|
Urmia Clashes
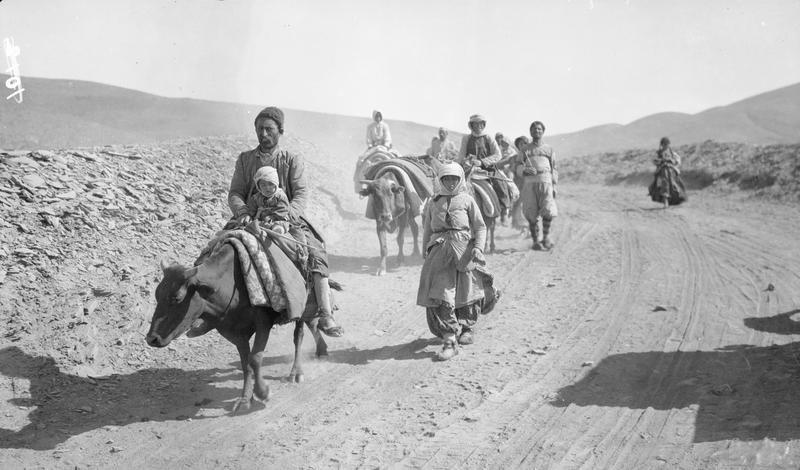
The Urmia clashes (February 1918) or the Urmia revolt was a series of clashes and an Islamist uprising in the city of Urmia between the Assyrian Volunteers, led by Agha Petros and Malik Khoshaba, against the city mayor Irshad Homayun and his supporters, including General Arshad el Moolk. This was caused by the Russian withdrawal from Qajar Iran due to the Russian Revolution. The motive for the uprising was to exterminate the Christian authority in the region. Background On January 11, the first battle between the Assyrians and the Iranian Government occurred when 55 Assyian soldiers out the 100 stationed left Salamas for Julfa to get clothing for the army where ambushed and killed by the Iranian army, soon after the Iranians attacked the Assyrians stationed in Khoy but where pushed back and the Assyrians would only retain 42 out of the original 100 after these clashes. This incident was quickly delivered to the Patriarch Mar Benyamin Shimun who, after seeing Iranian cavalry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urmia
Urmia (; ) is the largest city in West Azerbaijan Province of Iran. In the Central District of Urmia County, it is capital of the province, the county, and the district. The city is situated near the borders of Iran with Turkey and Iraq. The city lies at an altitude of above sea level along the Shahar River on the Urmia Plain. Lake Urmia, one of the world's largest salt lakes, lies to the east of the city, and the border with Turkey lies to the west. The city is the trading center for a fertile agricultural region where fruits (especially apples and grapes) and tobacco are grown. Even though the majority of the residents of Urmia are Muslims, the Christian history of Urmia is well preserved and is especially evident in the city's many churches and cathedrals. An important town by the 9th century, the city has had a diverse population which has at times included Muslims (Shias and Sunnis), Christians (Catholics, Protestants, Nestorians, and Orthodox), Jews, Baháʼ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andranik Ozanian
Andranik Ozanian, commonly known as General Andranik or simply Andranik (25 February 186531 August 1927), was an Armenian military commander and statesman, the best known '' fedayi'' and a key figure of the Armenian national liberation movement. He became active in an armed struggle against the Ottoman government and Kurdish irregulars in the late 1880s. Andranik joined the Armenian Revolutionary Federation (Dashnaktustyun) party and, along with other '' fedayi'' (militias), sought to defend the Armenian peasantry living in their ancestral homeland, an area known as Western (or Turkish) Armeniaat the time part of the Ottoman Empire. His revolutionary activities ceased and he left the Ottoman Empire after the unsuccessful uprising in Sasun in 1904. In 1907, Andranik left Dashnaktustyun because he disapproved of its cooperation with the Young Turks, the party which years later perpetrated the Armenian genocide. Between 1912 and 1913, together with Garegin Nzhdeh, Andranik l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assyrian Rebellion
The Assyrian rebellion (, "Nestorian Uprising") was an uprising by the Assyrians of Hakkari which was administered by tribal Assyrians at the time. It began in July 1924 and ended on 28 September that same year. This was the first rebellion in the newly formed Republic of Turkey. After the rebellion ended, 8,000 Assyrians were deported into Mandatory Iraq. (Another rebellion by the Assyrian community had taken place in 3–4 September 1924.) Background Assyrians of Tyari and Tkhuma returned to their ancestral land in Hakkari in 1922, shortly after World War I, without permission from the Turkish government. In 1924, the Vali (Ottoman term for governor) of Van wrote to Auli Beg who was the Agha of the village of Chal, telling him to inform the Assyrians in Hakkari not to worry about their visit. The Vali wanted to discuss whether they had come to Hakkari under the force of the British or wanted to live in Turkey as citizens. The Vali stated that if Assyrians were coming to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sayfo
The Sayfo (, ), also known as the Seyfo or the Assyrian genocide, was the mass murder and deportation of Assyrian people, Assyrian/Syriac Christians in southeastern Anatolia and Persia's Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan province by Ottoman Army (1861–1922), Ottoman forces and some Kurdish tribes during World War I. The Assyrians were divided into mutually antagonistic churches, including the Syriac Orthodox Church, the Assyrian Church of the East, and the Chaldean Catholic Church. Before World War I, they largely lived in mountainous and remote areas of the Ottoman Empire and Persia, some of which were effectively Stateless society, stateless. The Ottoman Empire's nineteenth-century centralization efforts led to increased violence and danger for the Assyrians. Mass killing of Assyrian civilians began during the Persian campaign (World War I), Ottoman occupation of Azerbaijan from January to May 1915, during which massacres were committed by Ottoman forces and pro-Ottoman Kur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Suldouze
The Battle of Suldouze (8–13 April 1918) was a military engagement between the Assyrian Volunteers led by Agha Petros And the Ottoman soldiers led by Kheiri Bey who were stationed in Suldouze. 1,500 Assyrian horsemen overcame the far larger Ottoman force of over 8,000. Background Over the summer of 1915 the Assyrians successfully held off the far bigger Ottoman army, Kurdish militia and tribal forces fighting with the Ottomans. The Ottomans, unable to break the Assyrians, then brought in heavy artillery and ammunition that, together with an overwhelming advantage in numbers and supplies, eventually overwhelmed the lightly armed and outnumbered Assyrians. The Russian Army Corps had promised reinforcements, which came too late. Assyrians defended themselves against tremendous odds and conducted an orderly retreat. Survivors of fighting age joined the Assyrians of northwest Persia, northern Iraq and northeast Syria, including those from Salamas and Urmia to form an Assyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Charah
The Battle of Charah (12–17 March 1918) or Charah Expedition took place between the Assyrian Volunteers led by Agha Petros and Malik Khsoshaba against Shekak tribesmen led by Simko Shikak in revenge for the assassination of Mar Benyamin Shimun. Simko Shikak, who was responsible for the murder of the Assyrian patriarch Mar Shimun was staying in the fortress. The fortress had never been conquered despite numerous attempts by the Iranian government. Background In March 1918, Mar Shimun and many of his 150 bodyguards were assassinated by Simko Shikak (Ismail Agha Shikak), a Kurdish agha, in the town of Kuhnashahir in Salmas (Persia) under a truce flag. Following the death of Mar Shimun, Assyrian forces under the command of Agha Petros launched an assault on Simko’s city of Kuhnashahir, bombing it with heavy artillery, resulting in the deaths of approximately 1,500 Kurds. Caught off guard, Simko escaped the city and fled to Charah, where the Battle of Charah would later ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allies Of World War I
The Allies or the Entente (, ) was an international military coalition of countries led by the French Republic, the United Kingdom, the Russian Empire, the United States, the Kingdom of Italy, and the Empire of Japan against the Central Powers of the German Empire, Austria-Hungary, the Ottoman Empire, and the Kingdom of Bulgaria in World War I (1914–1918). By the end of the first decade of the 20th century, the major European powers were divided between the Triple Entente and the Triple Alliance. The Triple Entente was made up of the United Kingdom, France, and Russia. The Triple Alliance was originally composed of Germany, Austria–Hungary, and Italy, but Italy remained neutral in 1914. As the war progressed, each coalition added new members. Japan joined the Entente in 1914 and, despite proclaiming its neutrality at the beginning of the war, Italy also joined the Entente in 1915. The term "Allies" became more widely used than "Entente", although the United Kingdom, Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toma Audo
Mar Toma Audo (), also spelled Thomas Audo (October 10, 1854 - July 27, 1918) was Archbishop of the Chaldean Catholic Archeparchy of Urmia (1890-1918), within the Chaldean Catholic Church. catholic-hierarchy.org Life He was born on October 11, 1855, in to ethnic Assyrian parents. His uncle Joseph Audo, who was the Patriarch of the Chaldean Catholic Church ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabriz
Tabriz (; ) is a city in the Central District (Tabriz County), Central District of Tabriz County, in the East Azerbaijan province, East Azerbaijan province of northwestern Iran. It serves as capital of the province, the county, and the district. It is the List of largest cities of Iran, sixth-most-populous city in Iran. Tabriz is in the Quri Chay, Quru River valley in Iran's historic Azerbaijan (Iran), Azerbaijan region between long ridges of volcanic cones in the Sahand and Eynali mountains. Tabriz's elevation ranges between above sea level. The valley opens up into a plain that gently slopes down to the eastern shores of Lake Urmia, to the west. The city was named World Carpet Weaving City by the World Crafts Council in October 2015 and Exemplary Tourist City of 2018 by the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. With a population of over 1.7 million (2016), Tabriz is the largest economic hub and metropolitan area in northwest Iran. The population is bilingual with most peopl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khoy
Khoy (, ) is a city in the Central District (Khoy County), Central District of Khoy County, West Azerbaijan province, West Azerbaijan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Occupied since Medes, Median times, it shares a long history as an important Christianity, Christian center.Andrew Burke, "Iran" pp. 138. Lonely Planet. History Khoy was named in ancient times for the salt mines that made it an important spur of the Silk Route. 3000 years ago, a city existed on the area where Khoy is located nowadays, but its name became Khoy only in the 14th centuries ago.Lida Balilan Asl, Elham Jafari. "Khoy's Expansion from Early Islam to Late Qajar According to Historical Documents" published spring 2013. vol 3 In 714 BC, Sargon II passed the region of which Khoy is part of in a campaign against Urartu. During the reign of Kingdom of Armenia (antiquity), Greater Armenia this city was a part of Nor-Shirakan province (ashkar). Khoy was mentioned in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jolfa, Iran
Jolfa () is a city in the Central District of Jolfa County, East Azerbaijan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Jolfa is separated by the Aras River The Aras is a transboundary river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, fin ... from its namesake, the town of Julfa on the Azerbaijan side of the border. The two towns are linked by a road bridge and a railway bridge. Demographics Population At the 2006 National Census, the city's population was 4,983 in 1,365 households. The following census in 2011 counted 5,628 people in 1,448 households. At the 2016 census, the population was 8,810 people in 2,543 households. Climate Historical monuments * Saint Stepanos Monastery * Jolfa Water Mill * Chapel of Chupan See also Notes References Cities in E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmas County
Salmas County () is in West Azerbaijan province, Iran. Its capital is the city of Salmas. Demographics Ethnicity The county is populated largely by Kurds and a smaller minority of Azerbaijanis. Also a few hundred Assyrians live in the district, and comprise the second largest population of minorities in the province after Urmia County Urmia County () is in West Azerbaijan province, Iran. Its capital is the city of Urmia. Demographics Ethnicity The county is mainly populated by Azerbaijanis, Persians and Kurds Kurds (), or the Kurdish people, are an Iranian peopl .... Population At the time of the 2006 National Census, the county's population was 180,708 in 40,298 households. The following census in 2011 counted 192,591 people in 48,872 households. The 2016 census measured the population of the county as 196,546 in 53,907 households. Administrative divisions Salmas County's population history and administrative structure over three consecutive censuses a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |