|
Uriens
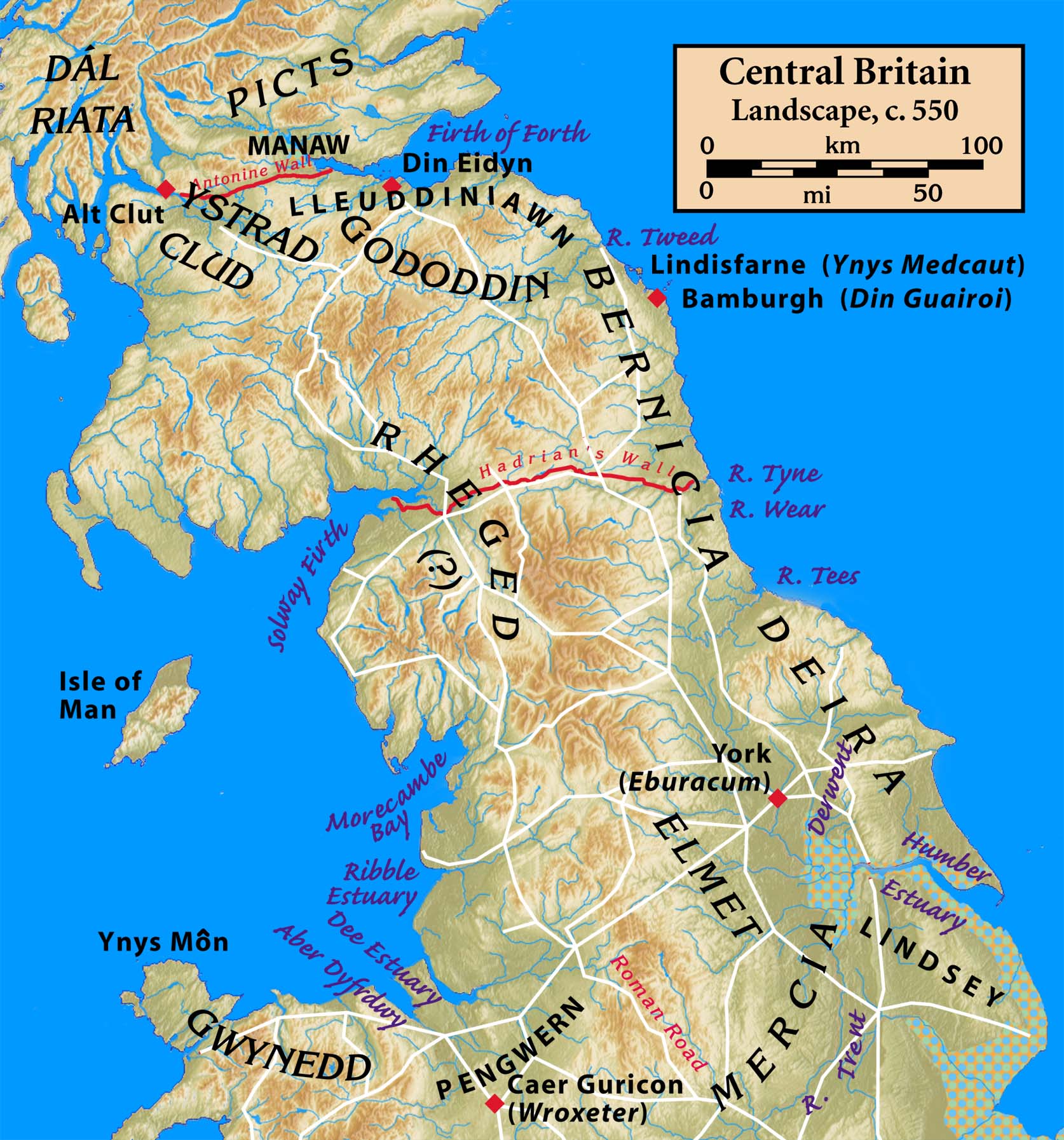
Urien ap Cynfarch Oer () or Urien Rheged (, Old Welsh: or , ) was a powerful sixth-century Brittonic-speaking figure who was possibly the ruler of the territory or kingdom known as Rheged. He is one of the best-known and best documented of the British figures of the ' Old North'. His kingdom was most likely centred around the Solway Firth. According to the ''Historia Brittonum'' (), Urien gained the decisive advantage in a conflict against the Anglo-Saxons in northern Britain led an alliance with three other kings: Rhydderch Hen, Gwallog ap Llênog, and Morgan. The alliance led by Urien penned the Anglo-Saxons in at Lindisfarne, though this siege came to an abrupt end when Urien was murdered on the orders of his erstwhile ally Morgan. The most secure evidence for his existence comes the ''Historia Brittonum'' and eight praise-poems in Middle Welsh dedicated to him surviving in a fourteenth-century manuscript. Despite their being found in Middle Welsh orthography, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhys Ap Thomas
Sir Rhys ap Thomas (1449–1525) was a Welsh soldier and landholder who rose to prominence during the Wars of the Roses, and was instrumental in the victory of Henry Tudor at the Battle of Bosworth. He remained a faithful supporter of Henry and was rewarded with lands and offices in South Wales. Some sources claim that he personally delivered the death blow to King Richard III at Bosworth with his poleaxe. Early life Rhys was the youngest legitimate son of Thomas ap Gruffydd ap Nicolas of Llandeilo in Carmarthenshire, and Elizabeth, daughter of Sir John Gruffydd of Abermarlais, also in Carmarthenshire. His grandfather was Gruffudd ap Nicolas, lord of Dinefwr. His maternal great-grandfather, Sir Thomas Griffith, who married Anne, daughter of Sir Walter Blount, was the grandson of Sir Rhys ap Gruffydd, and through him, was a descendant of Ednyfed Fychan as well as of Lord Rhys, Prince of Wales and member of the royal House of Dinefwr. In 1460, after decades of increa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Assassination
Assassination is the willful killing, by a sudden, secret, or planned attack, of a personespecially if prominent or important. It may be prompted by political, ideological, religious, financial, or military motives. Assassinations are ordered by both individuals and organizations, and are carried out by their accomplices. Acts of assassination have been performed since ancient times. A person who carries out an assassination is called an assassin. Etymology ''Assassin'' comes from the Italian and French Assissini, believed to derive from the word '' hashshashin'' (), and shares its etymological roots with '' hashish'' ( or ; from ').''The Assassins: a radical sect in Islam'' – Bernard Lewis, pp. 11–12 It referred to a group of Nizari Ismailis known as the Order of Assassins who worked against various political targets. Founded by Hassan-i Sabbah, the Assassins were active in the Near East from the 11th to the 13th centuries. The group killed members of the Ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from ) is a city in the Cumberland district of Cumbria, England. Carlisle's early history is marked by the establishment of a settlement called Luguvalium to serve forts along Hadrian's Wall in Roman Britain. Due to its proximity to Scotland (being located south of the current Anglo-Scottish border), Carlisle Castle and the city became an important military stronghold in the Middle Ages. The castle served as a prison for Mary, Queen of Scots in 1568 and currently hosts the Duke of Lancaster's Regiment and the Border Regiment Museum. A priory was built in the early 12th century, which subsequently became Carlisle Cathedral in 1133 on the creation of the Diocese of Carlisle. As the seat of a diocese, Carlisle therefore gained city status. Carlisle also served as the county town of the historic county of Cumberland from the county's creation in the 12th century. In the 19th century, the introduction of textile manufacture during the Industrial Revolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hywel Ab Owain Gwynedd
Hywel ab Owain Gwynedd (c. 1120–1170), King of Gwynedd in 1170, was a Welsh poet and military leader. Hywel was the son of Owain Gwynedd, king of Gwynedd and an Irishwoman named Pyfog. In recognition of this, he was also known as ''Hywel ap Gwyddeles'' (Hywel son of the Irishwoman). Hywel is also known as the Poet Prince for his bardic skills. Biography Military campaigns Hywel's father Owain Gwynedd and uncle Cadwaladr came to blows in 1143 when Cadwaladr was implicated in the murder of Prince Anarawd ap Gruffydd of Deheubarth, Owain's ally and future son-in-law, on the eve of Anarawd's wedding to Owain's daughter. Owain followed a diplomatic policy of binding other Welsh rulers to Gwynedd through dynastic marriages, and Cadwaladr's border dispute and murder of Anarawd threatened Owain's efforts and credibility. As ruler of Gwynedd, Owain stripped Cadwaladr of his lands assigning them to Hywel in 1139 and dispatched Hywel to the Kingdom of Ceredigion where he burned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solway Firth
The Solway Firth is an inlet on the west coast of Great Britain, forming part of the border between England and Scotland. The firth (a Scottish term for an inlet of the sea) divides Cumbria (including the Solway Plain) from Dumfries and Galloway. The Isle of Man is also very near to the firth. The firth comprises part of the Irish Sea. The firth's coastline is characterised by lowland hills and small mountains. It is a mainly rural area, with mostly small villages and settlements (such as Powfoot). Fishing, hill farming, and some arable farming play a large part in the local economy, although tourism is increasing. The northern part of the English coast of the Solway Firth was designated as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, known as the Solway Coast, in 1964. Construction of the Robin Rigg Wind Farm in the firth began in 2007. Within the firth, there are some Salt marsh, salt marshes and mud flats that can be dangerous, due to their frequently shifting patches of quicksa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ifor Williams
Sir Ifor Williams, (16 April 1881 – 4 November 1965) was a Welsh scholar who laid the foundations for the academic study of Old Welsh, particularly early Welsh poetry. Early life and education Ifor Williams was born at Pendinas, Tregarth near Bangor, Wales, the son of John Williams, a quarryman, and his wife Jane. His maternal grandfather, Hugh Derfel Hughes, was a noted local historian who wrote a well-regarded book on the history of the area. He went to Friars School, Bangor, in 1894 but had only been there for just over a year when he suffered a serious accident. This left him with back injuries that made him bedridden for several years. Having recovered, he attended Clynnog School in 1901 and in 1902 won a scholarship to University College of North Wales. In 1905 he graduated with honours in Greek, then in 1906 in Welsh. He spent the 1906–07 academic year at the Department of Welsh working for his M.A. degree and assisting Sir John Morris-Jones, the Professor of We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yr Hen Ogledd
Hen Ogledd (), meaning the Old North, is the historical region that was inhabited by the Brittonic people of sub-Roman Britain in the Early Middle Ages, now Northern England and the southern Scottish Lowlands, alongside the fellow Brittonic Celtic Kingdom of Elmet, in Yorkshire. Its population spoke a variety of the Brittonic language known as Cumbric which is closely related to, if not a dialect of Old Welsh. The people of Wales and the Hen Ogledd considered themselves to be one people, and both were referred to as Cymry ('fellow-countrymen') from the Brittonic word ''combrogi''. The Hen Ogledd was distinct from the parts of Great Britain inhabited by the Picts, Anglo-Saxons, and Scoti. The major kingdoms of the Hen Ogledd were Elmet, Gododdin, Rheged, and the Kingdom of Strathclyde (Welsh: ''Ystrad Clud''). Smaller kingdoms included Aeron and Calchfynydd. Eidyn, Lleuddiniawn, and Manaw Gododdin were evidently parts of Gododdin. The later Anglian kingdoms of Deira and B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Britons
The Britons (Linguistic reconstruction, *''Pritanī'', , ), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were the Celts, Celtic people who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age until the High Middle Ages, at which point they diverged into the Welsh people, Welsh, Cornish people, Cornish, and Bretons (among others). They spoke Common Brittonic, the ancestor of the modern Brittonic languages. The earliest written evidence for the Britons is from Greco-Roman world, Greco-Roman writers and dates to the Iron Age. Ancient Britain was made up of many tribes and kingdoms, associated with various Hillforts in Britain, hillforts. The Britons followed an ancient Celtic religion overseen by druids. Some of the southern tribes had strong links with mainland Europe, especially Gaul and Gallia Belgica, Belgica, and Celtic currency of Britain, minted their own coins. The Roman Empire Roman conquest of Britain, conquered most of Britain in the 1st century AD, creating th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Brittonic
Common Brittonic (; ; ), also known as British, Common Brythonic, or Proto-Brittonic, is a Celtic language historically spoken in Britain and Brittany from which evolved the later and modern Brittonic languages. It is a form of Insular Celtic, descended from Proto-Celtic, a theorized parent language that, by the first half of the first millennium BC, was diverging into separate dialects or languages. Pictish is linked, most probably as a sister language or a descendant branch. Evidence from early and modern Welsh shows that Common Brittonic was significantly influenced by Latin during the Roman period, especially in terms related to the church and Christianity. By the sixth century AD, the languages of the Celtic Britons were rapidly diverging into Neo-Brittonic: Welsh, Cumbric, Cornish, Breton, and possibly the Pictish language. Over the next three centuries, Brittonic was replaced by Scottish Gaelic in most of Scotland, and by Old English (from which descend M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Welsh
Old Welsh () is the stage of the Welsh language from about 800 AD until the early 12th century when it developed into Middle Welsh.Koch, p. 1757. The preceding period, from the time Welsh became distinct from Common Brittonic around 550, has been called "Primitive"Koch, p. 1757. or "Archaic Welsh". Phonology The phonology of Old Welsh is as follows. * Older was diphthongized into in (stressed) final syllables, but it was retained elsewhere. Whilst this persisted as a diphthong in Middle Welsh, in Modern Welsh /aw/ has collapsed to following the stress shift to the penultimate, except in monosyllables. * and were allophones of and in unstressed non-final syllables. In Middle Welsh these merged to . * Old Welsh and became and in Modern Welsh final syllables, in dialects where /ɨ/ has not merged with /i/. Texts The oldest surviving text entirely in Old Welsh is understood to be that on a gravestone now in Tywyn – the Cadfan Stone – thought to date from the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gweith Gwen Ystrat
''Gweith Gwen Ystrat'' (in English: ''The Battle of Gwen Ystrad''), is a late Old Welsh or Middle Welsh heroic poem found uniquely in the Book of Taliesin, where it forms part of the ''Canu Taliesin'', a series of poems attributed to the 6th-century court poet of Rheged, Taliesin. Content Put in the mouth of a first-person eyewitness, the poem glorifies a victory by Urien, prince of Rheged, in which he led his warband in defence against a host of invaders at a site called Llech Gwen in Gwen Ystrad (Gwen valley). The heavy, prolonged fighting is said to have taken place since dawn at the entrance to a ford. Sir Ifor Williams suggests that the personal name Gwên may lie behind the forms ''Llech Gwen'' and possibly ''Gwen Ystrad'', but the site cannot be identified. Urien's champions are described as the "men of Catraeth" (line 1), a place often equated with Catterick (North Yorkshire), and the enemy forces as the "men of Britain" (''gwyr Prydein'', line 6), who have come in large ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Catraeth
The Battle of Catraeth was fought around AD 600 between a force raised by the Gododdin, a Brythonic people of the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" of Britain, and the Angles of Bernicia and Deira. It was evidently an assault by the Gododdin party on the Angle stronghold of Catraeth, perhaps Catterick, North Yorkshire. The Gododdin force was said to have consisted of warriors from all over the Hen Ogledd, and even some from as far afield as Gwynedd in North Wales and Pictland. The battle was disastrous for the Britons, who were nearly all killed. The slain warriors were commemorated in the important early poem ''Y Gododdin'', attributed to Aneirin. Battle In his ''Canu Aneirin'' Ifor Williams interpreted ''mynydawc mwynvawr'' in the text of ''Y Gododdin'' to refer to a person, Mynyddog Mwynfawr in modern Welsh. Mynyddog, in Williams' reading, was the king of the Gododdin, with his chief seat at Din Eidyn (modern Edinburgh). Around the year 600 Mynyddog gathered about 300 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |