|
Used Coffee Grounds
Used coffee grounds are the result of brewing coffee, and are the final product after preparation of coffee. Despite having several highly-desirable chemical components, used coffee grounds are generally regarded as waste, and they are usually thrown away or composted. As of 2019, it was estimated that over 15 million tonnes of spent coffee grounds are generated annually. Due to this quantity of waste and the chemical properties of used coffee grounds, they have several potential uses. In the late 19th century, used coffee grounds were used to adulterate pure coffee. Chemical composition Most used coffee grounds are similar in chemical composition, although coffee grounds used to make instant coffee have fewer chemicals in them due to a more extensive extraction process. Used coffee grounds are rich in sugars, which comprise about half of their weight. A further 20% is made up of proteins, and a further 20% is lignins. The dry coffee grounds contain significant amounts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ground Coffee In Boxes
Ground may refer to: Geology * Land, the solid terrestrial surface of the Earth * Soil, a mixture of clay, sand and organic matter present on the surface of the Earth Electricity * Ground (electricity), the reference point in an electrical circuit from which voltages are measured * Earthing system, part of an electrical installation that connects with the Earth's conductive surface * Ground and neutral, closely related terms Law * Ground (often grounds), in law, a rational motive or basis for a belief, conviction, or action taken, such as a legal action or argument: * Grounds for divorce, regulations specifying the circumstances under which a person will be granted a divorce Music * ''Ground'' (album), the second album by the Nels Cline Trio * "Ground" (song), one of the songs in the debut album of the Filipino rock band Rivermaya * Ground bass, in music, a bass part that continually repeats, while the melody and harmony over it change * '' The Ground'', a 2005 album by Norwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knockbox
Used coffee grounds are the result of brewing coffee, and are the final product after preparation of coffee. Despite having several highly-desirable chemical components, used coffee grounds are generally regarded as waste, and they are usually thrown away or composted. As of 2019, it was estimated that over 15 million tonnes of spent coffee grounds are generated annually. Due to this quantity of waste and the chemical properties of used coffee grounds, they have several potential uses. In the late 19th century, used coffee grounds were used to adulterate pure coffee. Chemical composition Most used coffee grounds are similar in chemical composition, although coffee grounds used to make instant coffee have fewer chemicals in them due to a more extensive extraction process. Used coffee grounds are rich in sugars, which comprise about half of their weight. A further 20% is made up of proteins, and a further 20% is lignins. The dry coffee grounds contain significant amounts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phytotoxic
Phytotoxins are substances that are poisonous or toxic to the growth of plants. Phytotoxic substances may result from human activity, as with herbicides, or they may be produced by plants, by microorganisms, or by naturally occurring chemical reactions. The term is also used to describe toxic chemicals produced by plants themselves, which function as defensive agents against their predators. Most examples pertaining to this definition of phytotoxin are members of various classes of specialised or secondary metabolites, including alkaloids, terpenes, and especially phenolics, though not all such compounds are toxic or serve defensive purposes. Phytotoxins may also be toxic to humans. Toxins produced by plants Alkaloids Alkaloids are derived from amino acids, and contain nitrogen. They are medically important by interfering with components of the nervous system affecting membrane transport, protein synthesis, and enzyme activities. They generally have a bitter taste. Alkaloids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil Amendment
A soil conditioner is a product which is added to soil to improve the soil’s physical qualities, usually its fertility (ability to provide nutrition for plants) and sometimes its mechanics. In general usage, the term "soil conditioner" is often thought of as a subset of the category soil amendments (or soil improvement, soil condition), which more often is understood to include a wide range of fertilizers and non-organic materials. In the context of construction soil conditioning is also called soil stabilization. Soil conditioners can be used to improve poor soils, or to rebuild soils which have been damaged by improper soil management. They can make poor soils more usable, and can be used to maintain soils in peak condition. Composition A wide variety of materials have been described as soil conditioners due to their ability to improve soil quality. Some examples include biochar, bone meal, blood meal, coffee grounds, compost, compost tea, coir, manure, straw, peat, sphagn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bioresource Technology
''Bioresource Technology'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published biweekly by Elsevier, covering the field of bioresource technology. The journal was established in 1979 as ''Agricultural Wastes'' and renamed to ''Biological Wastes'' in 1987, before obtaining its current title in 1991. It covers all areas concerning biomass, biological waste treatment, bioenergy Bioenergy is a type of renewable energy that is derived from plants and animal waste. The Biomass (energy), biomass that is used as input materials consists of recently living (but now dead) organisms, mainly plants. Thus, Fossil fuel, fossil fu ..., biotransformations and bioresource systems analysis, and technologies associated with conversion or production. Ashok Pandey, the longtime serving executive editor and editor-in-chief, was found involved in publication scandal. Elsevier found that in 43 of research papers he co-authored in the journal, he added his name and violated the journal policies in the pee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
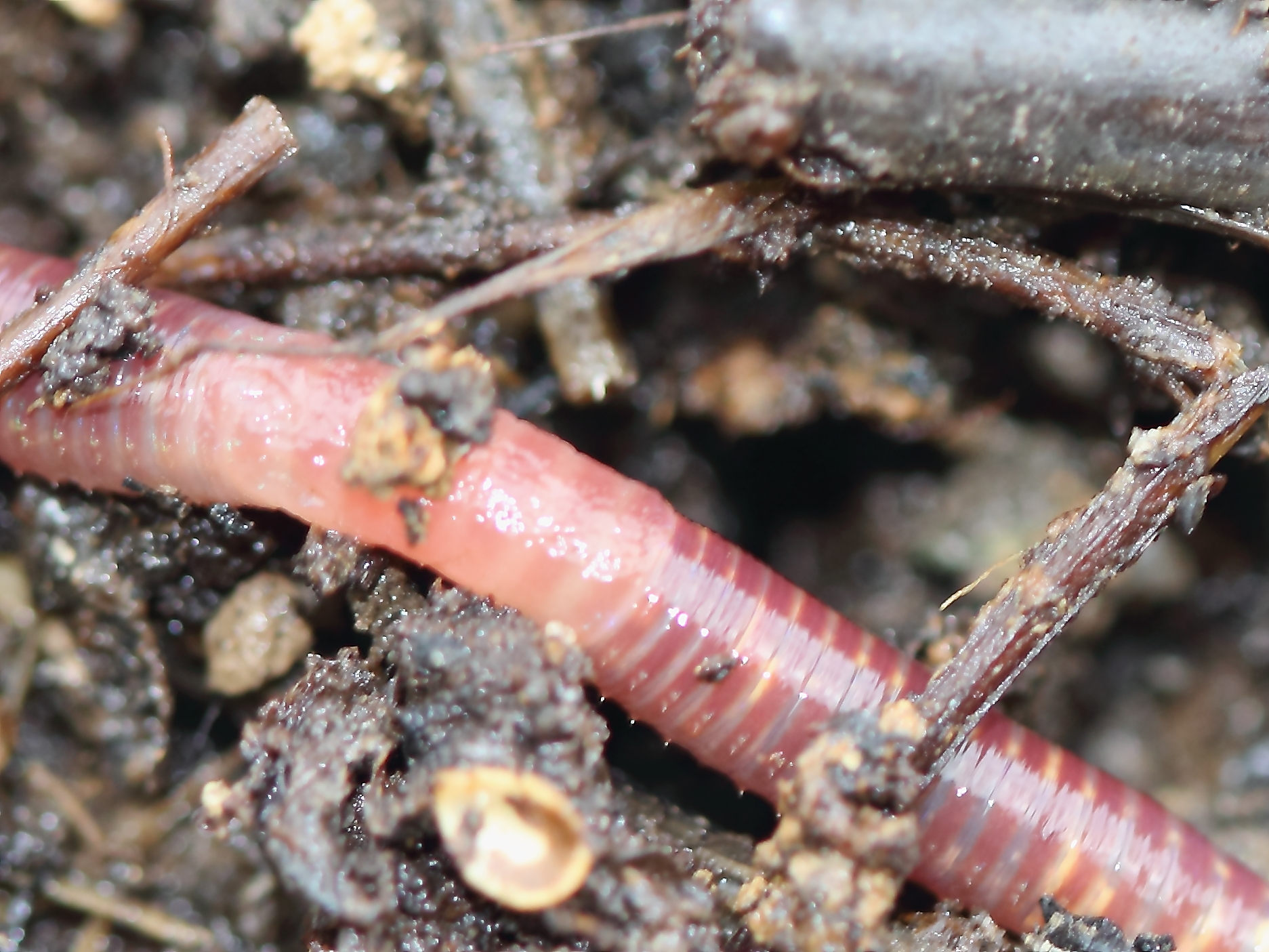
Red Wiggler
''Eisenia fetida'', known under various common names such as manure worm, redworm, brandling worm, panfish worm, trout worm, tiger worm, red wiggler worm, etc., is a species of earthworm adapted to decaying organic material. These worms thrive in rotting vegetation, compost, and manure. They are epigean, rarely found in soil. In this trait, they resemble ''Lumbricus rubellus''. The red wiggler is reddish-brown in color, has small rings around its body, and has a yellowish tail. Groups of bristles (called setae) on each segment of the worm move in and out to grip nearby surfaces as it stretches and contracts its muscles to push itself forward or backward. ''E. fetida'' worms are native to Europe, but have been introduced (both intentionally and unintentionally) to every other continent except Antarctica. ''E. fetida'' also possesses a unique natural defense system in its coelomic fluid; cells called coelomocytes secrete a protein called lysenin, which is a pore-forming tox ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
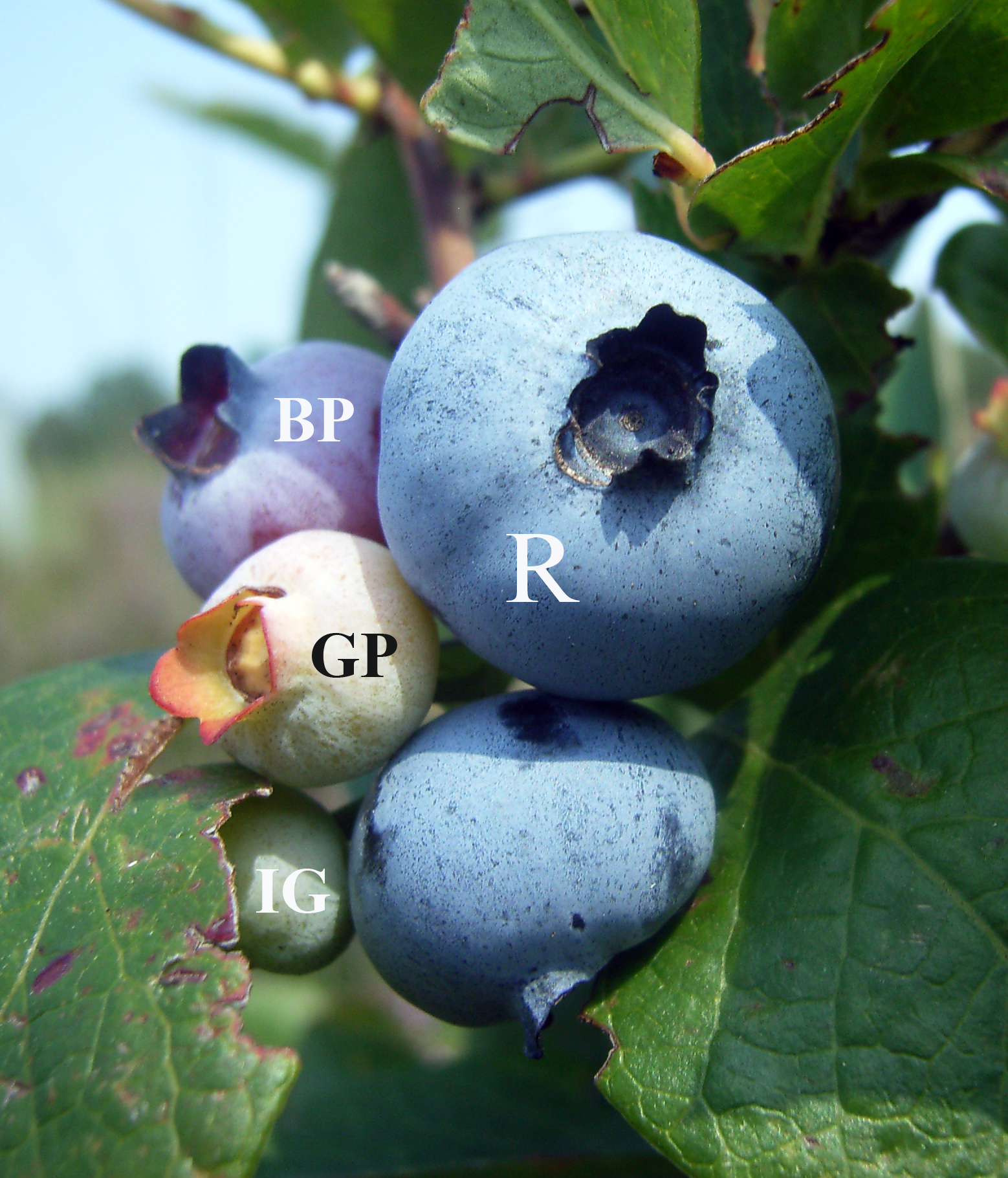
Blueberries
Blueberries are a widely distributed and widespread group of perennial flowering plants with blue or purple berries. They are classified in the section ''Cyanococcus'' with the genus ''Vaccinium''. Commercial blueberries—both wild (lowbush) and cultivated (highbush)—are all native to North America. The highbush varieties were introduced into Europe during the 1930s. Blueberries are usually prostrate shrubs that can vary in size from to in height. In the commercial production of blueberries, the species with small, pea-size berries growing on low-level bushes are known as "lowbush blueberries" (synonymous with "wild"), while the species with larger berries growing on taller, cultivated bushes are known as "highbush blueberries". Canada is the leading producer of lowbush blueberries, while the United States produces some 40% of the world's supply of highbush blueberries. Description Many species of blueberries grow wild in North America, including '' Vaccinium myrtilloi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil PH
Soil pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity (alkalinity) of a soil. Soil pH is a key characteristic that can be used to make informative analysis both qualitative and quantitatively regarding soil characteristics. pH is defined as the negative logarithm (base 10) of the activity of hydronium ions ( or, more precisely, ) in a solution. In soils, it is measured in a slurry of soil mixed with water (or a salt solution, such as ), and normally falls between 3 and 10, with 7 being neutral. Acid soils have a pH below 7 and alkaline soils have a pH above 7. Ultra-acidic soils (pH 9) are rare. Soil pH is considered a master variable in soils as it affects many chemical processes. It specifically affects plant nutrient availability by controlling the chemical forms of the different nutrients and influencing the chemical reactions they undergo. The optimum pH range for most plants is between 5.5 and 7.5; however, many plants have adapted to thrive at pH values ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mulch
A mulch is a layer of material applied to the surface of soil. Reasons for applying mulch include conservation of soil moisture, improving soil fertility, fertility and health of the soil, reducing Weed control, weed growth, and enhancing the visual appeal of the area. A mulch is usually, but not exclusively, organic in nature. It may be permanent (e.g. plastic sheeting) or temporary (e.g. barkdust, bark chips). It may be applied to bare soil or around existing plants. Mulches of manure and compost will be incorporated naturally into the soil by the activity of worms and other organisms. The process is used both in commercial crop production and in gardening, and when applied correctly, can improve soil productivity. Living mulches include moss lawnsMoss Myths/ref> and other ground covers. Uses Many materials are used as mulches, which are used to retain soil moisture, regulate soil temperature, suppress weed growth, and for aesthetics. They are applied to the soil surface, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compost
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by Decomposition, decomposing plant and food waste, recycling organic materials, and manure. The resulting mixture is rich in plant nutrients and beneficial organisms, such as bacteria, protozoa, nematodes, and fungi. Compost improves soil fertility in gardens, landscaping, horticulture, urban agriculture, and organic farming, reducing dependency on commercial chemical fertilizers. The benefits of compost include providing nutrients to crops as fertilizer, acting as a soil conditioner, increasing the humus or Humic acids, humic acid contents of the soil, and introducing beneficial microbes that help to suppress pathogens in the soil and reduce soil-borne diseases. At the simplest level, composting requires gathering a mix of green waste (nitrogen-rich materials such as leaves, grass, and food scraps) and brown waste (woody ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Oxides
In atmospheric chemistry, is shorthand for nitric oxide () and nitrogen dioxide (), the nitrogen oxides that are most relevant for air pollution. These gases contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain, as well as affecting tropospheric ozone. gases are usually produced from the reaction between nitrogen and oxygen during combustion of fuels, such as hydrocarbons, in air; especially at high temperatures, such as in car engines. In areas of high motor vehicle traffic, such as in large cities, the nitrogen oxides emitted can be a significant source of air pollution. gases are also produced naturally by lightning. does not include nitrous oxide (), a fairly inert oxide of nitrogen that contributes less severely to air pollution, notwithstanding its involvement in ozone depletion and high global warming potential. is the class of compounds comprising and the compounds produced from the oxidation of which include nitric acid, nitrous acid (HONO), din ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |