|
VLEO
Very low Earth orbit is a range of orbital altitudes below , and is of increasing commercial importance in a variety of scenarios and for multiple applications, in both private and government satellite operations. Applications include Earth observation, radar, infrared, weather, telecommunications, and rural internet access among others. Spacecraft have entered into a highly elliptical orbit around Earth with a perigee as low as , surviving for multiple orbits. Sub-orbital flight and near space is sometimes considered to be the case up until 160 km of altitude above Earth. Interest In 2009 governments started showing interest in VLEO satellites, such as the European Space Agency's scientific satellite " Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explore" (GOCE), designed to take accurate measurements of Earth's gravitational field. It demonstrated a sustained orbit of between for three years from 2009 to 2013. The Chinese Space Agency launched the Tiangong-1 prototy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere-breathing Electric Propulsion
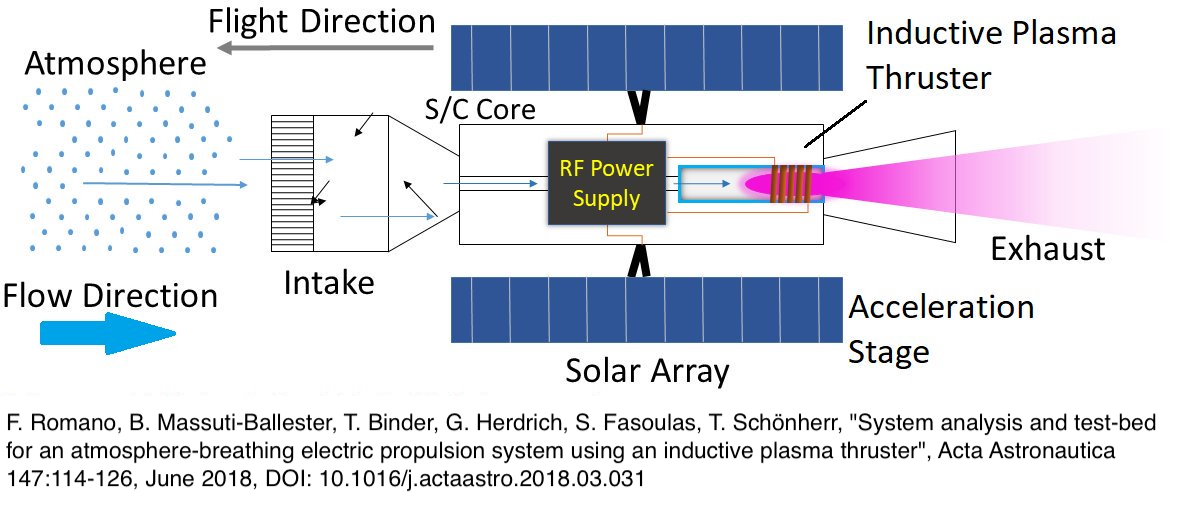
Atmosphere-breathing electric propulsion, or air-breathing electric propulsion, shortly ABEP, is a propulsion technology for spacecraft, which could allow thrust generation in low orbits without the need of on-board propellant, by using residual gases in the atmosphere as propellant. Atmosphere-breathing electric propulsion could make a new class of long-lived, low-orbiting missions feasible. The concept is currently being investigated by the European Space Agency (ESA), the EU-funded BREATHE project at Sant'Anna School of Advanced Studies in Pisa and the EU-funded DISCOVERER project. Current state-of-the-art conventional electric thrusters cannot maintain flight at low altitudes for any times longer than about 2 years, because of the limitation in propellant storage and in the amount of thrust generated, which force the spacecraft's orbit to decay. The ESA officially announced the first successful RAM-EP prototype on-ground demonstration in March 2018. Principle of operation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Super Low Altitude Test Satellite
Super Low Altitude Test Satellite (SLATS) or Tsubame was a JAXA satellite intended to demonstrate operations in very low Earth orbit (VLEO, below 200 km), using ion engines to counteract aerodynamic drag from the Earth's atmosphere which is substantial at such lower orbital altitudes. It was launched on 23 December 2017, and decommissioned on 1 October 2019. The spacecraft was equipped with sensors to determine atomic oxygen density, an exposure facility to measure material degradation in the 200 km orbit, and a small camera. Initial designs had conventional, though slightly canted, solar panels (compare to the aerodynamic shape and on-body solar panels of GOCE, which flew in a 255 km orbit). SLATS's nickname ''Tsubame'' is Japanese for barn swallow. According to JAXA the name was chosen because the thin, elongated satellite in super low orbit with its set of solar array wings was reminiscent of a swallow flying low to the ground. SLATS was launched 23 Decemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientific research, and Earth observation. Additional military uses are reconnaissance, early warning, signals intelligence and, potentially, weapon delivery. Other satellites include the final rocket stages that place satellites in orbit and formerly useful satellites that later become defunct. Except for passive satellites, most satellites have an electricity generation system for equipment on board, such as solar panels or radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTGs). Most satellites also have a method of communication to ground stations, called transponders. Many satellites use a standardized bus to save cost and work, the most popular of which are small CubeSats. Similar satellites can work together as groups, forming constellatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DARPA
The Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) is a research and development agency of the United States Department of Defense responsible for the development of emerging technologies for use by the military. Originally known as the Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA), the agency was created on February 7, 1958, by President Dwight D. Eisenhower in response to the Soviet Union, Soviet launching of Sputnik 1 in 1957. By collaborating with academia, industry, and government partners, DARPA formulates and executes research and development projects to expand the frontiers of technology and science, often beyond immediate U.S. military requirements.Dwight D. Eisenhower and Science & Technology, (2008). Dwight D. Eisenhower Memorial CommissionSource The name of the organization first changed from its founding name, ARPA, to DARPA, in March 1972, changing back to ARPA in February 1993, then reverted to DARPA in March 1996. ''The Economist'' has called DARPA "the agency that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allotropes Of Oxygen
There are several known allotropy, allotropes of oxygen. The most familiar is oxygen, molecular oxygen (), present at significant levels in Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere and also known as dioxygen or triplet oxygen. Another is the highly reactive ozone (). Others are: *Atomic oxygen (), a Radical (chemistry), free radical. *Singlet oxygen (), one of two metastable states of molecular oxygen. *Tetraoxygen (), another metastable form. *Solid oxygen, existing in six variously colored phases, of which one is octaoxygen (, red oxygen) and another one metallic (ζ-oxygen). Atomic oxygen Atomic oxygen, denoted O or O1, is very reactive, as the individual atoms of oxygen tend to quickly bond with nearby molecules. Its lowest-energy electronic state is a Triplet state, spin triplet, designated by the term symbol 3P. On Earth's surface, it exists naturally for a very short time. In outer space, the presence of ample ultraviolet radiation results in a low Earth orbit atmosphere in w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Space Station
The International Space Station (ISS) is a large space station that was Assembly of the International Space Station, assembled and is maintained in low Earth orbit by a collaboration of five space agencies and their contractors: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), European Space Agency, ESA (Europe), JAXA (Japan), and Canadian Space Agency, CSA (Canada). As the largest space station ever constructed, it primarily serves as a platform for conducting scientific experiments in microgravity and studying the space environment. The station is divided into two main sections: the Russian Orbital Segment (ROS), developed by Roscosmos, and the US Orbital Segment (USOS), built by NASA, ESA, JAXA, and CSA. A striking feature of the ISS is the Integrated Truss Structure, which connect the station’s vast system of solar panels and Spacecraft thermal control, radiators to its pressurized modules. These modules support diverse functions, including scientific research, crew habitation, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Square Law
In science, an inverse-square law is any scientific law stating that the observed "intensity" of a specified physical quantity is inversely proportional to the square of the distance from the source of that physical quantity. The fundamental cause for this can be understood as geometric dilution corresponding to point-source radiation into three-dimensional space. Radar energy expands during both the signal transmission and the reflected return, so the inverse square for both paths means that the radar will receive energy according to the inverse fourth power of the range. To prevent dilution of energy while propagating a signal, certain methods can be used such as a waveguide, which acts like a canal does for water, or how a gun barrel restricts hot gas expansion to one dimension in order to prevent loss of energy transfer to a bullet. Formula In mathematical notation the inverse square law can be expressed as an intensity (I) varying as a function of distance (d) from so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Power Density
Power density, defined as the amount of power (the time rate of energy transfer) per unit volume, is a critical parameter used across a spectrum of scientific and engineering disciplines. This metric, typically denoted in watts per cubic meter (W/m3), serves as a fundamental measure for evaluating the efficacy and capability of various devices, systems, and materials based on their spatial energy distribution. The concept of power density finds extensive application in physics, engineering, electronics, and energy technologies. It plays a pivotal role in assessing the efficiency and performance of components and systems, particularly in relation to the power they can handle or generate relative to their physical dimensions or volume. In the domain of energy storage and conversion technologies, such as batteries, fuel cells, motors, and power supply units, power density is a crucial consideration. Here, power density often refers to the volume power density, quantifying how much ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Debris
Space debris (also known as space junk, space pollution, space waste, space trash, space garbage, or cosmic debris) are defunct human-made objects in spaceprincipally in Earth orbitwhich no longer serve a useful function. These include derelict spacecraft (nonfunctional spacecraft and abandoned launch vehicle stages), mission-related debris, and particularly numerous in-Earth orbit, fragmentation debris from the breakup of derelict rocket bodies and spacecraft. In addition to derelict human-made objects left in orbit, space debris includes fragments from disintegration, erosion, or collisions; solidified liquids expelled from spacecraft; unburned particles from solid rocket motors; and even paint flecks. Space debris represents a risk to spacecraft. Space debris is typically a negative externality. It creates an external cost on others from the initial action to launch or use a spacecraft in near-Earth orbit, a cost that is typically not taken into account nor fully accoun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bellatrix Aerospace
Bellatrix Aerospace is an Indian private aerospace manufacturer and small satellite manufacturing company, headquartered in Bangalore, Karnataka. The company was established in 2015 and in June 2022, the company raised $8 million in a Series A funding round to pursue the development of in-space propulsion systems. Name The name ''Bellatrix'' is from the Latin ''bellātrix'' which means "female warrior". It was also used in naming the red supergiant star Bellatrix. History Bellatrix Aerospace had initially proposed the development of its small-lift orbital class launch vehicle named Chetak and had planned for its launch in 2023. The two-stage Chetak was to be powered by a number of its proposed Aeon engines which would use liquid methane as propellant. Later in 2019, water was proposed as a propellant for an electric propulsion system. On 8 February 2021, Bellatrix Aerospace announced its partnership with Skyroot Aerospace. However, on 9 February 2022, Founder Rohan Ganapathy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Satellite Constellation
A satellite constellation is a group of artificial satellites working together as a system. Unlike a single satellite, a constellation can provide permanent global or near-global pass (spaceflight), coverage, such that at any time everywhere on Earth at least one satellite is visible. Satellites are typically placed in sets of complementary orbital plane (astronomy), orbital planes and connect to globally distributed ground stations. They may also use Inter-satellite service, inter-satellite communication. Other satellite groups Satellite constellations should not be confused with: * ''satellite clusters'', which are groups of satellites moving very close together in almost identical orbits (see satellite formation flying); * '':Satellite series, satellite series'' or ''satellite programs'' (such as Landsat program, Landsat), which are generations of satellites launched in succession; * ''satellite fleets'', which are groups of satellites from the same manufacturer or operator tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High Frequency
High frequency (HF) is the ITU designation for the band of radio waves with frequency between 3 and 30 megahertz (MHz). It is also known as the decameter band or decameter wave as its wavelengths range from one to ten decameters (ten to one hundred meters). Frequencies immediately below HF are denoted '' medium frequency'' (MF), while the next band of higher frequencies is known as the '' very high frequency'' (VHF) band. The HF band is a major part of the shortwave band of frequencies, so communication at these frequencies is often called ''shortwave radio''. Because radio waves in this band can be reflected back to Earth by the ionosphere layer in the atmosphere – a method known as "skip" or "skywave" propagation – these frequencies can be used for long-distance communication across intercontinental distances and for mountainous terrains which prevent line-of-sight communications. The band is used by international shortwave broadcasting stations (3.95–25.8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |