|
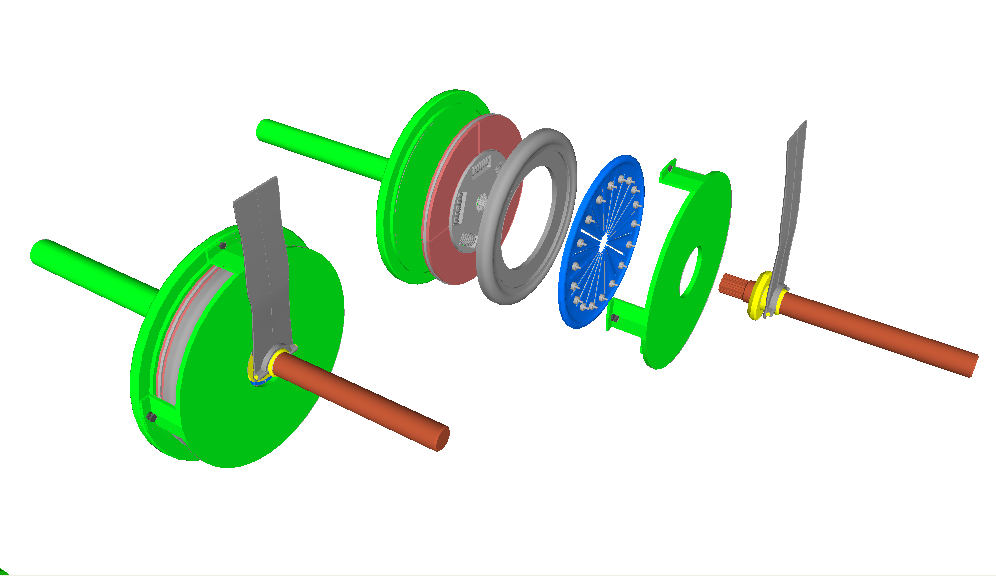
Vacamatic
The 1941 M4 Vacamatic transmission by Chrysler was, historically, the first semi-automatic transmission which was marketed by a major manufacturer. It was an attempt to compete against rivals' hydraulic automatic transmissions, though it still had a clutch, primarily to change range. In normal driving, the clutch is not used. The transmission itself was a fully-synchronized manual transmission, with four forward gears, one reverse; where the shifting was done 'automatically' by either vacuum cylinders (early, M4), or hydraulic cylinders (late, M6, Presto-Matic). The main difference was the addition of a fluid coupling between engine and clutch, and the shifting mechanism. Operation The range selector (looked like a column shift) had three positions: Low, High, and Reverse. Low consisted of what would be a first and second gear with an ordinary four-speed; High was third and fourth. The reverse was a single ratio. Driving one was/is quite different: Upon starting, one would dise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semi-automatic Transmission
A semi-automatic transmission is a multiple-speed Transmission (mechanics), transmission where part of its operation is Automation, automated (typically the actuation of the clutch), but the driver's input is still required to launch the vehicle from a standstill and to manually change gears. Semi-automatic transmissions were almost exclusively used in motorcycles and are based on conventional manual transmissions or sequential manual transmissions, but use an automatic clutch system. But some semi-automatic transmissions have also been based on standard hydraulic automatic transmissions with torque converters and Epicyclic gearing, planetary gearsets. Names for specific types of semi-automatic transmissions include ''clutchless manual'', ''auto-manual'', ''auto-clutch manual'', and ''paddle-shift'' transmissions. These systems facilitate gear shifts for the driver by operating the clutch system automatically, usually via switches that trigger an actuator or servomechanism, servo, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Drive
Fluid Drive is the trademarked name that Chrysler Corporation assigned to a transmission driveline combination which replaced the flywheel with a hydraulic coupling and performed the same function as a modern torque converter, only without torque multiplication. A conventional clutch, and three- or four-speed manual transmission was installed behind the fluid coupling. Fluid drive was used in many military vehicles produced for the US Armed Forces during the Second World War. It was offered for civilian use from 1939 through 1953 in Chryslers, 1940 through 1953 in DeSotos, and from 1941 through 1954 in Dodge models; a semi-automatic system was optional from Chrysler and DeSoto from 1941, and for Dodge from 1949. History The fluid coupling and torque converter was invented by the German engineer Foettinger in the early 1900s. For non-marine applications he licensed the development of the fluid coupling to the British engineer Harold Sinclair and his Fluidrive Engineering Co Ltd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presto-Matic
The M6 Presto-Matic was a Chrysler Corporation semi-automatic transmission produced from 1946 to 1953. It was a special manual transmission with a fluid coupling. Although it had just two forward gears, an electric overdrive unit was attached and useful in either gear for a total of four forward speeds. The driver would use the clutch pedal any time when selecting low, high, or reverse gear. Once underway, the accelerator could be eased and the car would engage the overdrive. With the Fluid Drive coupling, the car could be brought to a halt in gear without releasing the clutch and would creep like an automatic. The Presto-Matic name was only used on Chrysler-brand cars. DeSoto called the transmission the Tip-Toe Shift, while Dodge used Gyro-Matic, Fluid-Matic, Fluidtorque, or Gyro-Torque. Chrysler and DeSoto sold the unit from 1946 to 1953, while Dodge did not introduce it until 1948. Plymouth Plymouth ( ) is a port city status in the United Kingdom, city and unitary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Chrysler Transmissions
Chrysler produces a number of automobile transmissions in-house. Semi-automatic * 1941–1942 M4 Vacamatic — 4-speed (2-range manual control with automatic 2-speed shift vacuum operated) with clutch and fluid coupling ( Fluid Drive); also known as Simplimatic, Powermatic * 1946–1953 M5/M6 Presto-Matic — 4-speed (2 gear manual with electric overdrive) with clutch and fluid coupling ( Fluid Drive) or torque converter (Fluid Torque Drive); also known as Tip-Toe Shift, Gyro-Matic, Fluid-Matic, Gyro-Torque * 1953–1954 Hy-Drive — 3-speed manual transmission behind a torque converter Automatic * 1954–1961 PowerFlite — 2-speed automatic * 1956–2007 TorqueFlite ** 1956–1961 A466 — 3-speed automatic ** 1962–1994 A727 (36RH/37RH) — 3-speed automatic ** 1960–2002 A904 (30RH) — 3-speed automatic ** A998 (31RH) — 3-speed automatic ** A999 (32RH) — 3-speed automatic ** 1988–2004 A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chrysler
FCA US, LLC, Trade name, doing business as Stellantis North America and known historically as Chrysler ( ), is one of the "Big Three (automobile manufacturers), Big Three" automobile manufacturers in the United States, headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan. It is the American subsidiary of the multinational automotive company Stellantis. Stellantis North America sells vehicles worldwide under the Chrysler (brand), Chrysler, Dodge, Jeep, and Ram Trucks nameplates. It also includes Mopar, its automotive parts and accessories division, and Street and Racing Technology, SRT, its performance automobile division. The division also distributes Alfa Romeo, Fiat, and Maserati vehicles in North America. The original Chrysler Corporation was founded in 1925 by Walter Chrysler from the remains of the Maxwell Motor Company. In 1998, it merged with Daimler AG, Daimler-Benz, which renamed itself DaimlerChrysler but in 2007 sold off its Chrysler stake. The company operated as Chrysler LLC thr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Automatic Transmission
An automatic transmission (AT) or automatic gearbox is a multi-speed transmission (mechanics), transmission used in motor vehicles that does not require any input from the driver to change forward gears under normal driving conditions. The 1904 Sturtevant "horseless carriage gearbox" is often considered to be the first true automatic transmission. The first mass-produced automatic transmission is the General Motors ''Hydramatic'' two-speed hydraulic automatic, which was introduced in 1939. Automatic transmissions are especially prevalent in vehicular drivetrains, particularly those subject to intense mechanical acceleration and frequent idle/transient operating conditions; commonly commercial/passenger/utility vehicles, such as buses and waste collection vehicles. Prevalence Vehicles with internal combustion engines, unlike electric vehicles, require the engine to operate in a narrow range of rates of rotation, requiring a gearbox, operated manually or automatically, to drive t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clutch
A clutch is a mechanical device that allows an output shaft to be disconnected from a rotating input shaft. The clutch's input shaft is typically attached to a motor, while the clutch's output shaft is connected to the mechanism that does the work. In a motor vehicle, the clutch acts as a mechanical linkage between the engine and transmission. By disengaging the clutch, the engine speed (RPM) is no longer determined by the speed of the driven wheels. Another example of clutch usage is in electric drills. The clutch's input shaft is driven by a motor and the output shaft is connected to the drill bit (via several intermediate components). The clutch allows the drill bit to either spin at the same speed as the motor (clutch engaged), spin at a lower speed than the motor (clutch slipping) or remain stationary while the motor is spinning (clutch disengaged). Types Dry clutch A ''dry clutch'' uses dry friction to transfer power from the input shaft to the output shaft, f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manual Transmission
A manual transmission (MT), also known as manual gearbox, standard transmission (in Canadian English, Canada, British English, the United Kingdom and American English, the United States), or stick shift (in the United States), is a multi-speed motor vehicle Transmission (mechanical device), transmission system where gear changes require the driver to manually select the gears by operating a gear stick and clutch (which is usually a foot pedal for cars or a hand lever for motorcycles). Early automobiles used ''sliding-mesh'' manual transmissions with up to three forward gear ratios. Since the 1950s, ''constant-mesh'' manual transmissions have become increasingly commonplace, and the number of forward ratios has increased to 5-speed and 6-speed manual transmissions for current vehicles. The alternative to a manual transmission is an automatic transmission. Common types of automatic transmissions are the Automatic transmission#Hydraulic automatic transmissions, hydraulic automatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum
A vacuum (: vacuums or vacua) is space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective (neuter ) meaning "vacant" or "void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often discuss ideal test results that would occur in a ''perfect'' vacuum, which they sometimes simply call "vacuum" or free space, and use the term partial vacuum to refer to an actual imperfect vacuum as one might have in a laboratory or in space. In engineering and applied physics on the other hand, vacuum refers to any space in which the pressure is considerably lower than atmospheric pressure. The Latin term ''in vacuo'' is used to describe an object that is surrounded by a vacuum. The ''quality'' of a partial vacuum refers to how closely it approaches a perfect vacuum. Other things equal, lower gas pressure means higher-quality vacuum. For example, a typical vacuum cleaner produces enough suction to reduce air pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydraulic Cylinder
A hydraulic cylinder (also called a linear hydraulic motor) is a mechanical actuator that is used to give a unidirectional force through a unidirectional stroke. It has many applications, notably in construction equipment ( engineering vehicles), manufacturing machinery, elevators, and civil engineering. A hydraulic cylinder is a hydraulic actuator that provides linear motion when hydraulic energy is converted into mechanical movement. It can be likened to a muscle in that, when the hydraulic system of a machine is activated, the cylinder is responsible for providing the motion. Operation Hydraulic cylinders get their power from pressurized hydraulic fluid, which is incompressible. Typically oil is used as hydraulic fluid. The hydraulic cylinder consists of a cylinder barrel, in which a piston connected to a piston rod moves back and forth. The barrel is closed on one end by the cylinder bottom (also called the cap) and the other end by the cylinder head (also called th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluid Coupling
A fluid coupling or hydraulic coupling is a hydrodynamics, hydrodynamic or 'hydrokinetic' device used to transmit rotating mechanical power.Fluid coupling ''encyclopedia2.thefreedictionary.com'' It has been used in automobile Transmission (mechanics), transmissions as an alternative to a mechanical clutch. It also has widespread application in marine and industrial machine drives, where variable speed operation and controlled start-up without Shock (mechanics), shock loading of the power transmission system is essential. Hydrokinetic drives, such as this, should be distinguished from hydrostatic drives, such as hydraulic pump and hydraulic motor, motor combinations. History The fluid coupling originates from the work of Hermann Föttinger, who was the chief designer at the AG Vulcan Stettin, AG Vulcan Wo ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flathead Engine
A flathead engine, also known as a sidevalve engine''American Rodder'', 6/94, pp.45 & 93. or valve-in-block engine, is an internal combustion engine with its poppet valves contained within the engine block, instead of in the cylinder head, as in an overhead valve engine. Flatheads were widely used internationally by automobile manufacturers from the late 1890s until the mid-1960s but were replaced by more efficient overhead valve and overhead camshaft engines. They are currently experiencing a revival in low-revving aero-engines such as the D-Motor. The side-valve design The valve gear comprises a camshaft sited low in the cylinder block which operates the poppet valves via tappets and short pushrods (or sometimes with no pushrods at all). The flathead system obviates the need for further valvetrain components such as lengthy pushrods, rocker arms, overhead valves or overhead camshafts. The sidevalves are typically adjacent, sited on one side of the cylinder(s), though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |