|
Ustka
Ustka (, , ) is a spa town in the Middle Pomerania region of northern Poland with 17,100 inhabitants (2001). It is part of Słupsk County in Pomeranian Voivodeship. It is located on the Slovincian Coast on the Baltic Sea. It is a port town and popular summer seaside resort of Poland. History The first settlers arrived at present-day Ustka as early as the 9th century, and established a fishing settlement with the original name of ''Ujść''.Alicja Deck-Partyka, Poland, a Unique Country & Its People'' Authorhouse - 2006, p. 135. Accessed 2008-29-04. In the 10th century, it became part of the emerging country of Poland under its first ruler Mieszko I. The first historic records mention the village under the names of ''Ujść'' or ''Ujście'' in 1310. The area at the mouth of the river Słupia was ceded to the nearby city of Słupsk in 1337 with the purpose of building a fishing harbour and a commercial port there to the Baltic Sea. According to documents in 1355 a church was bui ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Słupsk County
__NOTOC__ Słupsk County (, ) is a unit of territorial administration and local government (powiat) in Pomeranian Voivodeship, northern Poland, on the Baltic coast. It came into being on 1 January 1999, as a result of the Polish local government reforms passed in 1998. Its administrative seat is the city of Słupsk, although the city is not part of the county (it constitutes a separate city county). The only towns in Słupsk County are Ustka, a coastal resort north-west of Słupsk, and Kępice, south of Słupsk. The county covers an area of . As of 2019 its total population is 98,793, out of which the population of Ustka is 15,460, that of Kępice is 3,580, and the rural population is 79,753. ''Słupsk County on a map of the counties of Pomeranian Voivodeship'' Apart from the city of Słupsk, Słupsk County is also bordered by Lębork County to the east, Bytów County to the south-east, and Koszalin County and Sławno County to the west. It also borders the Baltic Sea to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Słupsk
Słupsk (; ; ) is a city with powiat rights located on the Słupia River in the Pomeranian Voivodeship in northern Poland, in the historical region of Pomerania or more specifically in its part known in contemporary Poland as Central Pomerania () within the wider West Pomerania (). According to Statistics Poland, it has a population of 88,835 inhabitants while occupying , thus being one of the most densely populated cities in the country as of December 2021. In addition, the city is the administrative seat of Słupsk County and the rural Gmina Słupsk, despite belonging to neither. Słupsk had its origins as a Pomeranian settlement in the early Middle Ages. In 1265, it was given city rights. By the 14th century, the city had become a centre of local administration and trade and a Hanseatic League associate. Between 1368 and 1478, it was a residence of the Duchy of Słupsk, Dukes of Słupsk, until 1474 vassals of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland, Kingdom of Poland. According to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
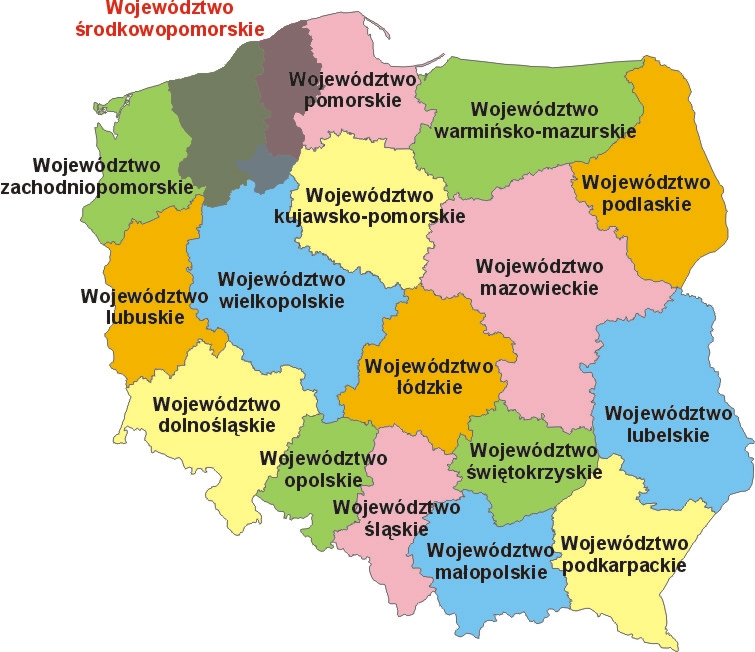
Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship ( ; ) is a Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk. The voivodeship was established on January 1, 1999, out of the former voivodeships of Gdańsk Voivodeship (1975–1998), Gdańsk, Elbląg Voivodeship, Elbląg and Słupsk Voivodeship, Słupsk, pursuant to the Polish local government reforms adopted in 1997. It is bordered by the West Pomeranian Voivodeship to the west, Greater Poland Voivodeship, Greater Poland and the Kuyavian-Pomeranian Voivodeship to the south, the Warmian-Masurian Voivodeship to the east, and the Baltic Sea to the north. It also shares a short land border with Russia (Kaliningrad Oblast), on the Vistula Spit. The bulk of the voivodeship is located in the historic region of Pomerania, with the territories on the eastern bank of the Vistula being part of Powiśle (region), Powiśle. The Pomeranian part of the region comprises most of Pomerelia (the easternmost part of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovincian Coast
The Slovincian Coast (; ) (Regions of Poland, 313.41) is a Mesoregion (geomorphology), mesoregion, the northernmost part of the Koszalin Coast, with an area of 1132 km2. The highest hill is Rowokół, at 114,8 metres above sea level. The coast stretches from the west at Kołobrzeg, up to the east at Karwia. The landscape mainly compromises of dunes, marshland and lakes (such as Łebsko Lake). The region is sparsely populated. The towns of Łeba, Ustka, Darłowo and Mielno are located on the coast. In the region of the Slovincian Coast is the Słowiński National Park, and the spas of Ustka and Dąbki, West Pomeranian Voivodeship, Dąbki. References Regions of Poland {{Poland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Pomerania
The term Middle or Central Pomerania can refer to two distinct areas, depending on whether it is used as a translation of the corresponding German or Polish terms Mittelpommern (also Mittelpommerscher Keil) or Pomorze Środkowe, respectively. Mittelpommern Mittelpommern in historical usage denotes the central parts of the former Duchy, later Province of Pomerania, located approximately between the rivers Peene and Rega, including the towns Trzebiatów, Resko and Nowogard. Mittelpommerscher Keil Mittelpommerscher Keil (Middle Pomeranian Wedge) is a term used in ethnolinguistics, which carries a narrower meaning; it corresponds to the south-central part of Mittelpommern, roughly between the rivers Zarow and Ihna (Ina).Wolfgang Wilhelminus et al, ''Pommern. Geschichte, Kultur, Wissenschaft'', University of Greifswald, 1990, pp.325ff This area differed from the rest of the duchy or province by the dialect of the inhabitants, who spoke the Mittelpommersch variety closely rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by the countries of Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden, and the North European Plain, North and Central European Plain regions. It is the world's largest brackish water basin. The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from 10°E to 30°E longitude. It is a Continental shelf#Shelf seas, shelf sea and marginal sea of the Atlantic with limited water exchange between the two, making it an inland sea. The Baltic Sea drains through the Danish straits into the Kattegat by way of the Øresund, Great Belt and Little Belt. It includes the Gulf of Bothnia (divided into the Bothnian Bay and the Bothnian Sea), the Gulf of Finland, the Gulf of Riga and the Bay of Gdańsk. The "Baltic Proper" is bordered on its northern edge, at latitude 60°N, by Åland and the Gulf of Bothnia, on its northeastern edge by the Gulf of Finland, on its eastern edge by the Gulf of Riga, and in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Roads In Poland
According to classes and categories of public roads in Poland, a national road () is a public trunk road controlled by the Polish central government authority, the General Directorship of National Roads and Motorways (). All motorways and expressways in Poland are classified as part of the national roads network. Other types of roads in Poland are under the control of entities at voivodeship, powiat and gmina levels: voivodeship roads, powiat roads and gmina roads. National roads network National roads include: * motorways and expressways and other roads that are planned to be upgraded to motorways or expressways * International E-road network, almost all of which has been upgraded to either Motorway or Expressway by late 2023. * roads connecting the national road network * roads to or from border crossings * roads which are alternatives to toll roads * beltways of major cities and metropolitan areas * roads of military importance Currently, there are 96 national ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Słupia
Słupia () is a river in north-western Poland, a tributary of the Baltic Sea, with a length of 138 kilometres and the basin area of 1,623 km². Cities: * Słupsk Towns: * Ustka Affluents: * Bytowa See also: Rivers of Poland, List of rivers of Europe This article lists the principal rivers of Europe with their main tributaries. Scope The border of Europe and Asia is here defined as from the Kara Sea, along the Ural Mountains and Ural River to the Caspian Sea. While the crest of the Ca .... References Rivers of Poland Rivers of Pomeranian Voivodeship {{Poland-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League was a Middle Ages, medieval commercial and defensive network of merchant guilds and market towns in Central Europe, Central and Northern Europe, Northern Europe. Growing from a few Northern Germany, North German towns in the late 12th century, the League expanded between the 13th and 15th centuries and ultimately encompassed nearly 200 settlements across eight modern-day countries, ranging from Tallinn in Estonia in the east, Bergen (Bjørgvin) in Norway to the North to the Netherlands in the west, and extended inland as far as Cologne, Prussia (region), the Prussian regions and Kraków, Poland. The League began as a collection of loosely associated groups of German traders and towns aiming to expand their commercial interests, including protection against robbery. Over time, these arrangements evolved into the League, offering traders toll privileges and protection on affiliated territory and trade routes. Economic interdependence and familial connections am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Słupsk
The Duchy of Pomerania-Stolp, also known as the Duchy of Stolp, and the Duchy of Słupsk, was a Feudalism, feudal Teilherzogtum, duchy in Farther Pomerania. Its capital was Słupsk. It was ruled by the House of Griffin, Griffin dynasty. It existed in the High Middle Ages era from 1368 to 1478. Background The Duchy of Pomerania was partitioned several times to satisfy the claims of the male members of the ruling House of Pomerania dynasty.Kyra T. Inachin, Die Geschichte Pommerns, Hinstorff Rostock, 2008, p.30, The partitions were named after the ducal residences: List of Pomeranian duchies and dukes#Duchy of Pomerania, Pomerania-Barth, -Demmin, -Rügenwalde, -Stettin, -Stolp, and -Wolgast. None of the partitions had a hereditary character,Norbert Buske, Pommern, Helms Schwerin 1997, p.21, the members of the House of Pomerania inherited the duchy in common. The duchy thus continued to exist as a whole despite its division. Creation: Partition of 1368/72 After the death of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crown Of The Kingdom Of Poland
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland (; ) was a political and legal concept formed in the 14th century in the Kingdom of Poland, assuming unity, indivisibility and continuity of the state. Under this idea, the state was no longer seen as the Patrimonialism, patrimonial property of the monarch or dynasty, but became a common good of the political community of the kingdom. This notion allowed the state to maintain stability even during periods of interregnum and paved the way for a unique political system in Poland, characterized by a noble-based parliament and the Free election (Poland), free election of the monarch. Additionally, the concept of the Crown extended beyond existing borders, asserting that previously lost territories still rightfully belonged to it. The term ''Crown of the Kingdom of Poland'' also referred to all the lands under the rule of the Polish king. This meaning became especially significant after the Union of Lublin, union with the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |