|
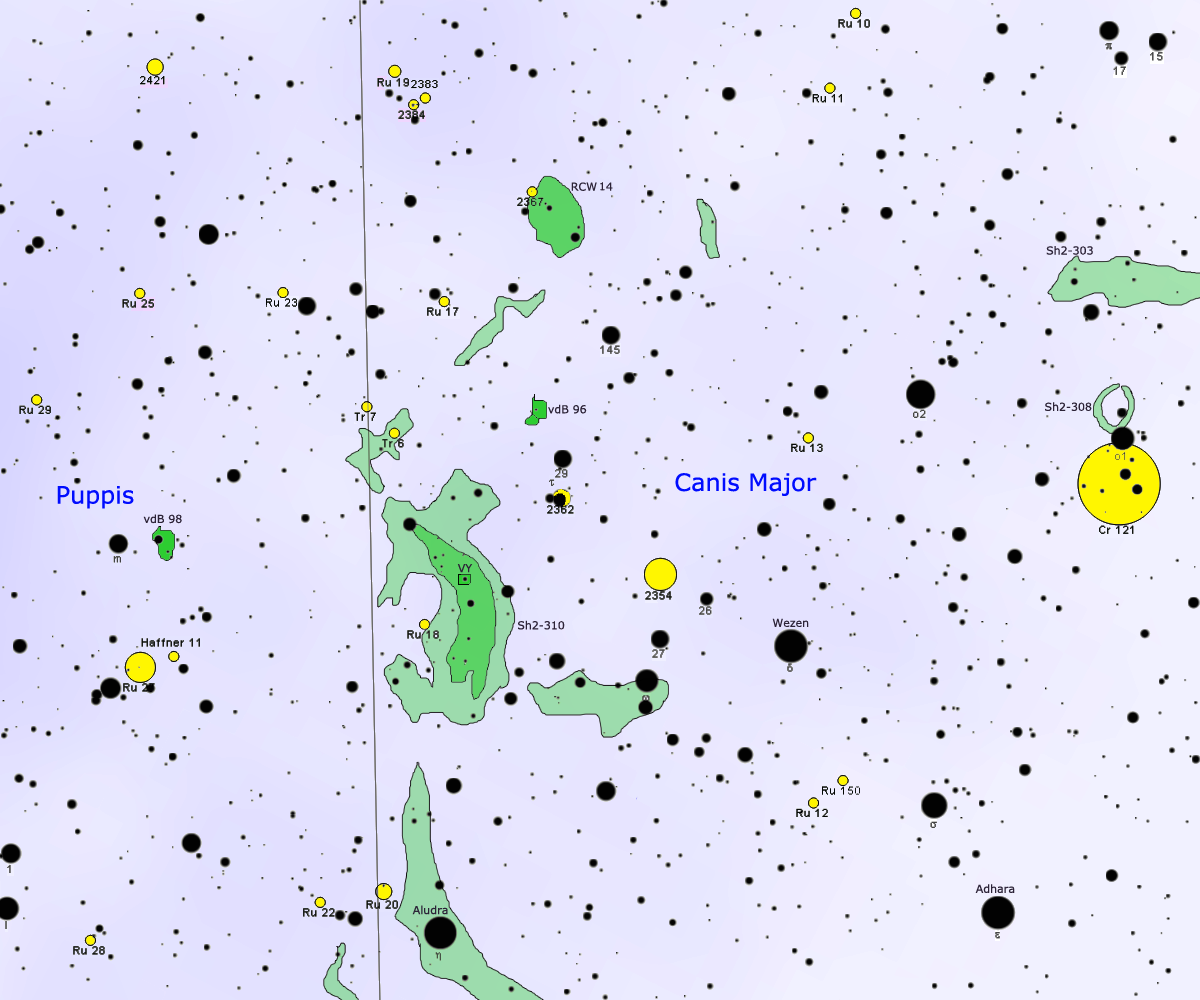
VY Canis Majoris
VY Canis Majoris (abbreviated to VY CMa) is an extreme oxygen-rich red hypergiant or red supergiant (O-rich RHG or RSG) and pulsating variable star from the Solar System in the slightly southern constellation of Canis Major. It is one of the largest known stars, one of the most luminous and massive red supergiants, and one of the most luminous stars in the Milky Way. No evidence has been found that it is part of a multiple-star system. Its great infrared (IR) excess makes it one of the brightest objects in the local part of the galaxy ( Orion Arm) at wavelengths of 5 to 20 microns (μm) and indicates a dust shell or heated disk. It is about times the mass of the Sun (). It is surrounded by a complex asymmetric circumstellar envelope (CSE) caused by its mass loss. It produces strong molecular maser emission and was one of the first radio masers discovered. VY CMa is embedded in the large molecular cloud Sh2-310, a large, quite local star-forming H II region— ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
J2000
In astronomy, an epoch or reference epoch is a moment in time used as a reference point for some time-varying astronomical quantity. It is useful for the celestial coordinates or orbital elements of a celestial body, as they are subject to perturbations and vary with time. These time-varying astronomical quantities might include, for example, the mean longitude or mean anomaly of a body, the node of its orbit relative to a reference plane, the direction of the apogee or aphelion of its orbit, or the size of the major axis of its orbit. The main use of astronomical quantities specified in this way is to calculate other relevant parameters of motion, in order to predict future positions and velocities. The applied tools of the disciplines of celestial mechanics or its subfield orbital mechanics (for predicting orbital paths and positions for bodies in motion under the gravitational effects of other bodies) can be used to generate an ephemeris, a table of values giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
M-type Star
In astronomy, stellar classification is the classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. Electromagnetic radiation from the star is analyzed by splitting it with a prism or diffraction grating into a spectrum exhibiting the rainbow of colors interspersed with spectral lines. Each line indicates a particular chemical element or molecule, with the line strength indicating the abundance of that element. The strengths of the different spectral lines vary mainly due to the temperature of the photosphere, although in some cases there are true abundance differences. The ''spectral class'' of a star is a short code primarily summarizing the ionization state, giving an objective measure of the photosphere's temperature. Most stars are currently classified under the Morgan–Keenan (MK) system using the letters ''O'', ''B'', ''A'', ''F'', ''G'', ''K'', and ''M'', a sequence from the hottest (''O'' type) to the coolest (''M'' type). Each letter class is then subdivided ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circumstellar Envelope
A circumstellar envelope (CSE) is a part of a star that has a roughly spherical shape and is not gravitationally bound to the star core. Usually circumstellar envelopes are formed from the dense stellar wind, or they are present before the formation of the star. Circumstellar envelopes of old stars ( Mira variables and OH/IR stars) eventually evolve into protoplanetary nebulae, and circumstellar envelopes of young stellar objects evolve into circumstellar discs. Types of circumstellar envelopes * Circumstellar envelopes of AGB stars * Circumstellar envelopes around young stellar objects See also * Circumstellar dust * Common envelopes * Stellar evolution Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is consi ... References External links The Structure and Evolution of En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Micron
The micrometre (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American English), also commonly known by the non-SI term micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Units (SI) equalling (SI standard prefix "micro-" = ); that is, one millionth of a metre (or one thousandth of a millimetre, , or about ). The nearest smaller common SI Unit, SI unit is the nanometre, equivalent to one thousandth of a micrometre, one millionth of a millimetre or one billionth of a metre (). The micrometre is a common unit of measurement for wavelengths of infrared radiation as well as sizes of biological cell (biology), cells and bacteria, and for grading wool by the diameter of the fibres. The width of a single human hair ranges from approximately 20 to . Examples Between 1 μm and 10 μm: * 1–10 μm – length of a typical bacterium * 3–8 μm – width of str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orion Arm
The Orion Arm, also known as the Orion–Cygnus Arm, is a minor spiral arm within the Milky Way Galaxy spanning in width and extending roughly in length. This galactic structure encompasses the Solar System, including Earth. It is sometimes referred to by alternate names such as the Local Arm or Orion Bridge, and it was previously identified as the Local Spur or the Orion Spur. It should not be confused with the outer terminus of the Norma Arm, known as the Cygnus Arm. Naming and brightness The arm is named after the Orion Constellation, one of the most prominent constellations of the Northern Hemisphere in winter (or the Southern Hemisphere in summer). Some of the brightest stars in the sky as well as other well-known celestial objects of the constellation (e.g. Betelgeuse, Rigel, the three stars of Orion's Belt, and the Orion Nebula) are found within it, as shown on Orion Arm's interactive map. Location The Orion arm is located between the Carina–Sagittarius Arm, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Excess
An infrared excess is a measurement of an astronomical source, typically a star, that in their spectral energy distribution has a greater measured infrared flux than expected by assuming the star is a blackbody radiator. Infrared excesses are often the result of circumstellar dust heated by starlight and reemitted at longer wavelengths. They are common in young stellar objects and evolved stars on the asymptotic giant branch or older. In addition, monitoring for infrared excess emission from stellar systems is one possible method that could enable a search for large-scale stellar engineering projects of a hypothetical extraterrestrial civilization; for example a Dyson sphere A Dyson sphere is a hypothetical megastructure that encompasses a star and captures a large percentage of its power output. The concept is a thought experiment that attempts to imagine how a spacefaring civilization would meet its energy re ... or Dyson swarm. This infrared excess would be the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milky Way
The Milky Way or Milky Way Galaxy is the galaxy that includes the Solar System, with the name describing the #Appearance, galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars in other arms of the galaxy, which are so far away that they cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy with a Galaxy#Isophotal diameter, D25 isophotal diameter estimated at , but only about 1,000 light-years thick at the spiral arms (more at the bulge). Recent simulations suggest that a dark matter area, also containing some visible stars, may extend up to a diameter of almost 2 million light-years (613 kpc). The Milky Way has several List of Milky Way's satellite galaxies, satellite galaxies and is part of the Local Group of galaxies, forming part of the Virgo Supercluster which is itself a component of the Laniakea Supercluster. It is estimated to contain 100–400 billion stars and at least that number of pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Most Massive Stars
This is a list of the most massive stars that have been discovered, in solar mass units (). Uncertainties and caveats Most of the masses listed below are contested and, being the subject of current research, remain under review and subject to constant revision of their masses and other characteristics. Indeed, many of the masses listed in the table below are inferred from theory, using difficult measurements of the stars' effective temperature, temperatures, metallicity, composition, and absolute magnitude, absolute brightnesses. All the masses listed below are uncertain: Both the theory and the measurements are pushing the limits of current knowledge and technology. Both theories and measurements could be incorrect. Complications with distance and obscuring clouds Since massive stars are rare, astronomers must look very far from Earth to find them. All the listed stars are many thousands of light years away, which makes measurements difficult. In addition to being far away, many ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Most Luminous Stars
This is a list of stars arranged by their absolute magnitude – their intrinsic stellar luminosity. This cannot be observed directly, so instead must be calculated from the apparent magnitude (the brightness as seen from Earth), the distance to each star, and a correction for interstellar extinction. The entries in the list below are further corrected to provide the bolometric magnitude, i.e. integrated over all wavelengths; this relies upon measurements in multiple photometric filters and extrapolation of the stellar spectrum based on the stellar spectral type and/or effective temperature. Entries give the bolometric luminosity in multiples of the luminosity of the Sun () and the bolometric absolute magnitude. As with all magnitude systems in astronomy, the latter scale is logarithmic and inverted i.e. more negative numbers are more luminous. Most stars on this list are not bright enough to be visible to the naked eye from Earth, because of their high distances, hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Largest Known Stars
A list is a set of discrete items of information collected and set forth in some format for utility, entertainment, or other purposes. A list may be memorialized in any number of ways, including existing only in the mind of the list-maker, but lists are frequently written down on paper, or maintained electronically. Lists are "most frequently a tool", and "one does not ''read'' but only ''uses'' a list: one looks up the relevant information in it, but usually does not need to deal with it as a whole".Lucie Doležalová,The Potential and Limitations of Studying Lists, in Lucie Doležalová, ed., ''The Charm of a List: From the Sumerians to Computerised Data Processing'' (2009). Purpose It has been observed that, with a few exceptions, "the scholarship on lists remains fragmented". David Wallechinsky, a co-author of '' The Book of Lists'', described the attraction of lists as being "because we live in an era of overstimulation, especially in terms of information, and lists help us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms Asterism (astronomy), a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object. The first constellations were likely defined in prehistory. People used them to relate stories of their beliefs, experiences, creation myth, creation, and mythology. Different cultures and countries invented their own constellations, some of which lasted into the early 20th century before today's constellations were internationally recognized. The recognition of constellations has changed significantly over time. Many changed in size or shape. Some became popular, only to drop into obscurity. Some were limited to a single culture or nation. Naming constellations also helped astronomers and navigators identify stars more easily. Twelve (or thirteen) ancient constellations belong to the zodiac (straddling the ecliptic, which the Sun, Moon, and planets all traver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Hemisphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. The celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres. Description Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on their actual distances. All celestial objects seem equally far away, as if fixed onto the inside of a sphere with a large but unknown radius, which appears to rotate westward over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |