|
Uraniborg Main Building
Uraniborg was an astronomical observatory and alchemy laboratory established and operated by the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe. It was the first custom-built observatory in modern Europe, and the last to be built without a telescope as its primary instrument. Uraniborg was built on Ven (Sweden), Ven, an island in the Øresund between Zealand (Denmark), Zealand and Scania, Sweden, which was part of Denmark at the time. It was expanded with the underground facility Stjerneborg () on an adjacent site. Brahe also innovated and invented many precision instruments which he used to carry out his studies in the observatory. Research was done in the fields of astronomy, alchemy, and meteorology by Tycho and his assistants. Brahe abandoned Uraniborg and Stjerneborg in 1597 after he fell out of favour with the Danish king, Christian IV of Denmark; Brahe left the country, and the institution was destroyed in 1601 after his death. Ven was later lost to Sweden, and the Rundetårn (Round ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ven (Sweden)
Ven (, older Swedish spelling ''Hven''), is a Swedish island in the Öresund strait laying between Scania, Sweden and Zealand, Denmark. A part of Landskrona Municipality, Skåne County, the island has an area of and 371 inhabitants as of 2020. During the 1930s, the population was at its peak, with approximately 1,300 inhabitants. There are four villages on the island: Bäckviken, Tuna By, Norreborg and Kyrkbacken. The island is best known as the location of the observatories Uraniborg and Stjerneborg, both of which were established and operated by the Danish Renaissance astronomer Tycho Brahe. Geography The island is a single plateau that rises up to 45 meters above sea level. This highest point is located in the middle of the island, where the remains of Tycho Brahe's castle and observatory are now located. The landscape is fertile thanks to the soil and the mild climate for Nordic conditions. The soil is moraine clay and therefore well suited for agriculture. It is one of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astronomy
Astronomy is a natural science that studies celestial objects and the phenomena that occur in the cosmos. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and their overall evolution. Objects of interest include planets, natural satellite, moons, stars, nebulae, galaxy, galaxies, meteoroids, asteroids, and comets. Relevant phenomena include supernova explosions, gamma ray bursts, quasars, blazars, pulsars, and cosmic microwave background radiation. More generally, astronomy studies everything that originates beyond atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere. Cosmology is a branch of astronomy that studies the universe as a whole. Astronomy is one of the oldest natural sciences. The early civilizations in recorded history made methodical observations of the night sky. These include the Egyptian astronomy, Egyptians, Babylonian astronomy, Babylonians, Greek astronomy, Greeks, Indian astronomy, Indians, Chinese astronomy, Chinese, Maya civilization, M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meridian (astronomy)
In astronomy, the meridian is the great circle passing through the celestial poles, as well as the zenith and nadir of an observer's location. Consequently, it contains also the north and south points on the horizon, and it is perpendicular to the celestial equator and horizon. Meridians, celestial and geographical, are determined by the pencil of planes passing through the Earth's rotation axis. For a location ''not'' on this axis, there is a unique meridian plane in this axial-pencil through that location. The intersection of this plane with Earth's surface defines two '' geographical meridians'' (either one east and one west of the prime meridian, or else the prime meridian itself and its anti-meridian), and the intersection of the plane with the celestial sphere is the celestial meridian for that location and time. There are several ways to divide the meridian into semicircles. In one approach, the observer's upper meridian extends from a celestial pole and passes t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altitude (astronomy)
The horizontal coordinate system is a celestial coordinate system that uses the observer's local horizon as the fundamental plane to define two angles of a spherical coordinate system: altitude and ''azimuth''. Therefore, the horizontal coordinate system is sometimes called the az/el system, the alt/az system, or the alt-azimuth system, among others. In an altazimuth mount of a telescope, the instrument's two axes follow altitude and azimuth. Definition This celestial coordinate system divides the sky into two hemispheres: The upper hemisphere, where objects are above the horizon and are visible, and the lower hemisphere, where objects are below the horizon and cannot be seen, since the Earth obstructs views of them. The great circle separating the hemispheres is called the ''celestial horizon'', which is defined as the great circle on the celestial sphere whose plane is normal to the local gravity vector (the vertical direction). In practice, the horizon can be define ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadrant (instrument)
A quadrant is an instrument used to measure angles up to 90°. Different versions of this instrument could be used to calculate various readings, such as longitude, latitude, and time of day. It was first proposed by Ptolemy as a better kind of astrolabe. Several different variations of the instrument were later produced by medieval Muslim astronomers. Mural quadrants were important astronomical instruments in 18th-century European observatories, establishing a use for positional astronomy. Etymology The term ''quadrant'', meaning one fourth, refers to the fact that early versions of the instrument were derived from astrolabes. The quadrant condensed the workings of the astrolabe into an area one fourth the size of the astrolabe face; it was essentially a quarter of an astrolabe. History During Rigvedic times in ancient India, quadrants called 'Tureeyam's were used to measure the extent of a great solar eclipse. The use of a Tureeyam for observing a solar eclipse by Ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
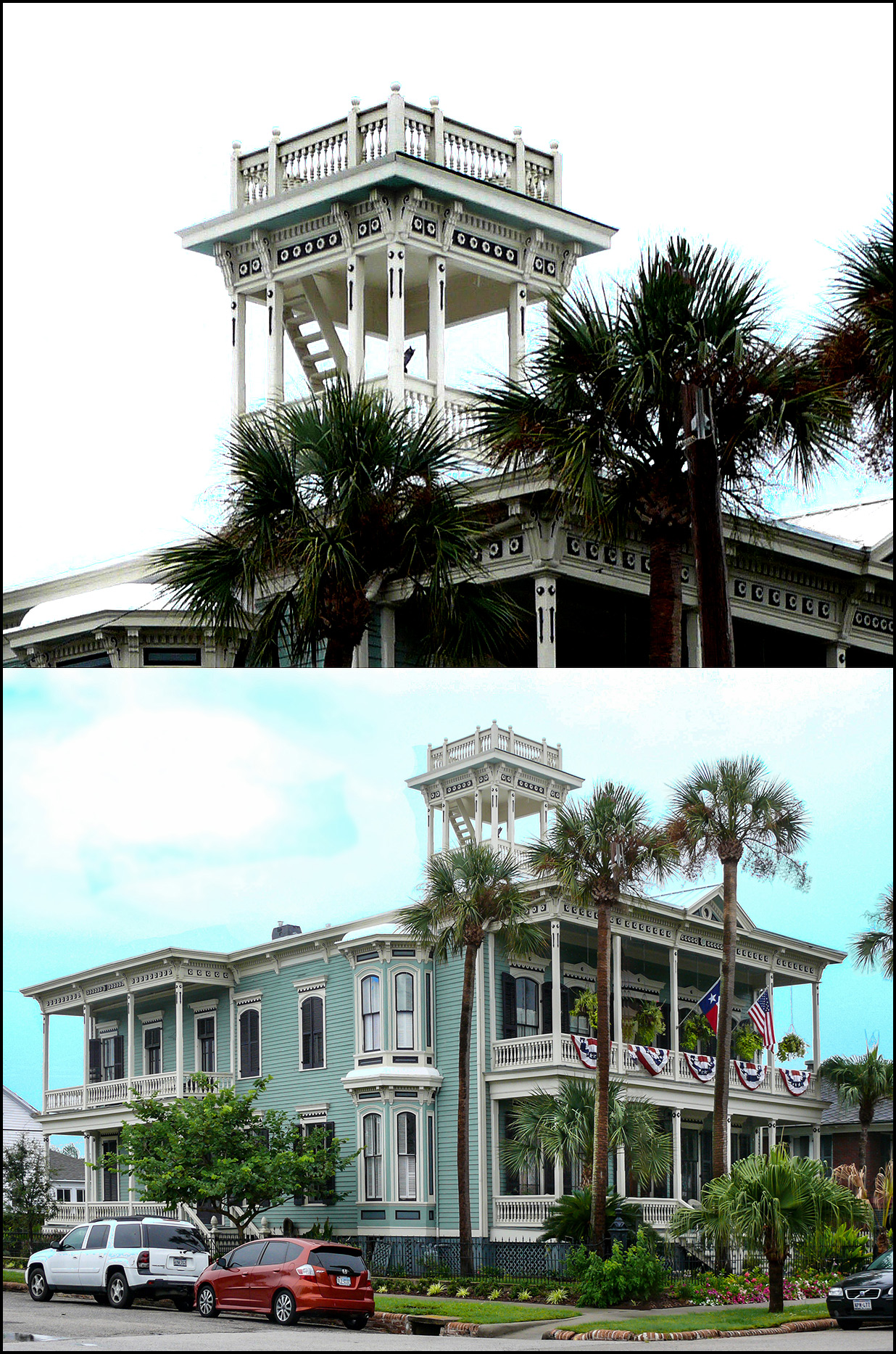
Widow's Walk
A widow's walk, also known as a widow's watch or roofwalk, is a railed rooftop platform often having an inner cupola/Turret (architecture), turret frequently found on 19th-century North American coastal houses. The name is said to come from the Wife, wives of Sailor, mariners, who would watch for their spouses' return, often in vain as the ocean took their lives, leaving the women widows. In other coastal communities, the platforms were called captain's walks, as they topped the homes of the more successful captains; supposedly, ship owners and captains would use them to search the horizon for ships due in port. However, there is little or no evidence that widow's walks were intended or regularly used to observe shipping. Widow's walks are in fact a standard decorative feature of Italianate architecture, which was very popular during the height of the Age of Sail in many North American coastal communities. The widow's walk is a variation of the Italianate cupola. The Italianate c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James VI And I
James VI and I (James Charles Stuart; 19 June 1566 – 27 March 1625) was King of Scotland as James VI from 24 July 1567 and King of England and King of Ireland, Ireland as James I from the union of the Scottish and English crowns on 24 March 1603 until Death and funeral of James VI and I, his death in 1625. Although he long tried to get both countries to adopt a closer political union, the kingdoms of Kingdom of Scotland, Scotland and Kingdom of England, England remained sovereign states, with their own parliaments, judiciaries, and laws, ruled by James in personal union. James was the son of Mary, Queen of Scots, and a great-great-grandson of Henry VII of England, Henry VII, King of England and Lord of Ireland, and thus a potential successor to all three thrones. He acceded to the Scottish throne at the age of thirteen months, after his mother was forced to abdicate in his favour. Although his mother was a Catholic, James was brought up as a Protestant. Four regents gove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johan Gregor Van Der Schardt
Johan (or Jan) Gregor van der Schardt (c. 1530/31 in Nijmegen, Netherlands – after 1581 in Denmark) was a sculptor from the Northern Renaissance. Life He toured Italy in the 1560s and among others worked in Bologna. From 1569 to 1576 he was in the service of Maximilian II, Holy Roman Emperor in Vienna, and subsequently took commissions in Nuremberg, where he specialised in painted terracotta busts. Such a bust includes a self-portrait of about 1573, one of the earliest such examples by a sculptor. From c. 1576 to c. 1580, he worked on the construction of the Uraniborg observatory of the Danish astronomer Tycho Brahe on the island of Hven. After 1576 he moved to the royal court of Denmark (with a return to Nuremberg in 1579) where he is presumed to have worked during the 1580s and died in the early 1590s, perhaps at Uraniborg on 30 November 1591. Unusually for a non-Italian artist, his work was praised by Giorgio Vasari. Gallery File:Merkur (Schardt, um 1570).jpg, Mercur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Van Emden
Hans van Steenwinckel the Elder (c. 1550 – 10 May 1601) was a Flemish-Danish architect and sculptor. He worked on a large number of the most important Danish buildings of his time, although the exact scope of his contributions in many cases remains uncertain and much have been demolished or redesigned later. The father of Hans van Steenwinckel the Younger and Lorenz van Steenwinckel, he also founded a dynasty of architects and sculptors in Denmark. Biography Hans van Steenwinckel was born in Antwerp c. 1550. The family fled to Emden, East Frisia, where his father, Lourens van Steenwinckel, became master builder. later city architect, and designed the Town Hall from 1567 onwards, later destroyed during World War II. Hans van Steenwinckel trained under his father, and it is known that he received payment for a design for the Town Hall's stairs and tower in 1574. In 1578 he travelled to Denmark, most likely as one of the master bricklayers which his countryman Anthonis van Obberg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flemish Renaissance
The Renaissance in the Low Countries was a cultural period in the Northern Renaissance that took place in around the 16th century in the Low Countries (corresponding to modern-day Belgium, the Netherlands and French Flanders). Culture in the Low Countries at the end of the 15th century was influenced by the Italian Renaissance, through trade via Bruges, which made Flanders wealthy. Its nobles commissioned artists who became known across Europe. In science, the anatomist Andreas Vesalius led the way; in cartography, Gerardus Mercator's map assisted explorers and navigators. In art, Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting went from the strange work of Hieronymus Bosch to the everyday life of Pieter Brueghel the Elder. In architecture, music and literature too, the culture of the Low Countries moved into the Renaissance style. Geopolitical situation and background In 1500, the Seventeen Provinces were in a personal union under the Burgundian Dukes, and with the Flemish cities as cen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone is a type of carbonate rock, carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material Lime (material), lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different Polymorphism (materials science), crystal forms of calcium carbonate . Limestone forms when these minerals Precipitation (chemistry), precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly Dolomite (rock), dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral Dolomite (mine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |