|
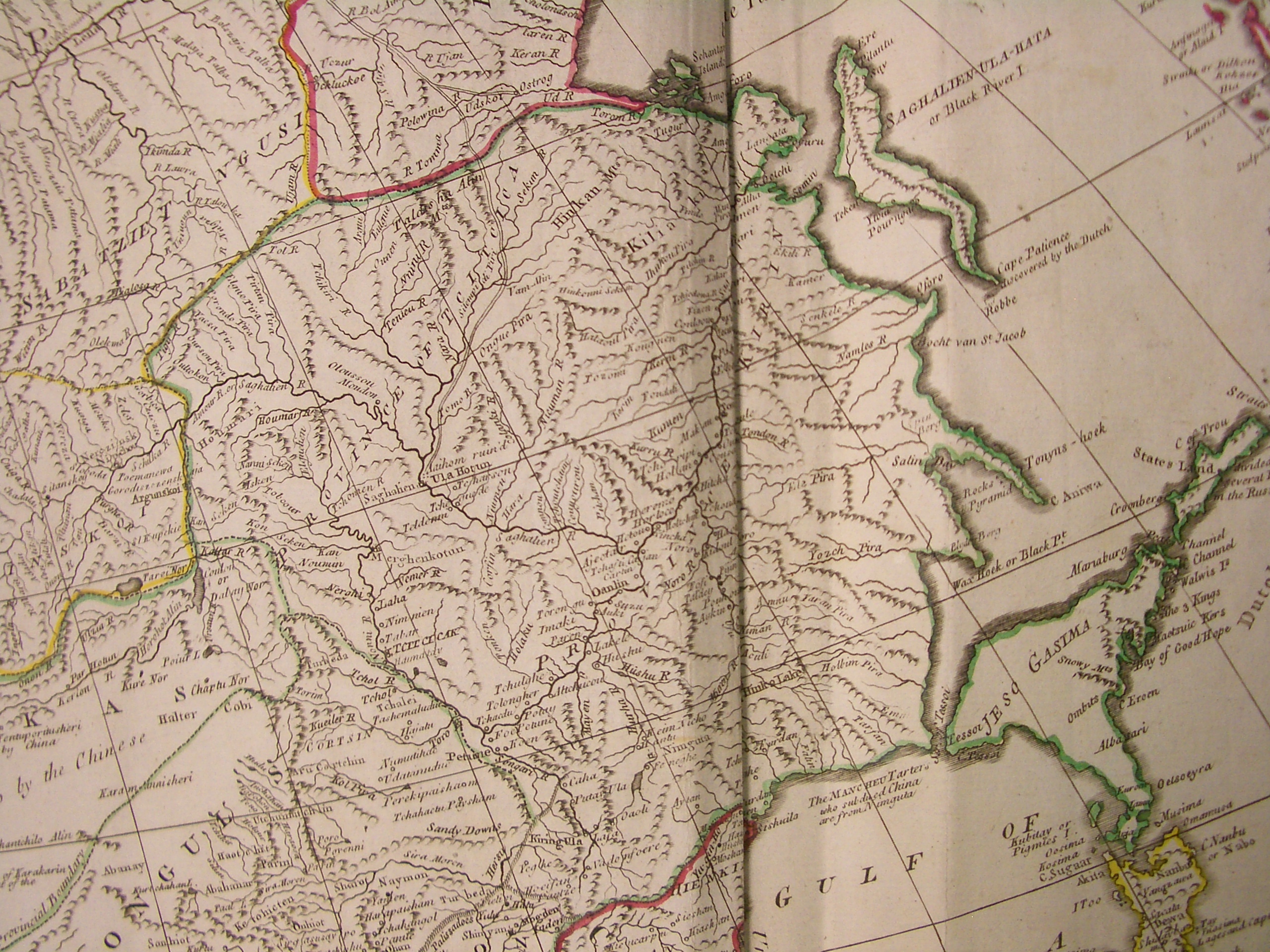
Ussuriysk Territory
Ussuriysk () is a city in Primorsky Krai, Russia, in the valley of the Razdolnaya River. The city is north of Vladivostok, the administrative center of the krai, and about from both the China–Russia border and the Pacific Ocean. It was previously known as ''Nikolskoye'' (until 1898), ''Nikolsk-Ussuriysky'' (until 1935) and ''Voroshilov'' (until 1957). History Medieval history The area of what now is Ussuriysk was settled by Yulou Mohe tribes. From the mid-9th century, it became Solbin-bu of the Balhae Kingdom. It is then populated by the Dōnghǎi Jurchens, under control of Liao dynasty. The city then become capital of Jīn Dynasty's Sùpín circuit (速頻路). Then it went under control of Yuan, Ming and Qing dynasties respectively and known as (). Modern era In 1866, the settlement of Nikolskoye () was founded on the area of today's Ussuriysk, named after Saint Nicholas. Due to its advantageous geographic location at the crossing of the transportation lines, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primorsky Krai
Primorsky Krai, informally known as Primorye, is a federal subjects of Russia, federal subject (a krais of Russia, krai) of Russia, part of the Far Eastern Federal District in the Russian Far East. The types of inhabited localities in Russia, city of Vladivostok on the southern coast of the krai is its administrative center, and the second largest city in the Russian Far East, behind Khabarovsk in the neighbouring Khabarovsk Krai. Primorsky Krai has the largest economy among the federal subjects in the Russian Far East, and a list of federal subjects of Russia by population, population of 1,845,165 as of the Russian Census (2021), 2021 Census. The krai has Russia's only North Korea–Russia border, border with North Korea, along the Tumen River in Khasansky District in the southwestern corner of the krai. Peter the Great Gulf, the largest gulf in the Sea of Japan, is on the south coast. The territory of the krai was historically part of Manchuria. It was Convention of Pek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saint Nicholas
Saint Nicholas of Myra (traditionally 15 March 270 – 6 December 343), also known as Nicholas of Bari, was an early Christian bishop of Greeks, Greek descent from the maritime city of Patara (Lycia), Patara in Anatolia (in modern-day Antalya Province, Turkey) during the time of the Roman Empire. Because of the many miracles attributed to his intercession, he is also known as Nicholas the Wonderworker. Saint Nicholas is the patron saint of sailors, merchants, archers, repentant thieves, children, brewers, pawnbrokers, toymakers, unmarried people, and students in various cities and countries around Europe. His reputation evolved among the pious, as was common for early Christian saints, and his legendary habit of secret gift-giving gave rise to the folklore of Santa Claus ("Saint Nick") through Sinterklaas. Little is known about the historical Saint Nicholas. The earliest accounts of his life were written centuries after his death and probably contain legendary elaborations. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
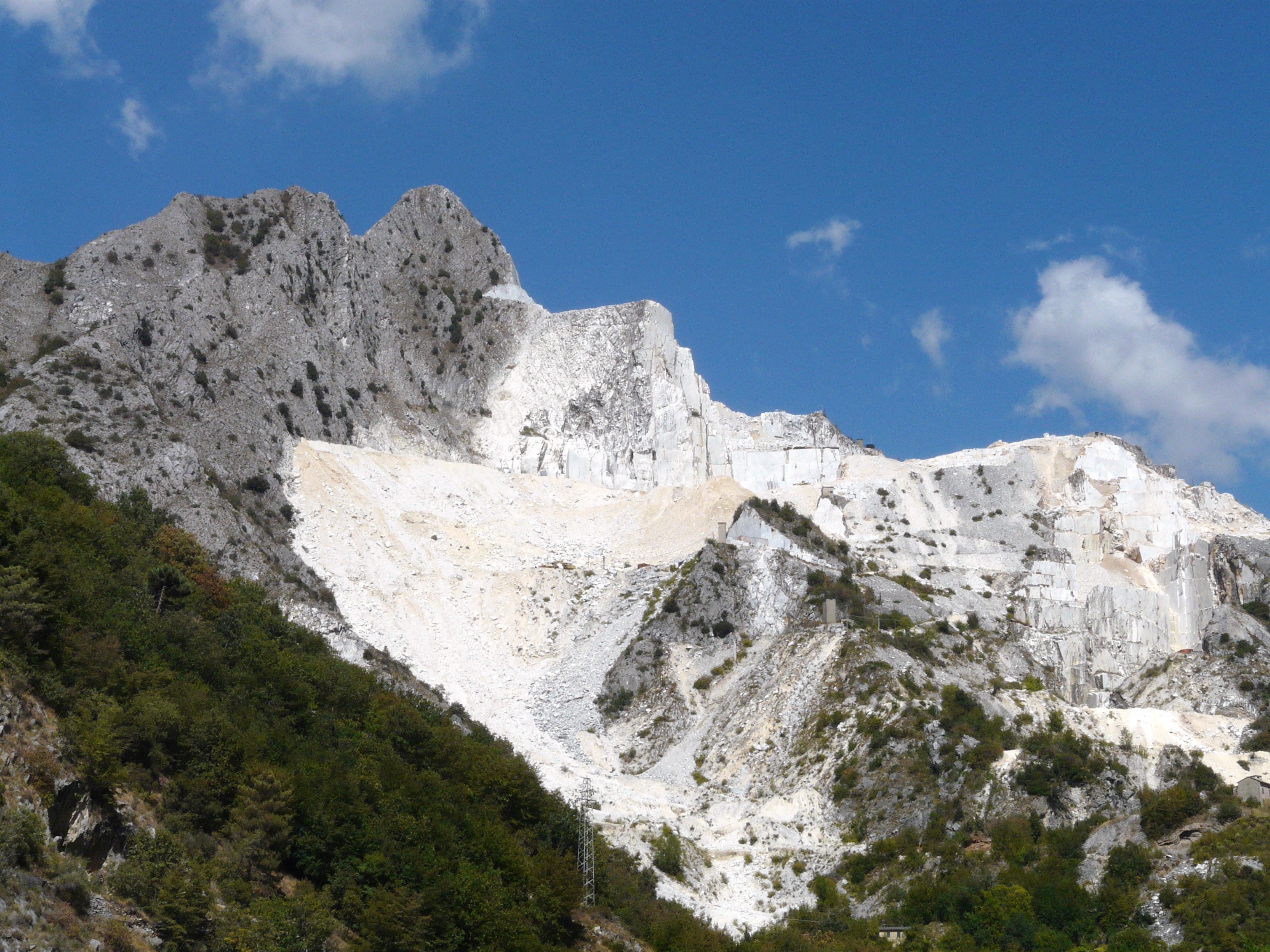
Quarry
A quarry is a type of open-pit mining, open-pit mine in which dimension stone, rock (geology), rock, construction aggregate, riprap, sand, gravel, or slate is excavated from the ground. The operation of quarries is regulated in some jurisdictions to manage their safety risks and reduce their environmental impact. The word ''quarry'' can also include the underground quarrying for stone, such as Bath stone. History For thousands of years, only hand tools had been used in quarries. In the eighteenth century, the use of drilling and blasting operations was mastered. Types of rock Types of rock extracted from quarries include: *Chalk *China clay *Scoria, Cinder *Clay *Coal *Construction aggregate (sand and gravel) *Coquina *Diabase *Gabbro *Granite *Gritstone *Gypsum *Limestone *Marble *Ores *Phosphate rock *Quartz *Sandstone *Slate *Travertine Methods of quarrying The method of removal of stones from their natural bed by using different operations is called quarryin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
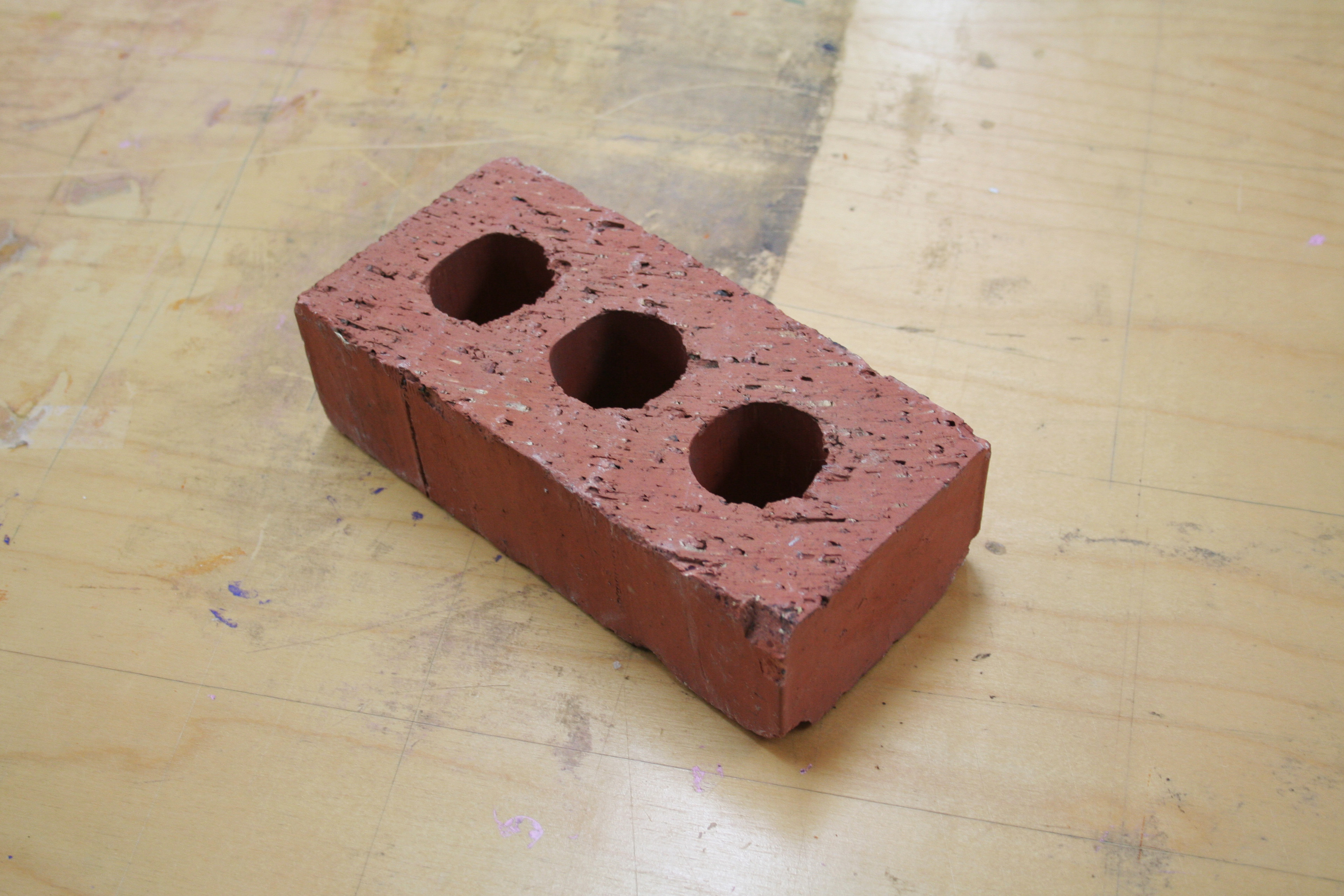
Brick
A brick is a type of construction material used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a unit primarily composed of clay. But is now also used informally to denote building units made of other materials or other chemically cured construction blocks. Bricks can be joined using Mortar (masonry), mortar, adhesives or by interlocking. Bricks are usually produced at brickworks in numerous classes, types, materials, and sizes which vary with region, and are produced in bulk quantities. Concrete masonry unit, ''Block'' is a similar term referring to a rectangular building unit composed of clay or concrete, but is usually larger than a brick. Lightweight bricks (also called lightweight blocks) are made from expanded clay aggregate. Fired bricks are one of the longest-lasting and strongest building materials, sometimes referred to as artificial stone, and have been used since . Air-dried bricks, also known as mudbricks ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brewery
A brewery or brewing company is a business that makes and sells beer. The place at which beer is commercially made is either called a brewery or a beerhouse, where distinct sets of brewing equipment are called plant. The commercial brewing of beer has taken place since at least 2500 BC; in ancient Mesopotamia, brewers derived social sanction and divine protection from the goddess Ninkasi. Brewing was initially a cottage industry, with production taking place at home; by the ninth century, monasteries and farms would produce beer on a larger scale, selling the excess; and by the eleventh and twelfth centuries larger, dedicated breweries with eight to ten workers were being built. The diversity of size in breweries is matched by the diversity of processes, degrees of automation, and kinds of beer produced in breweries. A brewery is typically divided into distinct sections, with each section reserved for one part of the brewing process. History Beer may have been known in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tanning (leather)
Tanning, or hide tanning, is the process of treating Skinning, skins and Hide (skin), hides of animals to produce leather. A tannery is the place where the skins are processed. Historically, vegetable based tanning used tannin, an acidic chemical compound derived from the bark of certain trees, in the production of leather. An alternative method, developed in the 1800s, is chrome tanning, where chromium salts are used instead of natural tannins. History Tanning hide into leather involves a process which permanently alters the protein structure of skin, making it more durable and less susceptible to decomposition and coloring. The place where hides are processed is known as a ''tannery''. The English word for tanning is from the medieval Latin verb , from the noun (oak bark). This term may be derived from a Celtic word related to the Proto-Indo-European *' meaning 'fir tree'. (The same root is the source for Old High German meaning 'fir', related to modern German ''Tannenb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soap
Soap is a salt (chemistry), salt of a fatty acid (sometimes other carboxylic acids) used for cleaning and lubricating products as well as other applications. In a domestic setting, soaps, specifically "toilet soaps", are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are used as thickeners, components of some lubricants, emulsifiers, and catalysts. Soaps are often produced by mixing fats and oils with a Base (chemistry), base. Humans have used soap for millennia; evidence exists for the production of soap-like materials in ancient Babylon around 2800 BC. Types Toilet soaps In a domestic setting, "soap" usually refers to what is technically called a toilet soap, used for household and personal cleaning. Toilet soaps are salts of fatty acids with the general formula (Carboxylate ion, RCO2−)M+, where M is Sodium, Na (sodium) or Potassium, K (potassium). When used for cleaning, soap solubilizes particles and g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dairy
A dairy is a place where milk is stored and where butter, cheese, and other dairy products are made, or a place where those products are sold. It may be a room, a building, or a larger establishment. In the United States, the word may also describe a dairy farm or the part of a mixed farm dedicated to milk for human consumption, whether from cows, buffaloes, goats, yaks, sheep, horses or camels. The attributive ''dairy'' describes milk-based products, derivatives, and processes, and the animals and workers involved in their production, for example dairyman, dairymaid, dairy cattle or dairy goat. A dairy farm produces milk and a dairy factory processes it into a variety of dairy products. These establishments constitute the global dairy industry, part of the food industry. The word ''dairy'' comes from an Old English word for ''female servant'', as milking was historically done by dairymaids. Terminology Terminology differs between countries. In the United States, for ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mill (grinding)
A mill is a device, often a structure, machine or kitchen appliance, that breaks solid materials into smaller pieces by grinding, crushing, or cutting. Such comminution is an important unit operation in many processes. There are many different types of mills and many types of materials processed in them. Historically, mills were powered by hand or by animals (e.g., via a hand crank), working animal (e.g., horse mill), wind ( windmill) or water (watermill). In the modern era, they are usually powered by electricity. The grinding of solid materials occurs through mechanical forces that break up the structure by overcoming the interior bonding forces. After the grinding the state of the solid is changed: the grain size, the grain size disposition and the grain shape. Milling also refers to the process of breaking down, separating, sizing, or classifying aggregate material (e.g. mining ore). For instance rock crushing or grinding to produce uniform aggregate size for construc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blagoveshchensk
Blagoveshchensk ( rus, Благовещенск, p=bləɡɐˈvʲeɕːɪnsk, ) is a types of inhabited localities in Russia, city and the administrative center of Amur Oblast, Russia. It is located at the confluence of the Amur River, Amur and the Zeya Rivers, opposite to the Chinese city of Heihe. Population: The Amur has formed China–Russia border, Russia's border with China since the 1858 Aigun Treaty and the 1860 Treaty of Peking. The area north of the Amur belonged to the Manchu Qing dynasty by the Treaty of Nerchinsk of 1689 until it was ceded to Russia by the Aigun Treaty in 1858. History Early history of the region The early residents of both sides of the Amur in the region of today's Blagoveshchensk were the Daur people, Daurs and Duchers. An early settlement in the area of today's Blagoveshchensk was the Ducher town whose name was reported by the Russian explorer Yerofey Khabarov as Aytyun in 1652, as Aigun from 1683 to 1685, and as Aigun Old Town from 1685 until 1900 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast. Although the Russian Far East is often considered as a part of Siberia abroad, it has been historically categorized separately from Siberia in Russian regional schemes (and previously during the history of the Soviet Union, Soviet era when it was called the Soviet Far East). Terminology In Russia, the region is usually referred to as simply th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War (8 February 1904 – 5 September 1905) was fought between the Russian Empire and the Empire of Japan over rival imperial ambitions in Manchuria and the Korean Empire. The major land battles of the war were fought on the Liaodong Peninsula and near Shenyang, Mukden in Southern Manchuria, with naval battles taking place in the Yellow Sea and the Sea of Japan. Russia had pursued an expansionist policy in Siberia and the Russian Far East, Far East since the reign of Ivan the Terrible in the 16th century. At the end of the First Sino-Japanese War, the Treaty of Shimonoseki of 1895 had ceded the Liaodong Peninsula and Lüshun Port, Port Arthur to Japan before the Triple Intervention, in which Russia, Germany, and France forced Japan to relinquish its claim. Japan feared that Russia would impede its plans to establish a sphere of influence in mainland Asia, especially as Russia built the Trans-Siberian Railway, Trans-Siberian Railroad, began making inroads in K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |