|
VERITAS (spacecraft)
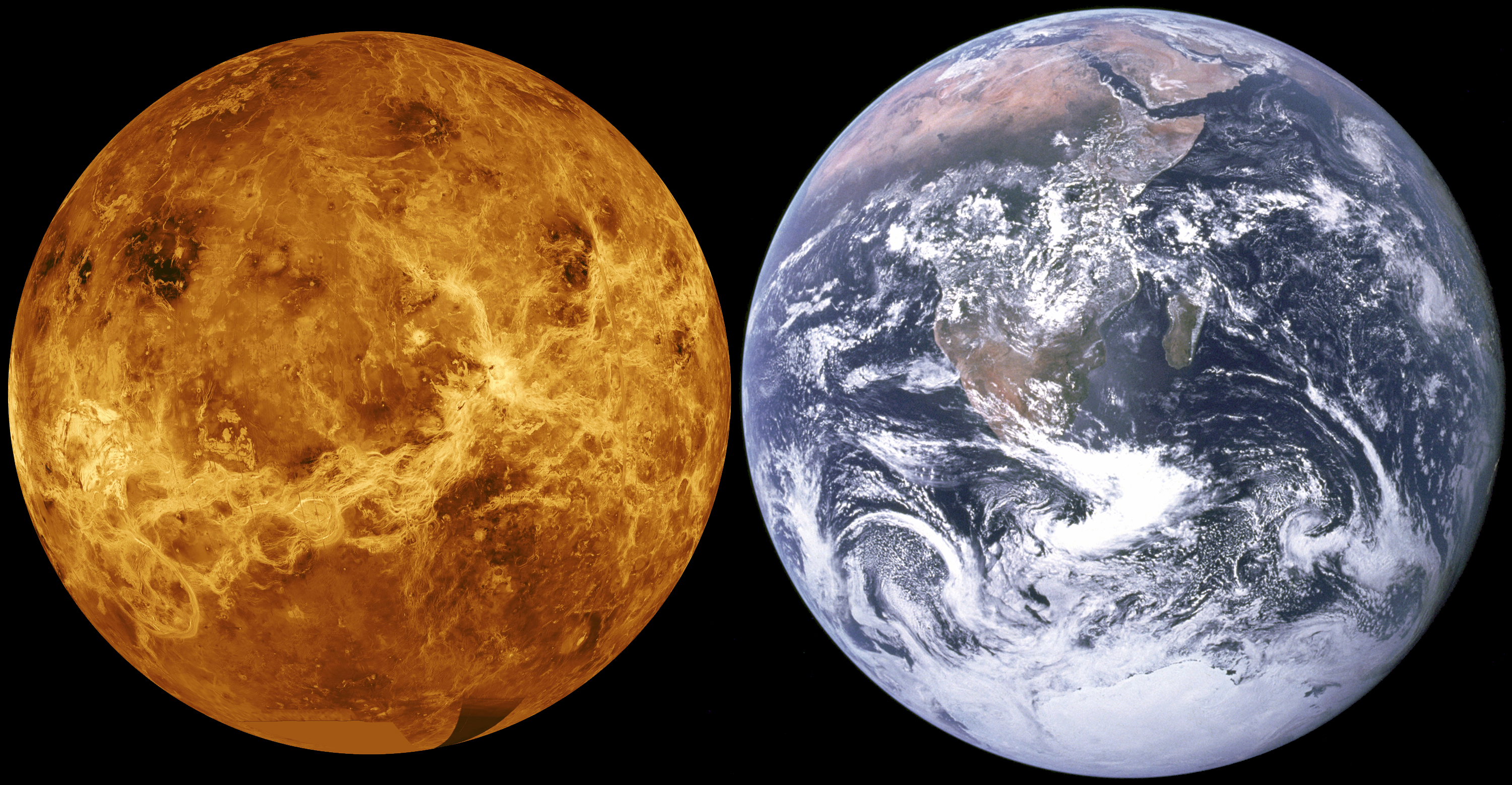
VERITAS (Venus Emissivity, Radio Science, InSAR, Topography, and Spectroscopy) is an upcoming mission from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) to map the surface of planet Venus in high resolution. The combination of topography, near-infrared spectroscopy, and radar image data will provide knowledge of Venus's tectonic and impact history, gravity, geochemistry, the timing and mechanisms of volcanic resurfacing, and the mantle processes responsible for them. Proposal history VERITAS was one of dozens of proposals submitted in 2015 to potentially become the 13th mission of NASA’s Discovery Program. Suzanne Smrekar of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) would serve as the principal investigator, and JPL would be the managing agency. On 30 September 2015, VERITAS was selected as one of five finalists. On 4 January 2017, two other proposals to study small bodies, ''Lucy'' and ''Psyche'', were selected as the 13th and 14th Discovery missions, respectively. VERITAS was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Extraterrestrial Orbiters
List of extraterrestrial orbiters is a listing of spacecraft that achieved an extraterrestrial orbit. Sun First artificial object on heliocentric orbit was Luna 1 (1959). Mercury Venus Moon Mars Jupiter Saturn Minor planets and comets References See also *Lunar orbit *Circumlunar trajectory *List of minor planets and comets visited by spacecraft *List of landings on extraterrestrial bodies *List of interplanetary voyages *Satellite system (astronomy) {{Spaceflight lists and timelines extraterrestrial extraterrestrial Extraterrestrial refers to any object or being beyond ( extra-) the planet Earth ( terrestrial). It is derived from the Latin words ''extra'' ("outside", "outwards") and ''terrestris'' ("earthly", "of or relating to the Earth"). It may be abbrevia ... * Non Earth orbiting satellites * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar
Interferometric synthetic aperture radar, abbreviated InSAR (or deprecated IfSAR), is a radar technique used in geodesy and remote sensing. This geodetic method uses two or more synthetic aperture radar (SAR) images to generate maps of surface deformation or digital elevation, using differences in the phase of the waves returning to the satellite or aircraft. The technique can potentially measure millimetre-scale changes in deformation over spans of days to years. It has applications for geophysical monitoring of natural hazards, for example earthquakes, volcanoes and landslides, and in structural engineering, in particular monitoring of subsidence and structural stability. Technique Synthetic aperture radar Synthetic aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar in which sophisticated processing of radar data is used to produce a very narrow effective beam. It can be used to form images of relatively immobile targets; moving targets can be blurred or displaced in the formed im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Missions To Venus ...
There have been 46 (including gravity-assist flybys) space missions to the planet Venus. Missions to Venus constitute part of the exploration of Venus. List As of 2020, the Soviet Union, United States, European Space Agency and Japan have conducted missions to Venus. ;Mission Type Legend: Future missions Under development Venus Missions by Organization/Company Proposed missions References External links * {{Venus Venus * Venus Missions to Venus There have been 46 (including gravity-assist flybys) space missions to the planet Venus. Missions to Venus constitute part of the exploration of Venus. List As of 2020, the Soviet Union, United States, European Space Agency and Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
STP-2
The Space Test Program (STP) is the primary provider of spaceflight for the United States Department of Defense (DoD) space science and technology community. STP is managed by a group within the Advanced Systems and Development Directorate, a directorate of the Space and Missile Systems Center of the United States Space Force. STP provides spaceflight via the International Space Station (ISS), piggybacks, secondary payloads and dedicated launch services. Past activities STP has actually been in existence for 50 years as of 2019, with several thousand launches it has been responsible for. For example, the initial experiments that led to the modern Global Positioning System (GPS) satellite constellation were STP-launched projects. 2001 During August 2001, STP conducted two successful activities using the Space Shuttle and ISS. STS-105 delivered and successfully deployed the Materials International Space Station Experiment (MISSE) externally on the ISS. MISSE was a passive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deep Space Atomic Clock
The Deep Space Atomic Clock (DSAC) was a miniaturized, ultra-precise mercury-ion atomic clock for precise radio navigation in deep space. DSAC was designed to be orders of magnitude more stable than existing navigation clocks, with a drift of no more than 1 nanosecond in 10 days. It is expected that a DSAC would incur no more than 1 microsecond of error in 10 years of operations. Data from DSAC is expected to improve the precision of deep space navigation, and enable more efficient use of tracking networks. The project was managed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and it was deployed as part of the U.S. Air Force's Space Test Program 2 (STP-2) mission aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket on 25 June 2019. The Deep Space Atomic Clock was activated on 23 August 2019. Following a mission extension in June 2020, DSAC was deactivated on 18 September 2021 after two years in operation. Overview Current ground-based atomic clocks are fundamental to deep space navigation; howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Water Vapor
(99.9839 °C) , - , Boiling point , , - , specific gas constant , 461.5 J/( kg·K) , - , Heat of vaporization , 2.27 MJ/kg , - , Heat capacity , 1.864 kJ/(kg·K) Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous phase of water. It is one state of water within the hydrosphere. Water vapor can be produced from the evaporation or boiling of liquid water or from the sublimation of ice. Water vapor is transparent, like most constituents of the atmosphere. Under typical atmospheric conditions, water vapor is continuously generated by evaporation and removed by condensation. It is less dense than most of the other constituents of air and triggers convection currents that can lead to clouds. Being a component of Earth's hydrosphere and hydrologic cycle, it is particularly abundant in Earth's atmosphere, where it acts as a greenhouse gas and warming feedback, contributing more to total greenhouse effect than non-condensable gases such as carbon dio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Aerospace Center
The German Aerospace Center (german: Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt e.V., abbreviated DLR, literally ''German Center for Air- and Space-flight'') is the national center for aerospace, energy and transportation research of Germany, founded in 1969. It is headquartered in Cologne with 35 locations throughout Germany. The DLR is engaged in a wide range of research and development projects in national and international partnerships. DLR also acts as the German space agency and is responsible for planning and implementing the German space programme on behalf of the German federal government. As a project management agency, DLR coordinates and answers the technical and organisational implementation of projects funded by a number of German federal ministries. As of 2020, the German Aerospace Center had a national budget of €1.261 billion. Overview DLR has approximately 10.000 employees at 30 locations in Germany. Institutes and facilities are spread over 13 site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Window
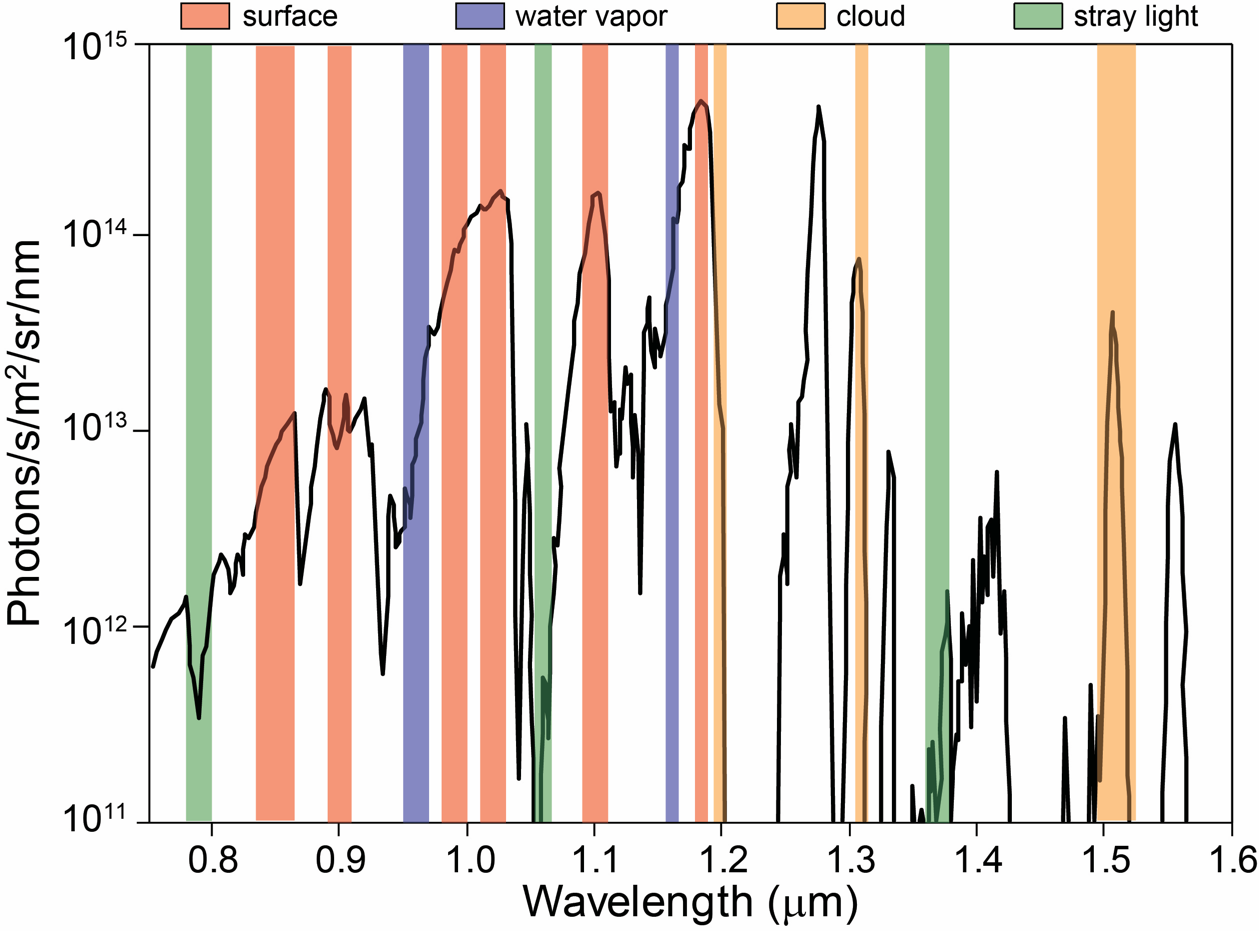
An atmospheric window is a range of wavelengths of the electromagnetic spectrum that can pass through the atmosphere of Earth. The optical, infrared and radio windows comprise the three main atmospheric windows. The windows provide direct channels for Earth's surface to receive electromagnetic energy from the Sun, and for thermal radiation from the surface to leave to space. Atmospheric windows are useful for astronomy, remote sensing, telecommunications and other science & technology applications. Role in Earth's energy budget Atmospheric windows, especially the optical and infrared, affect the distribution of energy flows and temperatures within Earth's energy balance. The windows are themselves dependent upon clouds, water vapor, trace greenhouse gases, and other components of the atmosphere. Out of an average 340 watts per square meter (W/m2) of solar irradiance at the top of the atmosphere, about 200 W/m2 reaches the surface via windows, mostly the optical and inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Venus Emissivity Mapper
The Venus Emissivity Mapper (VEM) is a spectrometer for mapping the surface composition of Venus through a distinct number of atmospheric spectral windows. It will be one of the two payloads onboard the ''VERITAS'' mission, and represents the VenSpec-M channel of the ''EnVision'' mission's spectrometer suite. Overview While Earth and Venus are similar in many aspects, they evolved very differently and currently have distinct surface and atmospheric environments. Where Earth's surface has liquid water and is crawling with life, Venus experiences a mean surface temperature of over 400 °C, and a carbon dioxide rich atmosphere with a surface pressure of about 92 times that of Earth at sea-level. As of 2021, not much is known about Venus' surface composition. The dense atmosphere and its cloud layers are quite impermeable to visible and infrared radiation, making remote sensing a challenge. As the signal travels through the atmosphere, it is attenuated by absorption and scatte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Instrument
A scientific instrument is a device or tool used for scientific purposes, including the study of both natural phenomena and theoretical research. History Historically, the definition of a scientific instrument has varied, based on usage, laws, and historical time period. Before the mid-nineteentcenturysuch tools were referred to as "natural philosophical" or "philosophical" apparatus and instruments, and older tools from antiquity to the Middle Ages (such as the astrolabe and pendulum clock) defy a more modern definition of "a tool developed to investigate nature qualitatively or quantitatively." Scientific instruments were made by instrument makers living near a center of learning or research, such as a university or research laboratory. Instrument makers designed, constructed, and refined instruments for purposes, but if demand was sufficient, an instrument would go into production as a commercial product. In a description of the use of the eudiometer by Jan Ingenhousz to s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geology Of Venus
Venus is a planet with striking geology. Of all the other planets in the Solar System, it is the one nearest to Earth and most like it in terms of mass, but has no magnetic field or recognizable plate tectonic system. Much of the ground surface is exposed volcanic bedrock, some with thin and patchy layers of soil covering, in marked contrast with Earth, the Moon, and Mars. Some impact craters are present, but Venus is similar to Earth in that there are fewer craters than on the other rocky planets that are largely covered by them. This is due in part to the thickness of the Venusian atmosphere disrupting small impactors before they strike the ground, but the paucity of large craters may be due to volcanic re-surfacing, possibly of a catastrophic nature. Volcanism appears to be the dominant agent of geological change on Venus. Some of the volcanic landforms appear to be unique to the planet. There are shield and composite volcanoes similar to those found on Earth. Given that Venu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps. Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary science and is concerned with local detail in general, including not only relief, but also natural, artificial, and cultural features such as roads, land boundaries, and buildings. In the United States, topography often means specifically ''relief'', even though the USGS topographic maps record not just elevation contours, but also roads, populated places, structures, land boundaries, and so on. Topography in a narrow sense involves the recording of relief or terrain, the three-dimensional quality of the surface, and the identification of specific landforms; this is also known as geomorphometry. In modern usage, this involves generation of elevation data in digital form ( DEM). It is often considered to include the graphic representat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |