|
V-by-One US
V-by-One US is an electrical digital signaling standard developed by THine Electronics. It succeeds V-by-One HS, offers four times the data rate per signaling lane and is used as internal interface of digital pixel displays. History THine announced the development of the transmission lines for V-by-One US on June 5, 2017. The new specification allows data rates up to 16 Gbit/s per lane, which is 4 times faster than the 4 Gbit/s of V-by-One HS. It enables 4K 60 Hz displays over 2 lanes and 8K 60 Hz displays over 8 lanes. On September 21, 2018, the company announced it had working samples of the V-by-One US chipset ready. The chipset supports two 16 Gbit/s signalling lanes, which enables a 4K display or four 1080p displays at 60 Hz. The chipset is able to data between 8-lane V-by-One HS and 2-lane V-by-One US. August 13, 2020, Silicon Creations announced that its Deserializer PMA was used as a V-by-One HS receiver in a 12nm SoC aimed at 8K TV's designed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
THine Electronics
THine Electronics Incorporated is a Japanese fabless LSI maker that provides mixed signal LSI and analog technologies, headquartered in Tokyo, Japan. THine Electronics also has subsidiaries in Seoul, Korea, Taipei, and Taiwan. Some of THine’s products have the most market shares in the world because of technical advantages. Its technologies include high-speed interfaces such as V-by-One HS, LVDS, timing controller, analog-to-digital converter (ADC), image signal processor (ISP), and power management in smart phone, tablets, flat screen televisions, LCD monitors, projectors, document processing, amusement, security systems, and automotive markets. History Start-up in Tsukuba THine was founded in Tsukuba, Japan, in 1991 by Dr. Tetsuya Iizuka as THine Microsystems. The name “THine” is after the Old English word “thine” which means “yours”. The capitalization stands for "Targeting High" and "Talented Human". In 1992 THine Microsystems and Samsung Electronics Corporatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V-by-One HS
V-by-One HS is an electrical digital signaling standard that can run at faster speeds over inexpensive twisted-pair copper cables than Low-voltage differential signaling, or LVDS. It was originally developed by THine Electronics, Inc. in 2007 for high-definition televisions but since 2010 V-by-One HS has been widely adopted in various markets such as document processing, automotive infotainment systems, industrial cameras and machine vision, robotics and amusement equipments. While high-definition televisions had generally used LVDS to transmit pixel data, timing-skew problems among conductors appeared by increasing data rate based on requirements of higher-resolution and more color-depth. V-by-One HS, by its SerDes and CDR(Clock recovery) technology, achieves the high speed of 3.75 Gbit/s for each pair of conductors, decreasing the number of conductors, therefore reducing the total costs including cables and connectors. This solves skew problems and reduces electromagnetic interf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
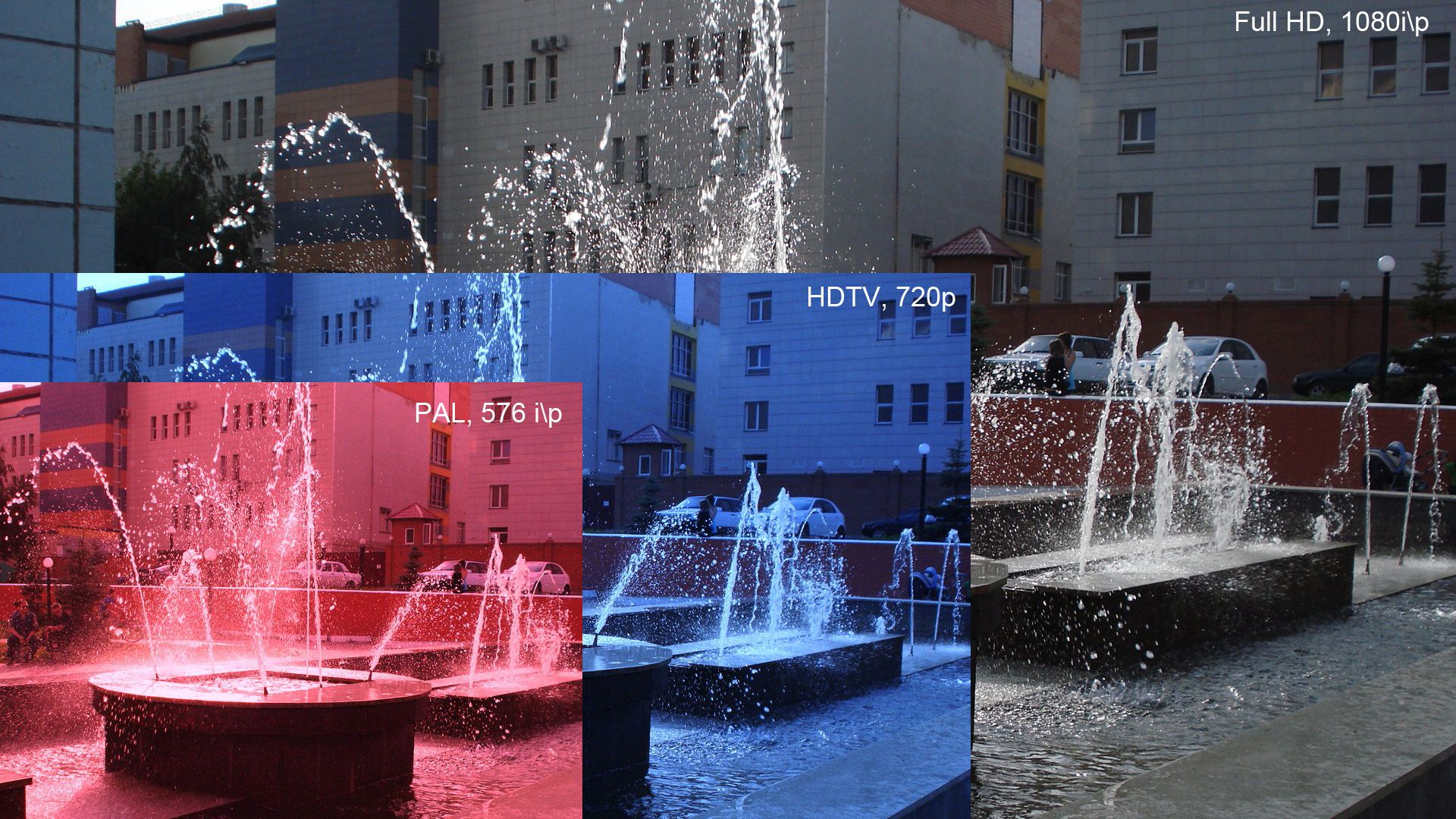
4K Resolution
4K resolution refers to a horizontal display resolution of approximately 4,000 pixels. Digital television and digital cinematography commonly use several different 4K resolutions. In television and consumer media, 38402160 (4K UHD) is the dominant 4K standard, whereas the movie projection industry uses 40962160 (DCI 4K). The 4K television market share increased as prices fell dramatically during 2014 and 2015. 4K standards and terminology The term "4K" is generic and refers to any resolution with a horizontal pixel count of approximately 4,000. Several different 4K resolutions have been standardized by various organizations. The terms "4K" and "Ultra HD" are used more widely in marketing than "2160p". While typically referring to motion pictures, some digital camera vendors have used the term "4K photo" for still photographs, making it appear like an especially high resolution even though 3840×2160 pixels equal approximately 8.3 megapixels, which is not considered to be es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
8K Resolution
8K resolution refers to an image or display resolution with a width of approximately 8,000 pixels. 8K UHD () is the highest resolution defined in the Rec. 2020 (UHDTV) standard. 8K display resolution is the successor to 4K resolution. TV manufacturers pushed to make 4K a new standard by 2017. At CES 2019, the first 8K TVs were unveiled. The feasibility of a fast transition to this new standard is questionable in view of the absence of broadcasting resources. It is predicted (2018 forecast by Strategy Analytics) that 8K-ready devices will still only account for 3% of UHD TVs by 2023 with global sales of 11 million units a year. However, TV manufacturers remain optimistic as the 4K market grew much faster than expected, with actual sales exceeding projections nearly six-fold in 2016. In 2013, a transmission network's capability to carry HDTV resolution was limited by internet speeds and relied on satellite broadcast to transmit the high data rates. The demand is expected to driv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1080p
1080p (1920×1080 progressively displayed pixels; also known as Full HD or FHD, and BT.709) is a set of HDTV high-definition video modes characterized by 1,920 pixels displayed across the screen horizontally and 1,080 pixels down the screen vertically; the ''p'' stands for progressive scan, ''i.e.'' non-interlaced. The term usually assumes a widescreen aspect ratio of 16:9, implying a resolution of 2.1 megapixels. It is often marketed as Full HD or FHD, to contrast 1080p with 720p resolution screens. Although 1080p is sometimes informally referred to as 2K, these terms reflect two distinct technical standards, with differences including resolution and aspect ratio. 1080p video signals are supported by ATSC standards in the United States and DVB standards in Europe. Applications of the 1080p standard include television broadcasts, Blu-ray Discs, smartphones, Internet content such as YouTube videos and Netflix TV shows and movies, consumer-grade televisions and p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon Creations
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron. Silicon is the eighth Abundance of the chemical elements, most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deserialize
In computing, serialization (or serialisation) is the process of translating a data structure or object state into a format that can be stored (e.g. files in secondary storage devices, data buffers in primary storage devices) or transmitted (e.g. data streams over computer networks) and reconstructed later (possibly in a different computer environment). When the resulting series of bits is reread according to the serialization format, it can be used to create a semantically identical clone of the original object. For many complex objects, such as those that make extensive use of references, this process is not straightforward. Serialization of object-oriented objects does not include any of their associated methods with which they were previously linked. This process of serializing an object is also called marshalling an object in some situations. The opposite operation, extracting a data structure from a series of bytes, is deserialization, (also called unserialization or unma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
14 Nm Process
The 14 nm process refers to the MOSFET technology node that is the successor to the 22nm (or 20nm) node. The 14nm was so named by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS). Until about 2011, the node following 22nm was expected to be 16nm. All 14nm nodes use FinFET (fin field-effect transistor) technology, a type of multi-gate MOSFET technology that is a non-planar evolution of planar silicon CMOS technology. Samsung Electronics taped out a 14 nm chip in 2014, before manufacturing 10 nm class NAND flash chips in 2013. The same year, SK Hynix began mass-production of 16nm NAND flash, and TSMC began 16nm FinFET production. The following year, Intel began shipping 14nm scale devices to consumers. History Background The basis for sub-20nm fabrication is the FinFET (Fin field-effect transistor), an evolution of the MOSFET transistor. FinFET technology was pioneered by Digh Hisamoto and his team of researchers at Hitachi Central Research Laboratory in 198 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
System On A Chip
A system on a chip or system-on-chip (SoC ; pl. ''SoCs'' ) is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include a central processing unit (CPU), memory interfaces, on-chip input/output devices, input/output interfaces, and secondary storage interfaces, often alongside other components such as radio modems and a graphics processing unit (GPU) – all on a single substrate or microchip. It may contain digital, analog, mixed-signal, and often radio frequency signal processing functions (otherwise it is considered only an application processor). Higher-performance SoCs are often paired with dedicated and physically separate memory and secondary storage (such as LPDDR and eUFS or eMMC, respectively) chips, that may be layered on top of the SoC in what's known as a package on package (PoP) configuration, or be placed close to the SoC. Additionally, SoCs may use separate wireless ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Novatek Microelectronics
Novatek (russian: ПАО «НОВАТЭК», , ) is Russia's second-largest natural gas producer (behind Gazprom), and the seventh-largest publicly traded company globally by natural gas production volume. The company was originally known as OAO FIK Novafininvest. Novatek is based in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Region in West Siberia, and maintains a sales office in Moscow. In the 2020 Forbes Global 2000, Novatek was ranked as the 316th-largest public company in the world. The company is not to be confused with Novatek Inc, a US company that produces synthetic diamonds for the oil and gas industry, or Novatek Microelectronics Corp., a supplier of display controller integrated circuits, or Novatek AS, a Norwegian engineering company. Operations In 2006, the company produced roughly thirty billion cubic metres (1.1 trillion cubic feet) of natural gas. By 2010, production had grown to , and in 2011 to In 2010, Novatek supplied 13% of the domestic market and accounted for 32% of n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |