|
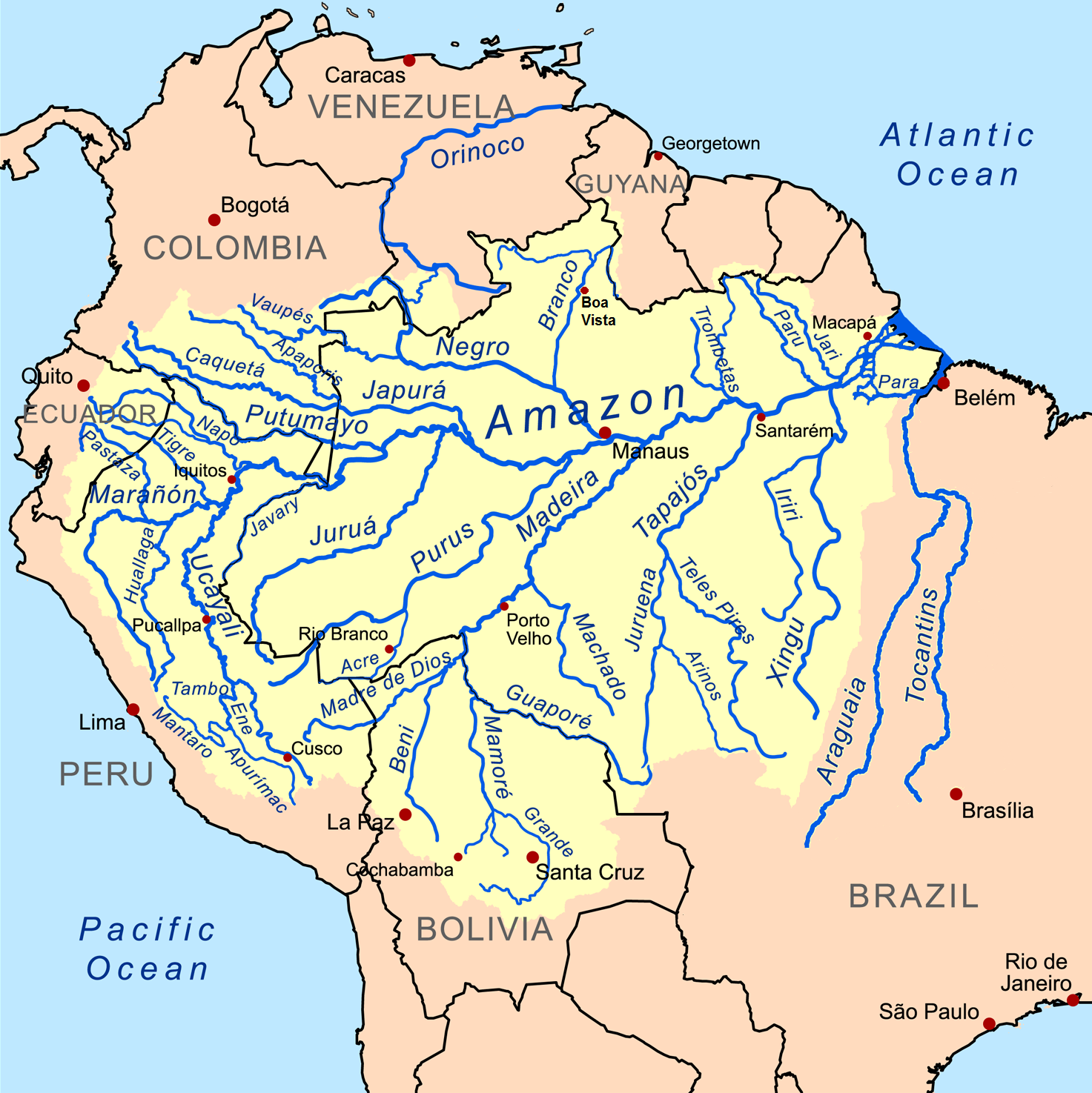
Urubamba River
The Urubamba River or Vilcamayo River (possibly from Quechua ''Willkamayu'', for "sacred river") is a river in Peru. Upstream it is called Vilcanota River (possibly from Aymara ''Willkanuta'', for "house of the sun"). Within the La Convención Province, the name changes to Urubamba. A partially navigable headwater of the Amazon River, the Urubamba rises in the Andes to the southeast of Cusco. It originates on the slopes of Cunurana in the Puno Region, Melgar Province, near the La Raya pass. It flows north-north-west for before coalescing with the Tambo River to form the Ucayali River. The Urubamba is divided into the Upper Urubamba and the Lower Urubamba, the dividing feature being the Pongo de Mainique, an infamous whitewater canyon, where the river narrows to a width of 45 metres (148 ft). Upper Urubamba The Upper Urubamba (''Alto Urubamba'') valley features a high population and extensive irrigation works. A number of ruins of the Inca Empire The Inca Empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amazon Basin
The Amazon basin is the part of South America drained by the Amazon River and its tributary, tributaries. The Amazon drainage basin covers an area of about , or about 35.5 percent of the South American continent. It is located in the countries of Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia, Ecuador, Guyana, Peru, Suriname, and Venezuela, as well as the territory of French Guiana. Most of the basin is covered by the Amazon rainforest, also known as Amazon rainforest, Amazonia. With a area of dense tropical forest, it is the largest rainforest in the world. Geography The Amazon River begins in the Andes, Andes Mountains at the west of the basin with its main tributary the Marañón River and Apurímac River, Apurimac River in Peru. The highest point in the Drainage divide, watershed of the Amazon is the second biggest peak of Yerupajá at . The Amazon River Basin occupies the entire central and eastern area of South America, lying to the east of the Andes mountain range and extending from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machiguenga
The Machiguenga (also Matsigenka, Matsigenga) are an indigenous people who live in the high jungle, or ''montaña'', area on the eastern slopes of the Andes and in the Amazon Basin jungle regions of southeastern Peru. Their population in 2020 amounted to about 18,000. Formerly they were hunter-gatherers but today the majority are sedentary swidden cultivators. The main crops grown are manioc, maize, and bananas, but today commercial crops such as coffee and cacao are increasingly important. Their main source of protein used to be peccary and monkeys but today fish has become more important as game animals have become increasingly scarce as a consequence of the encroachment from highland immigrants to the area and the exploitation of the Camisea gas finds. The Machiguenga people have a preference for self-sufficiency when it comes to cultivating essential crops, made possible by their generous land allocation per capita, and the lack of conflict in their area. Culture Most Machigue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salcca-Pucara Hydroelectric Project
Salcca-Pucara hydroelectric project is a hydropower project in Peru. The project envisages transferring water from the Río Salcca into the Vilcanota River and an electrical power output of 130 megawatt. The net worth of the project planned is $300,000,000. The start of construction work was planned to occur in September 2015. Concerns have been raised that electricity from the plant will primarily benefit mining companies and will result in soil contamination and damage to agriculture, as river flows will be altered. There has been opposition, including strikes in 2007 and protests in the two following years which resulted in a temporary suspension of the project. Nevertheless, after negotiations in December 2012 the last community whose permission was outstanding approved the project of the Cuzco-based company Ege Cuzco. Opposition nevertheless continued, with a 2014 report of the ombudsman An ombudsman ( , also ) is a government employee who investigates and tries to resol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raqch'i
Raqch'i (Quechua) is an Inca archaeological site in Peru located in the Cusco Region, Canchis Province, San Pedro District, near the populated place Raqch'i. It is 3480 meters above sea level and 110 kilometers from the city of Cuzco.Sillar (2013) pg 30 It also known as the ''Temple of Wiracocha'', one of its constituents. Both lie along the Vilcanota River. The site has experienced a recent increase in tourism in recent years, with 83,334 visitors to the site in 2006, up from 8,183 in 2000 and 452 in 1996. Layout The Inka site at Raqch'i was a primary control point on a road system that originated in Cusco and expanded as the Inka empire grew. It is located in a valley known for sacred sites.Suarez and George (2011) pg 106 Most of the Inka structures are enclosed by a 4 km-long perimeter wall, but just outside it, on the Inka road that entered Raqch'i from Cusco, an enclosure with eight rectangular buildings around a large courtyard was probably a '' tampu'' (a lodging ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pikillaqta
Pikillaqta ( Quechua ''piki'' flea, ''llaqta'' a place (village, town, community, country, nation), "flea place", also spelled ''Piki Llacta, Pikillacta, Piquillacta, Piquillaqta'') is a large Wari culture archaeological site east of Cusco in the Quispicanchi Province. Pikillaqta is a village of the Wari people. Wari was the centre village and other cities like Pikillaqta were influenced by it. The Wari also inhabited many other sites around the area. The site was occupied from about 550 to 1100 AD. Its main use was for ceremonies and the site was not complete when it was abandoned. Geography and environment Pikillaqta is located 3,200 meters above sea level in the Lucre Basin of the eastern Valley of Cusco, an area characterized by grassy hills mixed with rock and sand. The climate is cold and arid, averaging 300 millimeters of precipitation per month during winter and spring and 106 millimeters during late spring, summer, and fall. Temperature ranges between 60 degree ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patallaqta
Patallacta (possibly from Quechua language, Quechua ''pata'' elevated place / above, at the top / edge, bank (of a river), shore, ''llaqta'' place (village, town, city, country, nation), "settlement on a platform" pronounced "pahta-yakta"), Llactapata or Q'ente Marka (possibly from Quechua ''q'inti'' hummingbird, ''marka'' village, "hummingbird village") is an archaeological site in Peru located in the Cusco Region, Urubamba Province, Machupicchu District. It is situated southeast of the site Machu Picchu, at the confluence of the rivers Cusichaca River, Cusichaca and Urubamba River, Vilcanota on a mountain named Patallacta. On his way to Machu Picchu (at: ) Hiram Bingham III, Hiram Bingham, discoverer of many Incan sites, passed Patallacta, sometimes given the name of Llaqtapata as evidenced by the photograph of a sign from a check-point along the Inca trail. His associate Mr. Herman Tucker reported that the name of the town was ''Patallacta'' containing about one hundred hous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machu Picchu
Machu Picchu is a 15th-century Inca citadel located in the Eastern Cordillera of southern Peru on a mountain ridge at . Often referred to as the "Lost City of the Incas", it is the most familiar icon of the Inca Empire. It is located in the Machupicchu District within the Urubamba Province above the Sacred Valley, which is northwest of the city of Cusco. The Urubamba River flows past it, cutting through the Cordillera and creating a canyon with a subtropical mountain climate. The Inca civilization had no written language and following the first encounter by the Spanish soldier Baltasar Ocampo, no Europeans are recorded to have visited the site from the late 16th century until the 19th century. As far as historical knowledge extends, there are no existing written records detailing the site during its period of active use. The leading theory is that Machu Picchu was a private city for Incan royalty. The names of the buildings, their supposed uses, and their inhabitants, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sacred Valley
The Sacred Valley of the Incas (; ), or the Urubamba Valley, is a valley in the Andes of Peru, north of the Inca capital of Cusco. It is located in the present-day Peruvian region of Cusco. In colonial documents it was referred to as the "Valley of Yucay". The Sacred Valley was incorporated slowly into the incipient Inca Empire during the period from 1000 to 1400. The Sacred Valley is a major tourist destination. In 2019, 1.6 million people, the majority non-Peruvians, visited Machu Picchu, its most famous archaeological site. Many of the same tourists also visited other archaeological sites and modern towns in the Sacred Valley. Stretching from Pisac to Ollantaytambo, this fertile valley is irrigated by the Urubamba River. The Chanapata civilisation first utilised this area starting at around 800 BCE because of its rich soil used for agriculture. The Qotacalla civilization lived in the Sacred Valley from 500 to 900 CE. The Killke civilization then flourished in the Sacred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inca Empire
The Inca Empire, officially known as the Realm of the Four Parts (, ), was the largest empire in pre-Columbian America. The administrative, political, and military center of the empire was in the city of Cusco. The History of the Incas, Inca civilisation rose from the Peruvian highlands sometime in the early 13th century. The Portuguese explorer Aleixo Garcia was the first European to reach the Inca Empire in 1524. Later, in 1532, the Spanish Empire, Spanish began the conquest of the Inca Empire, and by 1572 Neo-Inca State, the last Inca state was fully conquered. From 1438 to 1533, the Incas incorporated a large portion of western South America, centered on the Andes, Andean Mountains, using conquest and peaceful assimilation, among other methods. At its largest, the empire joined modern-day Peru with what are now western Ecuador, western and south-central Bolivia, northwest Argentina, the southwesternmost tip of Colombia and Incas in Central Chile, a large portion of modern- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
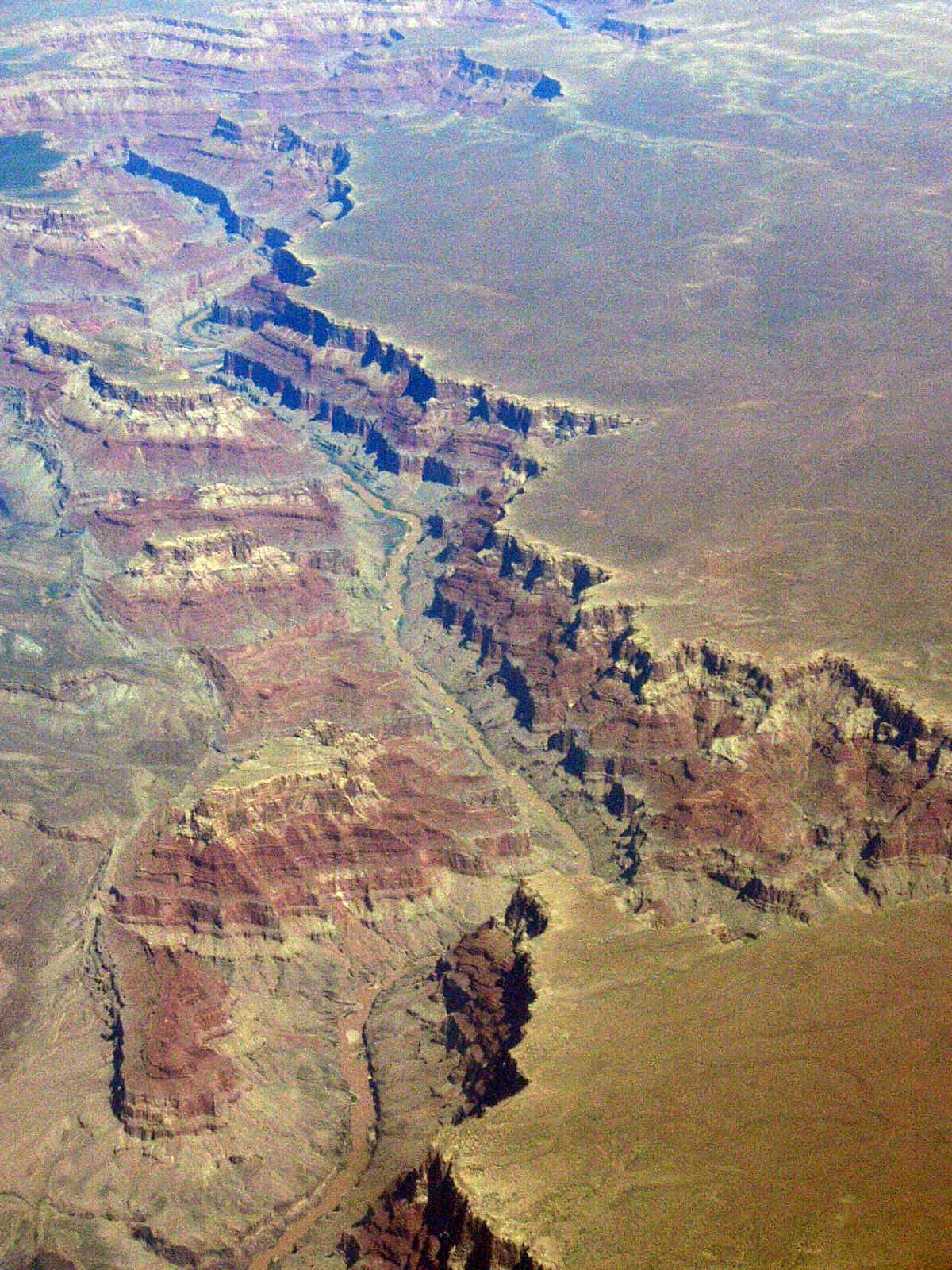
Canyon
A canyon (; archaic British English spelling: ''cañon''), gorge or chasm, is a deep cleft between escarpments or cliffs resulting from weathering and the erosive activity of a river over geologic time scales. Rivers have a natural tendency to cut through underlying surfaces, eventually wearing away rock layers as sediments are removed downstream. A river bed will gradually reach a baseline elevation, which is the same elevation as the body of water into which the river drains. The processes of weathering and erosion will form canyons when the river's headwaters and estuary are at significantly different elevations, particularly through regions where softer rock layers are intermingled with harder layers more resistant to weathering. A canyon may also refer to a rift between two mountain peaks, such as those in ranges including the Rocky Mountains, the Alps, the Himalayas or the Andes. Usually, a river or stream carves out such splits between mountains. Examples of mountain- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whitewater
Whitewater forms in the context of rapids, in particular, when a river's Stream gradient, gradient changes enough to generate so much turbulence that air is trapped within the water. This forms an unstable current that foam, froths, making the water appear opaque and white. The term "whitewater" also has a broader meaning, applying to any river or creek that has a significant number of rapids. The term is also used as an adjective describing boating on such rivers, such as whitewater canoeing or whitewater kayaking. Fast rivers Four factors, separately or in combination, can create rapids: gradient, constriction, obstruction, and flow rate. Gradient, constriction, and obstruction are streambed topography factors and are relatively consistent. Flow rate is dependent upon both seasonal variation in precipitation and snowmelt and upon release rates of upstream dams. Streambed topography Streambed topography is the primary factor in creating rapids, and is generally consist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |