is not as bright as that of measles. Lymphadenopathy, Swollen lymph nodes are common and may last a few weeks. A fever, sore throat, and fatigue may also occur. arthritis, Joint pain is common in adults. Complications may include bleeding problems, orchitis, testicular swelling, encephalitis, and neuritis, inflammation of nerves. Infection during early pregnancy may result in a miscarriage or a child born with congenital rubella syndrome (CRS). Symptoms of CRS manifest as problems with the eyes such as cataracts, deafness, as well as affecting the heart and brain. Problems are rare after the 20th week of pregnancy. Rubel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Measles
Measles (probably from Middle Dutch or Middle High German ''masel(e)'', meaning "blemish, blood blister") is a highly contagious, Vaccine-preventable diseases, vaccine-preventable infectious disease caused by Measles morbillivirus, measles virus. Other names include ''morbilli'', ''rubeola'', ''9-day measles, red measles'', and ''English measles''. Symptoms usually develop 10–12 days after exposure to an infected person and last 7–10 days. Initial symptoms typically include fever, often greater than , cough, Rhinitis, runny nose, and conjunctivitis, inflamed eyes. Small white spots known as Koplik's spots, Koplik spots may form inside the mouth two or three days after the start of symptoms. A red, flat rash which usually starts on the face and then spreads to the rest of the body typically begins three to five days after the start of symptoms. Common complications include diarrhea (in 8% of cases), Otitis media, middle ear infection (7%), and pneumonia (6%). These occur i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polio
Poliomyelitis ( ), commonly shortened to polio, is an infectious disease caused by the poliovirus. Approximately 75% of cases are asymptomatic; mild symptoms which can occur include sore throat and fever; in a proportion of cases more severe symptoms develop such as headache, neck stiffness, and paresthesia. These symptoms usually pass within one or two weeks. A less common symptom is permanent Flaccid paralysis, paralysis, and possible death in extreme cases.. Years after recovery, post-polio syndrome may occur, with a slow development of muscle weakness similar to what the person had during the initial infection. Polio occurs naturally only in humans. It is highly infectious, and is spread from person to person either through fecal–oral route, fecal–oral transmission (e.g. poor hygiene, or by ingestion of food or water contaminated by human feces), or via the oral–oral route. Those who are infected may spread the disease for up to six weeks even if no symptoms are pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haemophilus Influenzae
''Haemophilus influenzae'' (formerly called Pfeiffer's bacillus or ''Bacillus influenzae'') is a Gram-negative, Motility, non-motile, Coccobacillus, coccobacillary, facultative anaerobic organism, facultatively anaerobic, Capnophile, capnophilic pathogenic bacterium of the family Pasteurellaceae. The bacteria are Mesophile, mesophilic and grow best at temperatures between 35 and 37 °C. ''H. influenzae'' was first described in 1893 by Richard Friedrich Johannes Pfeiffer, Richard Pfeiffer during an influenza pandemic when he incorrectly identified it as the causative microbe, which is why the bacteria was given the name "influenzae". ''H. influenzae'' is responsible for a wide range of localized and invasive infections, typically in infants and children, including pneumonia, meningitis, or bloodstream infections. Treatment consists of antibiotics; however, ''H. influenzae'' is often resistant to the penicillin family, but amoxicillin/clavulanic acid can be used in mild cases ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |