|
Usk Anticline
The Usk Inlier is a domed outcrop of rock strata of Silurian age in Monmouthshire in south-eastern Wales. It is located in the countryside between the towns of Caerleon and Pontypool and the village of Raglan. The longer axis of the dome or ' pericline', often referred to as the Usk Anticline, is aligned north–south. The inlier is largely surrounded by a sequence of Old Red Sandstone rocks of Devonian The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian per ... age, though both these and the Silurian rocks are largely obscured by superficial deposits.British Geological Survey 1:50,000 scale geological map sheets 232, 233, 249 & 250 (England & Wales series) References Anticlines Landforms of Monmouthshire Geology of Wales Rock formations of Wales {{Monmouthshire-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
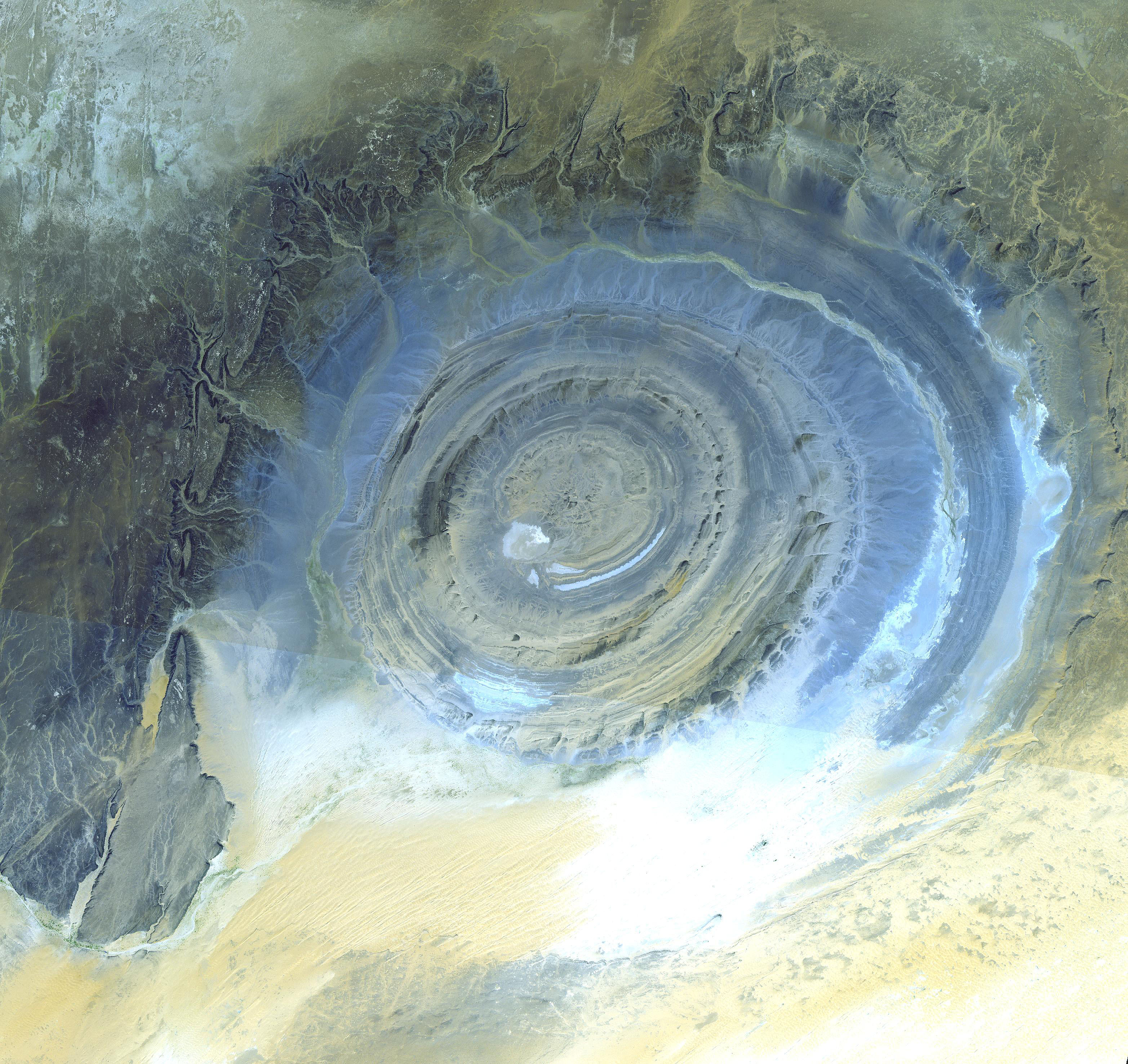
Dome (geology)
A dome is a feature in structural geology where a circular part of the Earth's surface has been pushed upward, tilting the pre-existing layers of earth away from the center. In technical terms, it consists of symmetrical anticlines that intersect each other at their respective wikt:apex, apices. Intact, domes are distinct, rounded, sphere, spherical-to-ellipsoidal-shaped protrusions on the Earth's surface. A slice parallel to Earth's surface of a dome features concentric rings of stratum, strata. If the top of a dome has been eroded flat, the resulting structure in Multiview_orthographic_projection#Plan, plan view appears as a Bullseye_(target), bullseye, with the youngest rock layers at the outside, and each ring growing progressively older moving inwards. These strata would have been horizontal at the time of Deposition_(geology), deposition, then later deformed by the Tectonic uplift, uplift associated with dome formation. Formation mechanisms There are many possible mechani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods ( myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monmouthshire
Monmouthshire ( ; ) is a Principal areas of Wales, county in the South East Wales, south east of Wales. It borders Powys to the north; the English counties of Herefordshire and Gloucestershire to the north and east; the Severn Estuary to the south, and Torfaen, Newport, Wales, Newport and Blaenau Gwent to the west. The largest town is Abergavenny, and the administrative centre is Usk. The county is administered by Monmouthshire County Council. It sends two directly-elected members to the Senedd at Cardiff and one elected member to the Parliament of the United Kingdom, UK parliament at Westminster. The county name is identical to that of the Monmouthshire (historic), historic county, of which the current local authority covers the eastern three-fifths. Between 1974 and 1996, the county was known as Gwent (county), Gwent, recalling Kingdom of Gwent, the medieval kingdom which covered a similar area. The present county was formed under the Local Government (Wales) Act 1994, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wales
Wales ( ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by the Irish Sea to the north and west, England to the England–Wales border, east, the Bristol Channel to the south, and the Celtic Sea to the south-west. , it had a population of 3.2 million. It has a total area of and over of Coastline of Wales, coastline. It is largely mountainous with its higher peaks in the north and central areas, including Snowdon (), its highest summit. The country lies within the Temperate climate, north temperate zone and has a changeable, Oceanic climate, maritime climate. Its capital and largest city is Cardiff. A distinct Culture of Wales, Welsh culture emerged among the Celtic Britons after the End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman withdrawal from Britain in the 5th century, and Wales was briefly united under Gruffudd ap Llywelyn in 1055. After over 200 years of war, the Conquest of Wales by Edward I, conquest of Wales by King Edward I o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caerleon
Caerleon ( ; ) is a town and Community (Wales), community in Newport, Wales. Situated on the River Usk, it lies northeast of Newport city centre, and southeast of Cwmbran. Caerleon is of archaeological importance, being the site of a notable Roman Empire, Roman legionary Castra, fortress, Isca Augusta, and an Iron Age hillfort. Close to the remains of Isca Augusta are the National Roman Legion Museum and the Roman Baths Museum. The town also has strong historical and literary associations: Geoffrey of Monmouth elevated the significance of Caerleon as a major centre of British history in his ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' (c. 1136), and Alfred Lord Tennyson wrote ''Idylls of the King'' (1859–1885) while staying in Caerleon. History Pre-Roman history The area around Caerleon is of considerable archaeological interest, with a number of important Neolithic sites. By the British Iron Age, Iron Age, the area was home to the powerful Silures tribe and appears to have been the centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pontypool
Pontypool ( ) is a town and the administrative centre of the county borough of Torfaen, within the Historic counties of Wales, historic boundaries of Monmouthshire (historic), Monmouthshire in South Wales. , it has a population of 29,062. Location It is situated on the Afon Lwyd river in the county borough of Torfaen. Located at the eastern edge of the South Wales coalfields, Pontypool grew around industries including iron and steel production, coal mining, and the growth of the railways. A rather artistic manufacturing industry which also flourished here alongside heavy industry was Japanning, a type of lacquer ware. Pontypool covers several areas, hamlets, villages and towns including New Inn, Torfaen, New Inn, Griffithstown, Sebastopol (Panteg.) Abersychan, Cwmffrwdoer, Pontnewynydd, Trevethin, Penygarn, Torfaen, Penygarn, Wainfelin, Tranch, Brynwern, Pontymoile, Blaendare, Cwmynyscoy, Talywain, Garndiffaith, Pentwyn, Torfaen, Pentwyn, and Varteg. History The name of the to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raglan, Monmouthshire
Raglan (; ) is a village and community in Monmouthshire, south-east Wales. It is located some 9 miles south-west of Monmouth, midway between Monmouth and Abergavenny on the A40 road very near to the junction with the A449 road. It is the location of Raglan Castle, built for William ap Thomas and now maintained by Cadw. The community includes the villages of Llandenny and Pen-y-clawdd. Raglan itself has a population of 1,183. History and buildings The village stands at the crossing point of two Roman roads, that from Gloucester to Usk, and that from Chepstow to Abergavenny. Raglan was first mentioned in the will of Walter de Clare. The earliest market in Raglan was recorded in 1354. The market cross stands in the edge of the crossroads between the church and the Beaufort Arms Inn. It now consists only of the base, with a lamp post mounted on top. In the large space around this stone the markets were held, the base of the cross forming the table on which bargains were struck ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pericline
:''Pericline also refers to a doubly plunging anticline or syncline.'' Pericline is a form of albite exhibiting elongate prismatic crystals. Pericline twinning is a type of crystal twinning which show fine parallel twin laminae typically found in the alkali feldspars microcline Microcline (KAlSi3O8) is an important igneous rock-forming tectosilicate mineral. It is a potassium-rich alkali feldspar. Microcline typically contains minor amounts of sodium. It is common in granite and pegmatites. Microcline forms during s .... The twinning results from a structural transformation between high temperature and low temperature forms.Tsatskis, I. and E.K.H. Salje (1996) ''Time evolution of pericline twin domains in alkali feldspars'', American Mineralogist, Volume 81, pages 800-81PDF/ref> References Crystallography Tectosilicates {{silicate-mineral-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inlier
An inlier is an area of older rocks surrounded by younger rocks. Inliers are typically formed by the erosion of overlying younger rocks to reveal a limited exposure of the older underlying rocks. Faulting or folding may also contribute to the observed outcrop pattern. A classic example from Great Britain is that of the inlier of folded Ordovician and Silurian rocks at Horton in Ribblesdale in North Yorkshire which are surrounded by the younger flat-lying Carboniferous Limestone. The location has long been visited by geology students and experts. Another example from South Wales is the Usk Inlier in Monmouthshire where Silurian age rocks are upfolded amidst Old Red Sandstone rocks of Devonian age. A similar outcrop pattern which results from movement on a thrust fault followed by erosion may be termed a window. Conversely an outlier is an area of younger rock surrounded by older rocks. An outlier is typically formed when sufficient erosion of surrounding rocks has taken plac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Red Sandstone
Old Red Sandstone, abbreviated ORS, is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the eastern seaboard of North America. It also extends northwards into Greenland and Svalbard. These areas were a part of the paleocontinent of Euramerica (Laurussia). In Britain it is a lithostratigraphic unit (a sequence of rock strata) to which stratigraphers accord supergroup status and which is of considerable importance to early paleontology. The presence of ''Old'' in the name is to distinguish the sequence from the younger New Red Sandstone which also occurs widely throughout Britain. Sedimentology The Old Red Sandstone describes a group of sedimentary rocks deposited in a variety of environments in the late Silurian, through the Devonian and into the earliest part of the Carboniferous. The body of rock, or facies, is dominated by terrigenous deposits and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a period (geology), geologic period and system (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic era (geology), era during the Phanerozoic eon (geology), eon, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the preceding Silurian period at million years ago (Megaannum, Ma), to the beginning of the succeeding Carboniferous period at Ma. It is the fourth period of both the Paleozoic and the Phanerozoic. It is named after Devon, South West England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant evolutionary radiation of history of life#Colonization of land, life on land occurred during the Devonian, as free-spore, sporing land plants (pteridophytes) began to spread across dry land, forming extensive coal forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of vascular plants had evolved leaf, leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants (Pteridospermatophyta, pteridospermatophyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anticlines
In structural geology, an anticline is a type of fold that is an arch-like shape and has its oldest beds at its core, whereas a syncline is the inverse of an anticline. A typical anticline is convex up in which the hinge or crest is the location where the curvature is greatest, and the limbs are the sides of the fold that dip away from the hinge. Anticlines can be recognized and differentiated from antiforms by a sequence of rock layers that become progressively older toward the center of the fold. Therefore, if age relationships between various rock strata are unknown, the term antiform should be used. The progressing age of the rock strata towards the core and uplifted center, are the trademark indications for evidence of anticlines on a geological map. These formations occur because anticlinal ridges typically develop above thrust faults during crustal deformations. The uplifted core of the fold causes compression of strata that preferentially erodes to a deeper str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |