|
VM2000
BS2000 is an operating system for IBM 390-compatible mainframe computers developed in the 1970s by Siemens (Data Processing Department EDV) and from early 2000s onward by Fujitsu Technology Solutions. Unlike other mainframe systems, BS2000 provides exactly the same user and programming interface in all operating modes (batch, interactive and online transaction processing) and regardless of whether it is running natively or as a guest system in a virtual machine. This uniformity of the user interface and the entire BS2000 software configuration makes administration and automation particularly easy. Currently, it is mainly used in Germany - making up to 83% of its total user base - as well as in the United Kingdom (8%), Belgium (4.8%) and other European countries (Austria, Czech Republic, Denmark, Italy, Luxembourg, Netherland, Spain, Switzerland) (4.2%). 63% of all SE/S Servers are installed at the German tourism industry, German Travel Association (DRV) and Federal Central Tax O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujitsu Siemens Computers
Fujitsu Siemens Computers GmbH was a Japanese and German vendor of information technology. The company was founded in 1999 as a 50/50 joint venture between Fujitsu of Japan and Siemens AG of Germany. On April 1, 2009, the company became Fujitsu Technology Solutions as a result of Fujitsu buying out Siemens' share of the company. The offerings of Fujitsu Siemens Computers extended from handheld and notebook PCs through desktops, server and storage, to IT data center products and services. Fujitsu Siemens Computers had a presence in key markets across Europe, the Middle East and Africa, while products marketed elsewhere were sold under the Fujitsu brand, with the services division extending coverage up to 170 countries worldwide. Fujitsu Siemens Computers placed a focus on "green" computers, and was considered a leader or innovator in Green IT, across ecological and environmental markings such as Energy Star and Nordic swan. Fujitsu Siemens sponsored McLaren Mercedes Formula- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fujitsu Technology Solutions
Fujitsu Technology Solutions GmbH (FTS) is a Munich-based information technology vendor in the so-called "EMEIA" markets: Europe, the Middle East, India and Africa. A subsidiary of Fujitsu in Tokyo, FTS was founded in 2009 when the parent firm bought out Siemens' 50% share of Fujitsu Siemens Computers. Products and services Fujitsu Technology Solutions provides a broad range of information and communications technology based products. Current Fujitsu Technology Solutions' current products and services include: * Media Center ** ESPRIMO Q * Notebooks ** CELSIUS ** LIFEBOOK * Desktop PC ** ESPRIMO * Workstation ** CELSIUS * Tablet PC ** STYLISTIC * Convertible PC ** LIFEBOOK T * Industry Standard Servers ** PRIMERGY ** PRIMERGY BladeFrame * Mission critical IA-64 servers ** PRIMEQUEST * UNIX system based servers ** SPARC Enterprise Servers ** PRIMEPOWER 250, 450, 900, 1500, 2500 * Storage ** ETERNUS * S/390-compatible Mainframes ** S- series, SX- series * Flat panel displays ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RCA Spectra 70
The RCA Spectra 70 is a line of mainframe computers and related electronic data processing (EDP) equipment that was manufactured by the Radio Corporation of America’s computer division beginning in April 1965. The Spectra 70 line included several CPU models, various configurations of core memory, mass-storage devices, terminal equipment, and a variety of specialized interface equipment. The system architecture and instruction set were largely compatible with the non-privileged instruction set of the IBM System/360, including use of the EBCDIC character set. While this degree of compatibility made some interchange of programs and data possible, differences in the operating system software precluded transparent movement of programs between the two systems. Competition in the mainframe market was fierce, and in 1971 the company sold the computer division and the Spectra 70 line to Sperry Rand, taking a huge write down in the process. System overview Five models of the Spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Process (computing)
In computing, a process is the Instance (computer science), instance of a computer program that is being executed by one or many thread (computing), threads. There are many different process models, some of which are light weight, but almost all processes (even entire virtual machines) are rooted in an operating system (OS) process which comprises the program code, assigned system resources, physical and logical access permissions, and data structures to initiate, control and coordinate execution activity. Depending on the OS, a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions Concurrency (computer science), concurrently. While a computer program is a passive collection of Instruction set, instructions typically stored in a file on disk, a process is the execution of those instructions after being loaded from the disk into memory. Several processes may be associated with the same program; for example, opening up several instances of the same progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
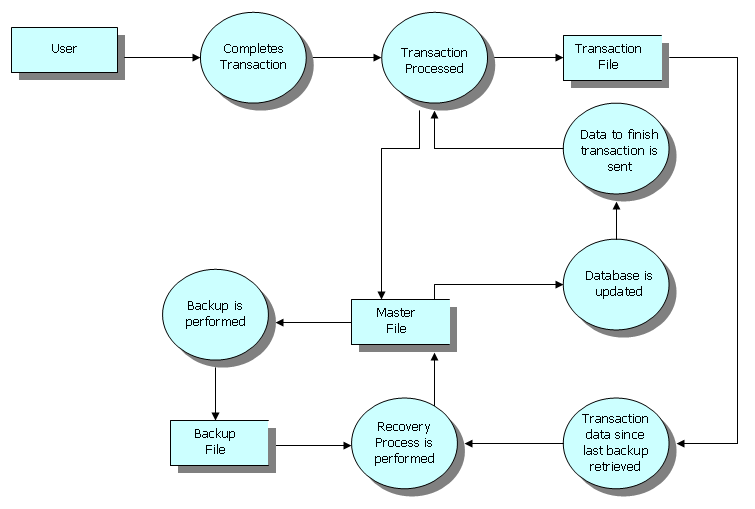
Transaction Processing Monitor
A transaction processing system (TPS) is a software system, or software/ hardware combination, that supports transaction processing. History The first transaction processing system was SABRE, made by IBM for American Airlines, which became operational in 1964. Designed to process up to 83,000 transactions a day, the system ran on two IBM 7090 computers. SABRE was migrated to IBM System/360 computers in 1972, and became an IBM product first as '' Airline control Program (ACP)'' and later as '' Transaction Processing Facility (TPF)''. In addition to airlines, TPF is used by large banks, credit card companies, and hotel chains. The Hewlett Packard Enterprise NonStop system (formerly Tandem NonStop) is a hardware and software system designed for ''Online Transaction Processing (OLTP)'' introduced in 1976. The system provides an extreme level of availability and data integrity. List of transaction processing systems * IBM Transaction Processing Facility (TPF) – 1960. Unlike most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Multiprocessing
Multiprocessing (MP) is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. There are many variations on this basic theme, and the definition of multiprocessing can vary with context, mostly as a function of how CPUs are defined ( multiple cores on one die, multiple dies in one package, multiple packages in one system unit, etc.). A multiprocessor is a computer system having two or more processing units (multiple processors) each sharing main memory and peripherals, in order to simultaneously process programs. A 2009 textbook defined multiprocessor system similarly, but noted that the processors may share "some or all of the system’s memory and I/O facilities"; it also gave tightly coupled system as a synonymous term. At the operating system level, ''multiprocessing'' is sometimes used to refer to the executi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Networking
A computer network is a collection of communicating computers and other devices, such as printers and smart phones. In order to communicate, the computers and devices must be connected by wired media like copper cables, optical fibers, or by wireless communication. The devices may be connected in a variety of network topologies. In order to communicate over the network, computers use agreed-on rules, called communication protocols, over whatever medium is used. The computer network can include personal computers, Server (computing), servers, networking hardware, or other specialized or general-purpose Host (network), hosts. They are identified by network addresses and may have hostnames. Hostnames serve as memorable labels for the nodes and are rarely changed after initial assignment. Network addresses serve for locating and identifying the nodes by communication protocols such as the Internet Protocol. Computer networks may be classified by many criteria, including the tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Online Transaction Processing
Online transaction processing (OLTP) is a type of database system used in transaction-oriented applications, such as many operational systems. "Online" refers to the fact that such systems are expected to respond to user requests and process them in real-time (process transactions). The term is contrasted with online analytical processing (OLAP) which instead focuses on data analysis (for example planning and management systems). Meaning of the term transaction The term "transaction" can have two different meanings, both of which might apply: in the realm of computers or database transactions it denotes an atomic change of state, whereas in the realm of business or finance, the term typically denotes an exchange of economic entities (as used by, e.g., Transaction Processing Performance Council or commercial transactions.) OLTP may use transactions of the first type to record transactions of the second type. Compared to OLAP OLTP is typically contrasted to online analytical p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paging
In computer operating systems, memory paging is a memory management scheme that allows the physical Computer memory, memory used by a program to be non-contiguous. This also helps avoid the problem of memory fragmentation and requiring compaction to reduce fragmentation. Paging is often combined with the related technique of allocating and freeing Page (computer memory), ''page frames'' and storing pages on and retrieving them from Computer data storage#Secondary storage, secondary storage in order to allow the aggregate size of the address spaces to exceed the physical memory of the system. For historical reasons, this technique is sometimes referred to as ''swapping''. When combined with virtual memory, it is known as Virtual memory#Paged virtual memory, ''paged virtual memory''. In this scheme, the operating system retrieves data from secondary storage in Block (data storage), blocks of the same size (pages). Paging is an important part of virtual memory implementations in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
VS/9
VS/9 is a computer operating system for the UNIVAC Series 90 mainframes (90/60, 90/70, and 90/80), used during the late 1960s through 1980s. The 90/60 and 90/70 were repackaged Univac 9700 computers. After the RCA acquisition by Sperry, it was determined that the RCA TSOS operating system was far more advanced than the Univac counterpart (named OS/7), so the company opted to merge the Univac hardware with the RCA software and introduced the 90/70. The 90/60 was introduced shortly thereafter as a slower, less expensive 90/70. It was not until the introduction of the 90/80 that VS/9 finally had a hardware platform optimized to take full advantage of its capability to allow both interactive and batch operations on the same computer. Background In September 1971, RCA decided to exit the mainframe computer business after losing about half a billion dollars trying (and failing) to compete against IBM. They sold most of the assets of the computer division to what was then Univa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fork (software Development)
In software development, a fork is a codebase that is created by duplicating an existing codebase and, generally, is subsequently modified independently of the original. Software built from a fork initially has identical behavior as software built from the original code, but as the source code is increasingly modified, the resulting software tends to have increasingly different behavior compared to the original. A fork is a form of branching, but generally involves storing the forked files separately from the original; not in the repository. Reasons for forking a codebase include user preference, stagnated or discontinued development of the original software or a schism in the developer community. Forking proprietary software (such as Unix) is prohibited by copyright law without explicit permission, but free and open-source software, by definition, may be forked without permission. Etymology The word ''fork'' has been used to mean "to divide in branches, go separate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |