|
Utinahica
Utinahica was a town that was the site of a Spanish mission, Santa Isabel de Utinahica. It may have been the chief town of a Timucua tribe and chiefdom in the 17th century, but Hann says there is not enough known about it to be sure. The name means "lord's village". Utinahica (or, rather, the mission of Santa Isabela), was called a "province" in one Spanish report. It was 30 leagues east of Arapaha, and 50 leagues northeast of the town of Tarihica in the Northern Utina Province. It was at or near where the Oconee and Ocmulgee rivers join to form the Altamaha River. The people of Utinahica apparently practiced a regional variant of the Lamar regional culture, unusual for a Timucuan-speaking people. Worth identifies the province of Utinahica with archaeological sites, including the Lind Landing site, Coffee Bluff site, and Bloodroot site, that have yielded artifacts of the Square Ground Lamar culture from before the 15th century until the middle of the 17th century. The Square G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Isabel De Utinahica
Santa Isabel de Utinahica (ca. 1610 – ca. 1640) was a 17th-century Spanish mission believed by the Fernbank Museum of Natural History to be located in modern-day Telfair County, Georgia, near Jacksonville. It served the Utinahica tribe, who lived in the area. The small mission was a part of a series of missions set up in what was then the northern reaches of the Spanish colony of Spanish Florida, similar to the Spanish Missions in California or Mexico. Operating for approximately two decades in the early 17th century, the mission was a religious outpost consisting of one Catholic friar sent out to convert and monitor the native people at the edges of the colony. The name Utinahica was taken from the local Native American chiefdom, themselves a part of the Timucua people and possibly ancestors of the current Creek people. The mission's exact location is not presently known with certainty. In April 2006 the Fernbank Museum of Natural History and Georgia Department of Natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Timucua
The Timucua were a Native American people who lived in Northeast and North Central Florida and southeast Georgia. They were the largest indigenous group in that area and consisted of about 35 chiefdoms, many leading thousands of people. The various groups of Timucua spoke several dialects of the Timucua language. At the time of European contact, Timucuan speakers occupied about in the present-day states of Florida and Georgia, with an estimated population of 200,000. Milanich notes that the population density calculated from those figures, is close to the population densities calculated by other authors for the Bahamas and for Hispaniola at the time of first European contact. The territory occupied by Timucua speakers stretched from the Altamaha River and Cumberland Island in present-day Georgia as far south as Lake George in central Florida, and from the Atlantic Ocean west to the Aucilla River in the Florida Panhandle, though it reached the Gulf of Mexico at no more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altamaha River
The Altamaha River is a major river in the U.S. state of Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia. It flows generally eastward for from its Source (river or stream), origin at the confluence of the Oconee River and Ocmulgee River towards the Atlantic Ocean, where it empties into the ocean near Brunswick, Georgia. No dams are directly on the Altamaha, though some are on the Oconee and the Ocmulgee. Including its tributaries, the Altamaha River's drainage basin is about in size, qualifying it among the larger river basins of the US Atlantic coast.The Altamaha River Course The Altamaha River originates at the confluence of the Oconee and Ocmulgee Rivers, near Lumber City, Georgia, Lumber City. At its source, the river forms the border between Jeff Davis County, Georgia, Jeff Davis ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Missions In Florida
Beginning in the second half of the 16th century, the Kingdom of Spain established Christian missions, missions in Spanish Florida (''La Florida'') in order to convert the Native Americans in the United States, indigenous tribes to Roman Catholicism, to facilitate control of the area, and to obstruct regional colonization by Protestants, particularly, those from Kingdom of England, England and Kingdom of France, France. Spanish Florida originally included much of what is now the Southeastern United States, although Spain never exercised long-term effective control over more than the northern part of what is now the State of Florida from present-day St. Augustine, Florida, St. Augustine to the area around Tallahassee, Florida, Tallahassee, southeastern Georgia (U.S. state), Georgia, and some coastal settlements, such as Pensacola, Florida. A few short-lived missions were established in other locations, including Mission Santa Elena in present-day South Carolina, around the Florida ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Buenaventura De Guadalquini
San Buenaventura de Guadalquini or San Buenaventura de Boadalquivi was a Spanish mission located on St. Simons, Georgia, St. Simon's Island, Georgia, United States from between 1597 and 1609 until 1684, when pirates burned the mission and its town. The mission moved to the north side of the St. Johns River near its mouth, in present day Duval County, Florida, Duval County, Florida under the name of Santa Cruz de Guadalquini or Santa Cruz y San Buenaventura de Guadalquini for a few years before merging with the mission San Juan del Puerto. Location and ethnicity ''Guadalquini'' was the Timucua language name for St. Simon's Island, which the Spanish called ''Isla de Ballenas'' (Isle of Whales). The name also appeared in several Spanish documents as . For most of the 20th century historians thought the mission of San Buenaventura de Guadalquini had been located on Jekyll Island, but examination of previously known and newly discovered documentary evidence has identified Gualdalquini wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arapaha
Arapaha (also Arapaja or Harapaha) was a Timucua town on the Alapaha River in the 17th century. The name was also sometimes used to designate a province or sub-province in Spanish Florida. Arapaha entered historical records with the establishment of the mission of Santa María de los Angeles de Arapaha in the 1620s. This mission was to the north of missions established in Timucua Province (in the original narrow sense of the territory of the Northern Utina), and northeast of Yustaga Province. The town of Arapaha was probably located on the Alapaha River. ("Arapaha" is presumed to have been changed to "Alapaha" by speakers of one of the Muskogean languages, which lack "r".) "Arapaha" likely meant "many houses" or "bear town" in the Timucuan language. The people referred to by the French as "Onatheaqua" in the 1560s may have been the same as the Northern Utina or Arapaha. Several other missions are associated with Santa María de los Angeles de Arapaha in Spanish records, inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Of The Timucua Chiefdoms Of Mainland Southeast Georgia
A map is a symbolic depiction of interrelationships, commonly spatial, between things within a space. A map may be annotated with text and graphics. Like any graphic, a map may be fixed to paper or other durable media, or may be displayed on a transitory medium such as a computer screen. Some maps change interactively. Although maps are commonly used to depict geographic elements, they may represent any space, real or fictional. The subject being mapped may be two-dimensional such as Earth's surface, three-dimensional such as Earth's interior, or from an abstract space of any dimension. Maps of geographic territory have a very long tradition and have existed from ancient times. The word "map" comes from the , wherein ''mappa'' meant 'napkin' or 'cloth' and ''mundi'' 'of the world'. Thus, "map" became a shortened term referring to a flat representation of Earth's surface. History Maps have been one of the most important human inventions for millennia, allowing humans t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native American Tribes In Georgia (U
Native may refer to: People * '' Jus sanguinis'', nationality by blood * '' Jus soli'', nationality by location of birth * Indigenous peoples, peoples with a set of specific rights based on their historical ties to a particular territory ** Native Americans (other) In arts and entertainment * Native (band), a French R&B band * Native (comics), a character in the X-Men comics universe * ''Native'' (album), a 2013 album by OneRepublic * ''Native'' (2016 film), a British science fiction film * ''The Native'', a Nigerian music magazine In science * Native (computing), software or data formats supported by a certain system * Native language, the language(s) a person has learned from birth * Native metal, any metal that is found in its metallic form, either pure or as an alloy, in nature * Native species, a species whose presence in a region is the result of only natural processes * List of Australian plants termed "native", whose common name is of the form "native . . . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cacique
A cacique, sometimes spelled as cazique (; ; feminine form: ), was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, who were the Indigenous inhabitants of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles at the time of European contact with those places. The term is a Spanish transliteration of the Taíno word . Cacique was initially translated as "king" or "prince" for the Spanish. In the colonial era, the conquistadors and the administrators who followed them used the word generically to refer to any leader of practically any indigenous group they encountered in the Western Hemisphere. In Hispanic and Lusophone countries, the term has also come to mean a political boss, similar to a ''caudillo,'' exercising power in a system of caciquism. Spanish colonial-era caciques The Taíno word descends from the Taíno word , which means "to keep house". In 1555 the word first entered the English language, defined as "prince". In Taíno culture, the rank was heredita ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Westo
The Westo were an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribe encountered in what became the Southeastern U.S. by Europeans in the 17th century. They probably spoke an Iroquoian languages, Iroquoian language. The Spanish called these people Chichimeco (not to be confused with Chichimeca in Mexico), and Virginia colonists may have called the same people Richahecrian. Their first appearance in the historical record is as a powerful tribe in colonial Colony and Dominion of Virginia, Virginia who had migrated from the mountains into the region around present-day Richmond. Their population provided a force of 700–900 warriors. Early academic analysis of the origin of the Westo posited that the so-called ''Rechahecrian/Rickohakan'' of Virginia were perhaps Cherokee or Yuchi, and that the Westo were a band of Yuchi. Anthropologist Marvin T. Smith (#refSmith1987, 1987:131–32) was the first to suggest that the Westo were a group of Erie (tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chisca
The Chisca were a tribe of Native Americans living in present-day eastern Tennessee and southwestern Virginia in the 16th century. Their descendants, the Yuchi lived in present-day Alabama, Georgia, and Florida in the 17th, 18th, and early 19th centuries, and were removed to Indian Territory in the 1830s. The Hernando de Soto expedition heard of, and may have had brief contact with, the Chisca in 1540. The Juan Pardo expeditions of 1566 and 1568 encountered the Chisca and fought them. By early in the 17th century, Chisca people were present in several parts of Spanish Florida, engaged at various times and places in alternately friendly or hostile relations with the Spanish and the peoples of the Spanish mission system. After the capture of a fortified Chisca town by the Spanish and Apalachee in 1677, some Chisca took refuge in northern Tennessee, where they were absorbed into the Shawnee, and in Muscogee towns in Alabama. Around the turn of the 18th century some Chisca, by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
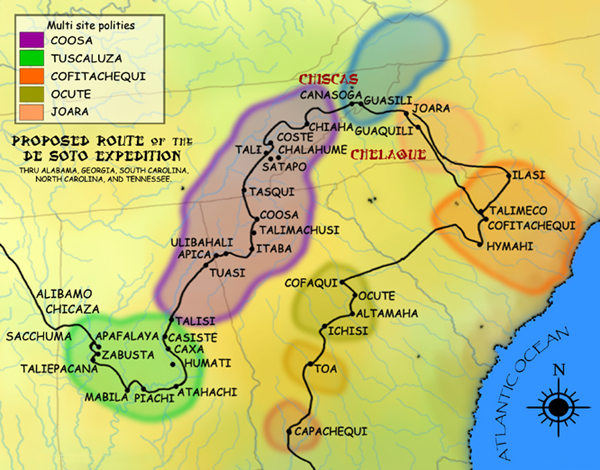
Ocute
Ocute, later known as Altamaha or La Tama and sometimes known conventionally as the Oconee province, was a Native American paramount chiefdom in the Piedmont region of the U.S. state of Georgia in the 16th and 17th centuries. Centered in the Oconee River valley, the main chiefdom of Ocute held sway over the nearby chiefdoms of Altamaha, Cofaqui, and possibly others. The Oconee valley area was populated for thousands of years, and the core chiefdoms of Ocute emerged following the rise of the Mississippian culture around 1100. Ocute was invaded by the expedition of the Spanish conquistador Hernando de Soto in 1539. At that time, Ocute was locked in a longstanding war with the rival paramount chiefdom of Cofitachequi in present-day South Carolina. The chiefdom remained a significant regional power into the 17th century, although Altamaha eclipsed Ocute as the primary center, leading the Spanish to refer to the paramountcy as La Tama. In the 1660s the chiefdom fragmented due to sla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |