|
User Datagram Protocol
In computer networking, the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) is one of the core communication protocols of the Internet protocol suite used to send messages (transported as datagrams in packets) to other hosts on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. Within an IP network, UDP does not require prior communication to set up communication channels or data paths. UDP is a connectionless protocol meaning that messages are sent without negotiating a connection and that UDP doesn't keep track of what it has sent. UDP provides checksums for data integrity, and port numbers for addressing different functions at the source and destination of the datagram. It has no handshaking dialogues and thus exposes the user's program to any unreliability of the underlying network; there is no guarantee of delivery, ordering, or duplicate protection. If error-correction facilities are needed at the network interface level, an application may instead use Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) or Stream C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David P
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''Dāwūd''; grc-koi, Δαυΐδ, Dauíd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ዳዊት, ''Dawit''; xcl, Դաւիթ, ''Dawitʿ''; cu, Давíдъ, ''Davidŭ''; possibly meaning "beloved one". was, according to the Hebrew Bible, the third king of the United Kingdom of Israel. In the Books of Samuel, he is described as a young shepherd and harpist who gains fame by slaying Goliath, a champion of the Philistines, in southern Canaan. David becomes a favourite of Saul, the first king of Israel; he also forges a notably close friendship with Jonathan, a son of Saul. However, under the paranoia that David is seeking to usurp the throne, Saul attempts to kill David, forcing the latter to go into hiding and effectively operate as a fugitive for several years. After Saul and Jonathan are both killed in battle against the Philistines, a 30-year-old David is anointed king over all of Israel and Judah. Following his rise to power, Dav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stream Control Transmission Protocol
The Stream Control Transmission Protocol (SCTP) is a computer networking communications protocol in the transport layer of the Internet protocol suite. Originally intended for Signaling System 7 (SS7) message transport in telecommunication, the protocol provides the message-oriented feature of the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), while ensuring reliable, in-sequence transport of messages with congestion control like the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). Unlike UDP and TCP, the protocol supports multihoming and redundant paths to increase resilience and reliability. SCTP is standardized by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF) in . The SCTP reference implementation was released as part of FreeBSD version 7, and has since been widely ported to other platforms. Formal oversight The IETF Signaling Transport ( SIGTRAN) working group defined the protocol (number 132) in October 2000, and the IETF Transport Area (TSVWG) working group maintains it. defines the protocol. provides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trivial File Transfer Protocol
Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) is a simple lockstep File Transfer Protocol which allows a client to get a file from or put a file onto a remote host. One of its primary uses is in the early stages of nodes booting from a local area network. TFTP has been used for this application because it is very simple to implement. TFTP was first standardized in 1981 and the current specification for the protocol can be found in . Overview Due to its simple design, TFTP can be easily implemented by code with a small memory footprint. It is therefore the protocol of choice for the initial stages of any network booting strategy like BOOTP, PXE, BSDP, etc., when targeting from highly resourced computers to very low resourced Single-board computers (SBC) and System on a Chip (SoC). It is also used to transfer firmware images and configuration files to network appliances like routers, firewalls, IP phones, etc. Today, TFTP is virtually unused for Internet transfers. TFTP's design w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DHCP
The Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) is a network management protocol used on Internet Protocol (IP) networks for automatically assigning IP addresses and other communication parameters to devices connected to the network using a client–server architecture. The technology eliminates the need for individually configuring network devices manually, and consists of two network components, a centrally installed network DHCP server and client instances of the protocol stack on each computer or device. When connected to the network, and periodically thereafter, a client requests a set of parameters from the server using DHCP. DHCP can be implemented on networks ranging in size from residential networks to large campus networks and regional ISP networks. Many routers and residential gateways have DHCP server capability. Most residential network routers receive a unique IP address within the ISP network. Within a local network, a DHCP server assigns a local IP addre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bootstrapping
In general, bootstrapping usually refers to a self-starting process that is supposed to continue or grow without external input. Etymology Tall boots may have a tab, loop or handle at the top known as a bootstrap, allowing one to use fingers or a boot hook tool to help pulling the boots on. The saying "to " was already in use during the 19th century as an example of an impossible task. The idiom dates at least to 1834, when it appeared in the ''Workingman's Advocate'': "It is conjectured that Mr. Murphee will now be enabled to hand himself over the Cumberland river or a barn yard fence by the straps of his boots."Jan FreemanBootstraps and Baron Munchausen '' Boston.com'', January 27, 2009 In 1860 it appeared in a comment on philosophy of mind: "The attempt of the mind to analyze itself san effort analogous to one who would lift himself by his own bootstraps." Bootstrap as a metaphor, meaning to better oneself by one's own unaided efforts, was in use in 1922. This metaphor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network File System
Network File System (NFS) is a distributed file system protocol originally developed by Sun Microsystems (Sun) in 1984, allowing a user on a client computer to access files over a computer network much like local storage is accessed. NFS, like many other protocols, builds on the Open Network Computing Remote Procedure Call (ONC RPC) system. NFS is an open IETF standard defined in a Request for Comments (RFC), allowing anyone to implement the protocol. Versions and variations Sun used version 1 only for in-house experimental purposes. When the development team added substantial changes to NFS version 1 and released it outside of Sun, they decided to release the new version as v2, so that version interoperation and RPC version fallback could be tested. NFSv2 Version 2 of the protocol (defined in RFC 1094, March 1989) originally operated only over User Datagram Protocol (UDP). Its designers meant to keep the server side stateless, with locking (for example ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remote Procedure Call
In distributed computing, a remote procedure call (RPC) is when a computer program causes a procedure (subroutine) to execute in a different address space (commonly on another computer on a shared network), which is coded as if it were a normal (local) procedure call, without the programmer explicitly coding the details for the remote interaction. That is, the programmer writes essentially the same code whether the subroutine is local to the executing program, or remote. This is a form of client–server interaction (caller is client, executor is server), typically implemented via a request–response message-passing system. In the object-oriented programming paradigm, RPCs are represented by remote method invocation (RMI). The RPC model implies a level of location transparency, namely that calling procedures are largely the same whether they are local or remote, but usually, they are not identical, so local calls can be distinguished from remote calls. Remote calls are usually order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IP Tunneling
An IP tunnel is an Internet Protocol (IP) network communications channel between two networks. It is used to transport another network protocol by encapsulation of its packets. IP tunnels are often used for connecting two disjoint IP networks that don't have a native routing path to each other, via an underlying routable protocol across an intermediate transport network. In conjunction with the IPsec protocol they may be used to create a virtual private network between two or more private networks across a public network such as the Internet. Another prominent use is to connect islands of IPv6 installations across the IPv4 Internet. In IP tunnelling, every IP packet, including addressing information of its source and destination IP networks, is encapsulated within another packet format native to the transit network. At the borders between the source network and the transit network, as well as the transit network and the destination network, gateways are used that establish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Network Time Protocol
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable- latency data networks. In operation since before 1985, NTP is one of the oldest Internet protocols in current use. NTP was designed by David L. Mills of the University of Delaware. NTP is intended to synchronize all participating computers to within a few milliseconds of Coordinated Universal Time (UTC). It uses the intersection algorithm, a modified version of Marzullo's algorithm, to select accurate time servers and is designed to mitigate the effects of variable network latency. NTP can usually maintain time to within tens of milliseconds over the public Internet, and can achieve better than one millisecond accuracy in local area networks under ideal conditions. Asymmetric routes and network congestion can cause errors of 100 ms or more. The protocol is usually described in terms of a client–server model, but can as eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Domain Name System
The Domain Name System (DNS) is a hierarchical and distributed naming system for computers, services, and other resources in the Internet or other Internet Protocol (IP) networks. It associates various information with domain names assigned to each of the associated entities. Most prominently, it translates readily memorized domain names to the numerical IP addresses needed for locating and identifying computer services and devices with the underlying network protocols. The Domain Name System has been an essential component of the functionality of the Internet since 1985. The Domain Name System delegates the responsibility of assigning domain names and mapping those names to Internet resources by designating authoritative name servers for each domain. Network administrators may delegate authority over sub-domains of their allocated name space to other name servers. This mechanism provides distributed and fault-tolerant service and was designed to avoid a single large ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Layer Protocol
In computer networking, encapsulation is a method of designing modular communication protocols in which logically separate functions in the network are abstracted from their underlying structures by inclusion or information hiding within higher-level objects. In other words, encapsulation "takes information from a higher layer and adds a header to it, treating the higher layer information as data". The physical layer is responsible for physical transmission of the data, link encapsulation allows local area networking, IP provides global addressing of individual computers, and TCP selects the process or application (i.e., the TCP or UDP port) that specifies the service such as a Web or TFTP server. During encapsulation, each layer builds a protocol data unit (PDU) by adding a header and optionally a trailer, both of which contain control information to the PDU from the layer above. For example, in the IP suite, the contents of a web page are encapsulated with an HTTP hea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
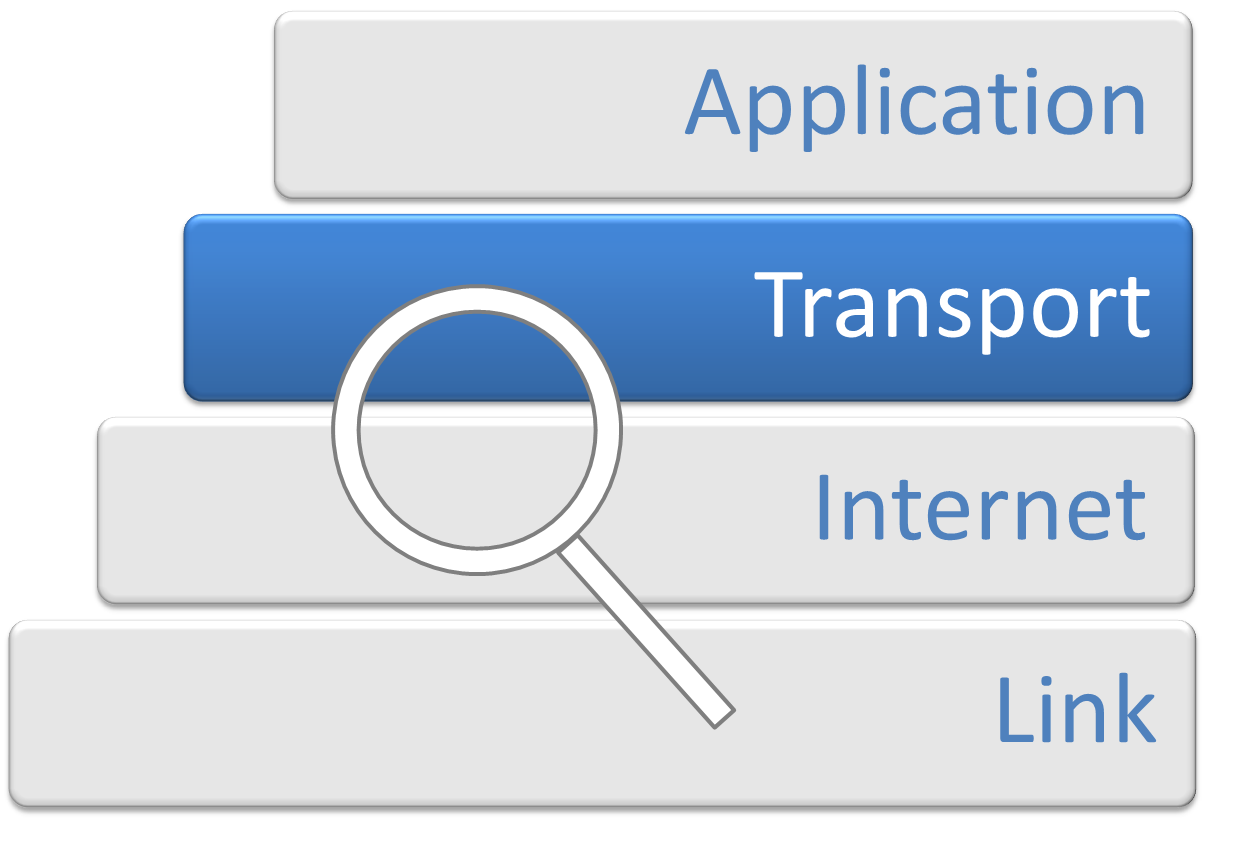
Transport Layer
In computer networking, the transport layer is a conceptual division of methods in the layered architecture of protocols in the network stack in the Internet protocol suite and the OSI model. The protocols of this layer provide end-to-end communication services for applications. It provides services such as connection-oriented communication, reliability, flow control, and multiplexing. The details of implementation and semantics of the transport layer of the Internet protocol suite, which is the foundation of the Internet, and the OSI model of general networking are different. The protocols in use today in this layer for the Internet all originated in the development of TCP/IP. In the OSI model the transport layer is often referred to as Layer 4, or L4, while numbered layers are not used in TCP/IP. The best-known transport protocol of the Internet protocol suite is the Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). It is used for connection-oriented transmissions, whereas the co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |