|
Urs Leupold
Urs Leupold (July 19, 1923 – October 9, 2006) was a Swiss geneticist whose studies of the fission yeast ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' were instrumental in establishing this organism as a key model system for eukaryotic cell and molecular biology. Leupold began his studies of ''S. pombe'' in 1946 upon encouragement by Øjvind Winge. In 1947, Leupold determined that a culture of ''S. pombe str. liquefaciens'' contained strains expressing four distinct mating types: ''h''40, ''h''90, ''h''+, and ''h''−. Most current ''S. pombe'' laboratory strains are derived from the ''h''90, ''h''+, and ''h''− strains known as 968, 975, and 972. Leupold went on to carry out postdoctoral studies with Norman Horowitz at Caltech and with Boris Ephrussi at the University of Paris. Notably, with Norman Horowitz, Leupold isolated the first conditional (temperature sensitive) mutations in the bacterium ''Escherichia coli'' as part of an effort to address criticisms raised by Max Delbrück of the on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leupold
Leupold & Stevens, Inc. is an American manufacturer of telescopic sights, red dot sights, binoculars, Rangefinding telemeter, rangefinders, spotting scopes, and Sunglasses, eyewear located in Beaverton, Oregon, United States. The company, started in 1907, is on its fifth generation of family ownership.Leeson, Fred (November 17, 1996). "All in the family". ''The Oregonian''. History Leupold & Stevens was founded by the German immigrant Markus Friedrich (Fred) Leupold and his brother-in-law Adam Voelpel in 1907, under the name Leupold & Voelpel. At the time, the company specialized in the repair of Surveying, survey equipment. In 1911, Leupold & Voelpel was contracted by John Cyprian (J.C.) Stevens to manufacture a water level recorder he had designed and patented. After the initial success of the product, he was made partner in 1914 and the company was renamed Leupold, Voelpel, and Co.Stevens, John Cyprian. ''The Autobiography of a Civil Engineer'', published 1959. Besides the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Zürich
The University of Zurich (UZH, ) is a public university, public research university in Zurich, Switzerland. It is the largest university in Switzerland, with its 28,000 enrolled students. It was founded in 1833 from the existing colleges of theology, law, medicine which go back to 1525, and a new Faculty (division), faculty of philosophy. Currently, the university has seven faculties: Philosophy, Medicine, Human Medicine, Economic Sciences, Law, Mathematics and Natural Sciences, Theology and Veterinary Medicine. The university offers the widest range of subjects and courses of any Swiss higher education institution. History The University of Zurich was founded on April 29, 1833, when the existing colleges of theology, the Carolinum, Zurich, ''Carolinum'' founded by Huldrych Zwingli in 1525, law and medicine were merged with a new faculty of Philosophy. It was the first university in Europe to be founded by the state rather than a monarch or church. Its Latin name is reminiscen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Zurich
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Academic Staff Of The University Of Bern
An academy (Attic Greek: Ἀκαδήμεια; Koine Greek Ἀκαδημία) is an institution of tertiary education. The name traces back to Plato's school of philosophy, founded approximately 386 BC at Akademia, a sanctuary of Athena, the goddess of wisdom and skill, north of Athens, Greece. The Royal Spanish Academy defines academy as scientific, literary or artistic society established with public authority and as a teaching establishment, public or private, of a professional, artistic, technical or simply practical nature. Etymology The word comes from the ''Academy'' in ancient Greece, which derives from the Athenian hero, ''Akademos''. Outside the city walls of Athens, the gymnasium was made famous by Plato as a center of learning. The sacred space, dedicated to the goddess of wisdom, Athena, had formerly been an olive grove, hence the expression "the groves of Academe". In these gardens, the philosopher Plato conversed with followers. Plato developed his sessions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murdoch Mitchison
John Murdoch Mitchison (11 June 1922, Oxford – 17 March 2011, Edinburgh) was a British zoologist. Background Family Mitchison was the son of the Labour politician Dick Mitchison and his wife, the writer Naomi (née Haldane). The biologist J.B.S. Haldane was his uncle, and the physiologist John Scott Haldane was his maternal grandfather. His elder brother is the bacteriologist Denis Mitchison, and his younger brother is the zoologist Avrion Mitchison. His wife was the historian Rosalind Mitchison. Education Mitchison went to Winchester College and Trinity College, Cambridge, later becoming Professor of Zoology at Edinburgh University in 1963 after working there for a decade. He was elected a fellow of the Royal Society of London in 1978. Career Considered a pioneer in the area of cellular biology, Mitchison developed the yeast ''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'' as a model system to study the mechanisms and kinetics of growth and the cell cycle. He was an academic adviso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Nurse
Sir Paul Maxime Nurse (born 25 January 1949) is an English geneticist, former President of the Royal Society and Chief Executive and Director of the Francis Crick Institute. He was awarded the 2001 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine, along with Leland Hartwell and Tim Hunt, for their discoveries of protein molecules that control the division of cells in the cell cycle. Early life and education Nurse's mother went from London to Norwich and lived with relatives while awaiting Paul's birth (at the age of 18) in order to hide illegitimacy. For the rest of their lives, his maternal grandmother pretended to be his mother, and his mother pretended to be his sister. Paul was brought up by his grandparents (whom he took to be his parents) in North West London. He was educated at Lyon Park school in Alperton and Harrow County Grammar School. He received his BSc degree in Biology in 1970 from the University of Birmingham and his PhD degree in 1973 from the University of East An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Bern
The University of Bern (, , ) is a public university, public research university in the Switzerland, Swiss capital of Bern. It was founded in 1834. It is regulated and financed by the canton of Bern. It is a comprehensive university offering a broad choice of courses and programs in eight faculty (division), faculties and some 150 institutes. With around 19,000 students, the University of Bern is the third largest university in Switzerland. Organization The University of Bern operates at three levels: university, faculties and institutes. Other organizational units include interfaculty and general university units. The university's highest governing body is the Senate, which is responsible for issuing statutes, rules and regulations. Directly answerable to the Senate is the University Board of Directors, the governing body for university management and coordination. The board comprises the rector, the vice-rectors and the administrative director. The structures and functions of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
One Gene-one Enzyme Hypothesis
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
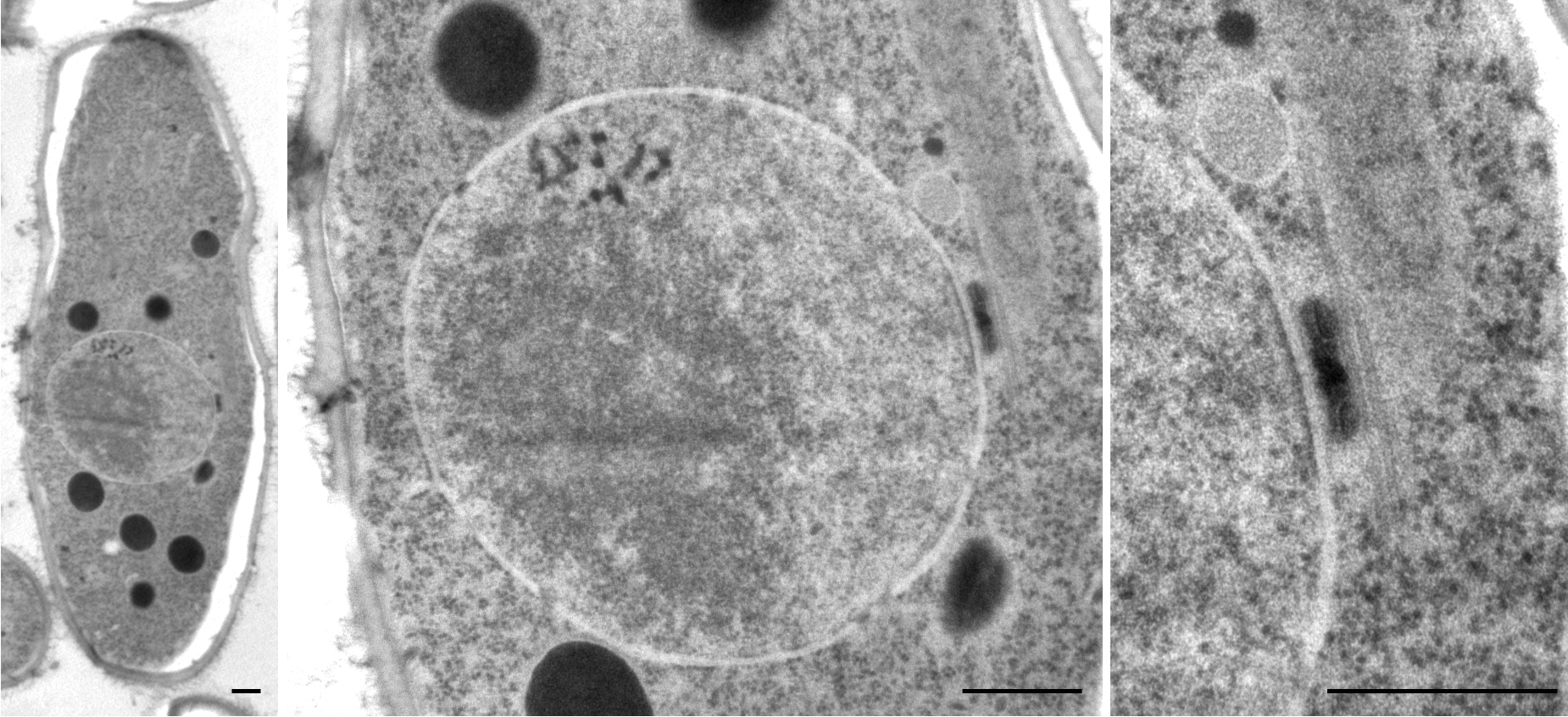
Schizosaccharomyces Pombe
''Schizosaccharomyces pombe'', also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length. Its genome, which is approximately 14.1 million base pairs, is estimated to contain 4,970 protein-coding genes and at least 450 non-coding RNAs. These cells maintain their shape by growing exclusively through the cell tips and divide by medial fission to produce two daughter cells of equal size, which makes them a powerful tool in cell cycle research. Fission yeast was isolated in 1893 by Paul Lindner from East African millet beer. The species name ''pombe'' is the Swahili word for beer. It was first developed as an experimental model in the 1950s: by Urs Leupold for studying genetics, and by Murdoch Mitchison for studying the cell cycle. Paul Nurse, a fission ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Delbrück
Max Ludwig Henning Delbrück (; September 4, 1906 – March 9, 1981) was a German–American biophysicist who participated in launching the molecular biology research program in the late 1930s. He stimulated physical science, physical scientists' interest into biology, especially as to basic research to physically explain genes, mysterious at the time. Formed in 1945 and led by Delbrück along with Salvador Luria and Alfred Hershey, the Phage Group made substantial headway unraveling important aspects of genetics. The three shared the 1969 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for their discoveries concerning the replication mechanism and the genetic structure of viruses"."The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine 1969" , Nobel Media AB 2013, ''Nobelprize.org'', Web access November 6, 2013 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' ( )Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. is a gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus '' Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are part of the normal microbiota of the gut, where they constitute about 0.1%, along with other facultative anaerobes. These bacteria are mostly harmless or even beneficial to humans. For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by harmful pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. coli'' and humans are a type of mutualistic biological relationship—where both the humans and the ''E. coli'' are benefitting each other. ''E. coli'' is expelled into the environment within fecal matter. The bacterium grows massi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |