|
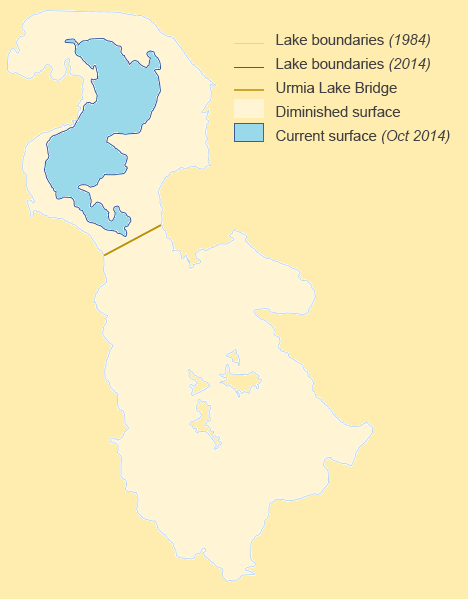
Urmia Lake
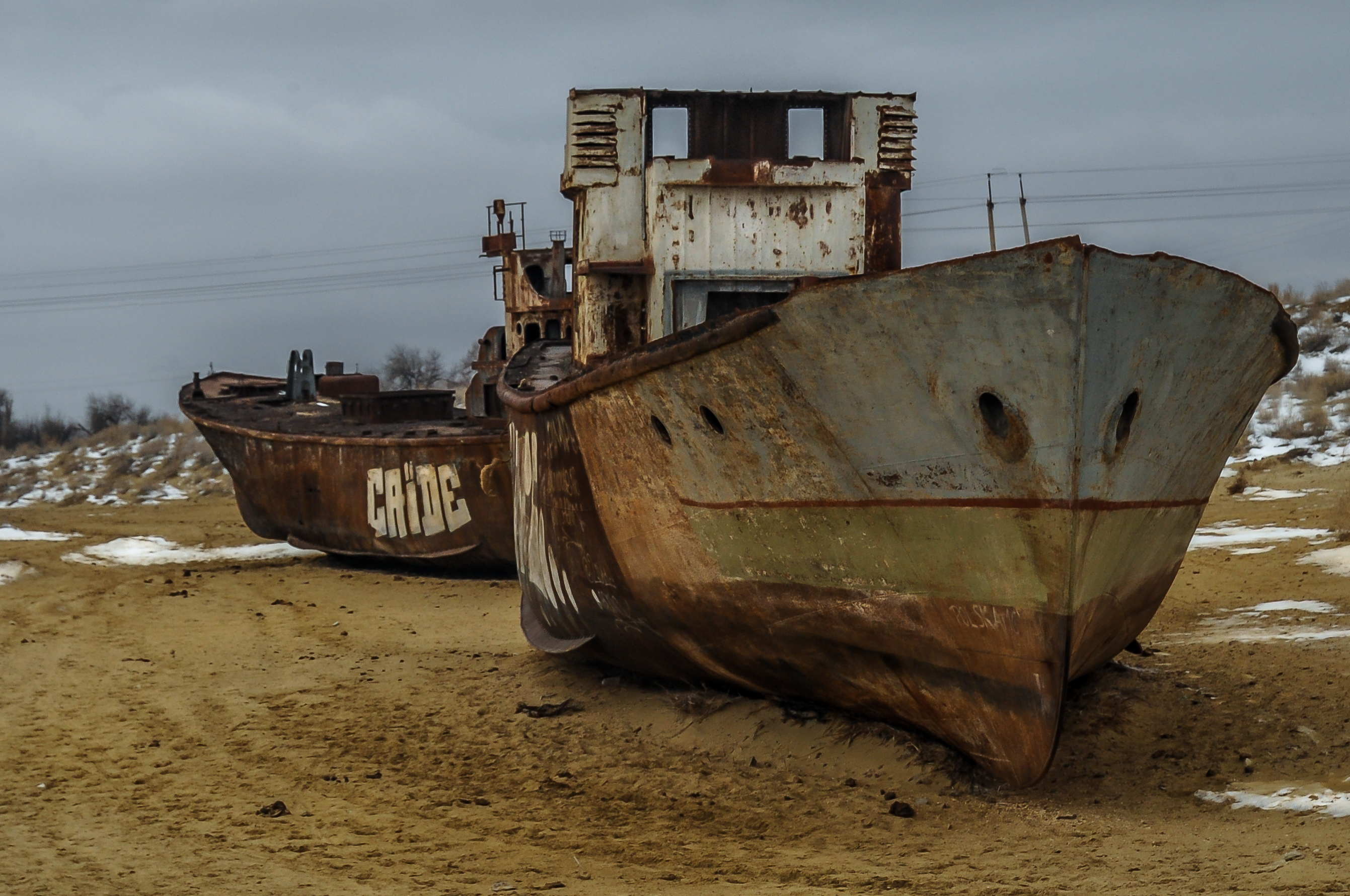
Lake Urmia is an endorheic lake, endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is located between the provinces of East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan in Iran, and west of the southern portion of the Caspian Sea. At its greatest extent, it was the largest lake in the Middle East. It is the sixth-largest Salt lake, saltwater lake on Earth, with a surface area of approximately , a length of , a width of , and a maximum depth of . By late 2017, the lake had shrunk to 10% of its former size (and 1/60 of water volume in 1998) due to persistent general drought in Iran, but also the damming of the local rivers that flow into it, and the pumping of groundwater from the surrounding area. This dry spell was broken in 2019 and the lake is now filling up once again, due to both increased rain and water diversion from the Great Zab, Zab River under the Urmia Lake Research Programme. Lake Urmia, along with its approximately 102 (former) islands, is protected as a national park by the Department of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake
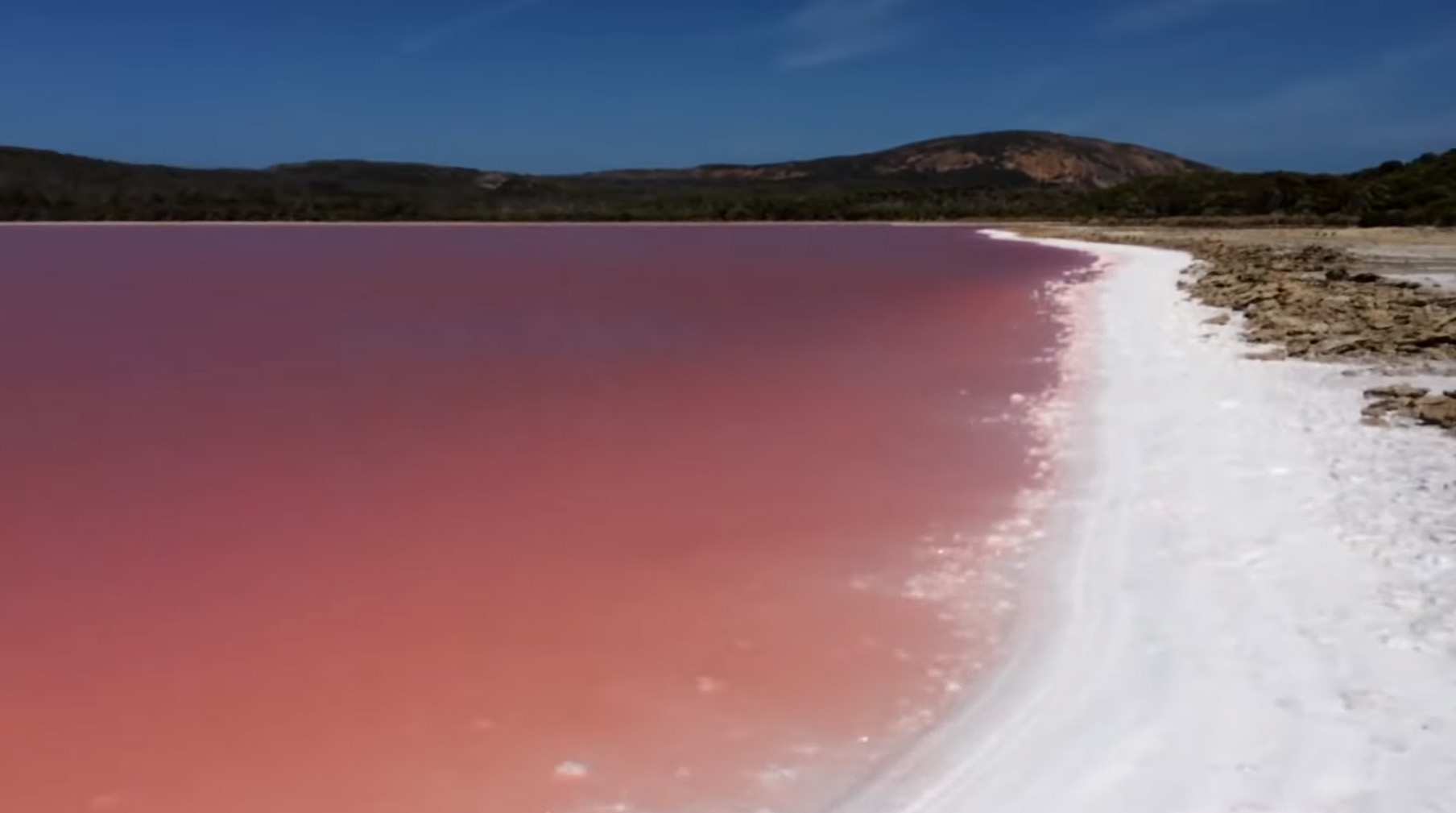
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per liter). In some cases, salt lakes have a higher concentration of salt than sea water; such lakes can also be termed hypersaline lake, and may also be pink lakes on account of their color. An alkalic salt lake that has a high content of carbonate is sometimes termed a soda lake. Salt lakes are classified according to salinity levels. The formation of these lakes is influenced by processes such as evaporation and deposition. Salt lakes face serious conservation challenges due to climate change, pollution and water diversion. Classification The primary method of classification for salt lakes involves assessing the chemical composition of the water within the lakes, specifically its salinity, pH, and the dominant ions present. Subsaline Sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endorheic Lake
An endorheic lake (also called a sink lake or terminal lake) is a collection of water within an endorheic basin, or sink, with no evident outlet. Endorheic lakes are generally Saline water, saline as a result of being unable to get rid of solutes left in the lake by evaporation. These lakes can be used as indicators of Human impact on the environment, anthropogenic change, such as irrigation or climate change, in the areas surrounding them. Lakes with subsurface drainage are called ''cryptorheic''. Components of endorheic lakes The two main ways that endorheic lakes accumulate water are through river flow into the lake (discharge) and precipitation falling into the lake. The collected water of the lake, instead of Discharge (hydrology), discharging, can only be lost due to either evapotranspiration or percolation (water sinking underground, e.g., to become groundwater in an aquifer). Because of this lack of an outlet, endorheic lakes are mostly salt water rather than fresh water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, described as the List of lakes by area, world's largest lake and usually referred to as a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia: east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia, south of the fertile plains of Southern Russia in Eastern Europe, and north of the mountainous Iranian Plateau. It covers a surface area of (excluding the highly saline lagoon of Garabogazköl to its east), an area approximately equal to that of Japan, with a volume of . It has a salinity of approximately 1.2% (12 g/L), about a third of the salinity of average seawater. It is bounded by Kazakhstan to the northeast, Russia to the northwest, Azerbaijan to the southwest, Iran to the south, and Turkmenistan to the southeast. The name of the Caspian Sea is derived from the ancient Iranian peoples, Iranic Caspians, Caspi people. The sea stretches from north to south, with an average width of . Its gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Azerbaijan
West Azerbaijan province () is one of the 31 provinces of Iran, provinces of Iran, whose capital and largest city is Urmia. It is in the Azerbaijan (Iran), northwest of the country, bordered by Turkey (Ağrı Province, Ağrı, Hakkâri Province, Hakkâri, Iğdır Province, Iğdır and Van Provinces), Iraq (Erbil Governorate, Erbil and Sulaymaniyah Governorates) and Azerbaijan's Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic, as well as the Iranian provinces of East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan, Zanjan province, Zanjan, and Kurdistan province, Kurdistan. West Azerbaijan province is part of Regions of Iran, Region Region 3, Iran, 3. It is separated from Armenia by Turkey's short border with the Azerbaijan Republic. The province covers an area of 39,487 km2, or 43,660 km2 including Lake Urmia. History The major known ancient civilization in the region was that of Mannaeans, a buffer state between Urartu, Urartian and Neo Assyrian Empire, Assyrian sphere of influence. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East Azerbaijan
East Azerbaijan province () is one of the 31 provinces of Iran. Its capital is the city of Tabriz. The province is located in Iranian Azerbaijan, bordering Armenia, the Republic of Azerbaijan, Ardabil province, West Azerbaijan province, and Zanjan province. East Azerbaijan is in Region 3 of Iran, with its secretariat located in its capital city, Tabriz. History East Azerbaijan is one of the most archaic territories in Iran. During the reign of Alexander III of Macedon in Iran (331 BCE), a warrior known as Attorpat led a revolt in this area, then a territory of the Medes, and thereafter it was called ''Attorpatkan''. Since then this vicinity has been known as ''Azarabadegan'', ''Azarbadgan'' and ''Azarbayjan''. Islamic researchers proclaim that the birth of the prophet Zoroaster was in this area, in the vicinity of Lake Orumieh (''Chichesht''), Konzak City. Needless to say, this province was subject to numerous political and economical upheavals, attracting the inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Gnaeus Pompeius Strabo, Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see things at great distance as if they were nearby was also called "Strabo". (; ''Strábōn''; 64 or 63 BC) was an ancient Greece, ancient Greek geographer who lived in Anatolia, Asia Minor during the transitional period of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is best known for his work ''Geographica'', which presented a descriptive history of people and places from different regions of the world known during his lifetime. Additionally, Strabo authored historical works, but only fragments and quotations of these survive in the writings of other authors. Early life Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amasya, Amaseia in Kingdom of Pontus, Pontus in around 64BC. His family had been involved in politics s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salt Lake
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of salt per liter). In some cases, salt lakes have a higher concentration of salt than sea water; such lakes can also be termed hypersaline lake, and may also be pink lakes on account of their color. An alkalic salt lake that has a high content of carbonate is sometimes termed a soda lake. Salt lakes are classified according to salinity levels. The formation of these lakes is influenced by processes such as evaporation and deposition. Salt lakes face serious conservation challenges due to climate change, pollution and water diversion. Classification The primary method of classification for salt lakes involves assessing the chemical composition of the water within the lakes, specifically its salinity, pH, and the dominant ions present. Subsaline Sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urmia Lake
Lake Urmia is an endorheic lake, endorheic salt lake in Iran. The lake is located between the provinces of East Azerbaijan and West Azerbaijan in Iran, and west of the southern portion of the Caspian Sea. At its greatest extent, it was the largest lake in the Middle East. It is the sixth-largest Salt lake, saltwater lake on Earth, with a surface area of approximately , a length of , a width of , and a maximum depth of . By late 2017, the lake had shrunk to 10% of its former size (and 1/60 of water volume in 1998) due to persistent general drought in Iran, but also the damming of the local rivers that flow into it, and the pumping of groundwater from the surrounding area. This dry spell was broken in 2019 and the lake is now filling up once again, due to both increased rain and water diversion from the Great Zab, Zab River under the Urmia Lake Research Programme. Lake Urmia, along with its approximately 102 (former) islands, is protected as a national park by the Department of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Urmia Shrinkage
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are fresh water and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions of oceans or large la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar site, Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. It is named after the city of Ramsar, Mazandaran, Ramsar in Iran, where the convention was signed in 1971. Every three years, representatives of the contracting parties meet as the Ramsar Convention#Conference of the Contracting Parties, Conference of the Contracting Parties (COP), the policy-making organ of the wetland conservation, convention which adopts decisions (site designations, resolutions and recommendations) to administer the work of the convention and improve the way in which the parties are able to implement its objectives. In 2022, COP15 was held in Montreal, Canada. List of wetlands of international importance The list of wetlands of international importance included 2,531 Ramsar site, Ramsar sites in Februa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Islands Of Iran
This is a list of notable islands of Iran. Coastal islands Persian Gulf ;Inhabited * Bent * Buneh * Dara * Farsi * Faror * Farvargan * Hendorabi * Hengam * Hormuz * Jonobi * Kharg * Kish * Larak * Lavan * Minu * Qabre Nakhoda * Qeshm * Shidvar Island * Shif * Shomali * Sirri * Abu Musa * Greater Tunb * Lesser Tunb ;Uninhabited * Farvargan (Lesser Farvar) * Shidvar * Abbasak * Sheif * Tahmadu (Jabrin) * Ommol-korm * Nakhiloo * Naaz islands * Om-e-Sile (Khan) * Germ * Bouneh * Dara * Ghabr-e-Nakhoda (Captain Grave) * Kharv * Mouliat * Se Dandun (Three Dents) * Motaf * Morghi * Cheraghi Oman Sea * Devil's Island (Iran) Caspian Sea * Ashuradeh Island Inland islands ;Aras River 427 islands shared with Turkey and Azerbaijan, including: * Khorameh * Buiduz * Pirwaltra * Gharebagh * Kasiri ;Arvand Rud * Abadan Island * Minoo Island ;Bakhtegan Lake * Menak Island ;Tashk Lake Tashk Lake is located at * Gonban Island * Narg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |