|
Uolchefit
Uolchefit is a place in Amhara Region, Ethiopia. Its time zone is Africa/Addis_Ababa (UTC). It is also written Wolchefit, Wolkefit or Wilkifit. The distance from Uolchefit to Ethiopia's capital Addis Ababa is approximately . It is both a village and a pass (2,835 m). It was an Italian stronghold on the road to Gondar from the north, during the Italian occupation of Ethiopia. Uolchefit closest urban location is Debarq (also spelled Dabareq and Debark, Amharic ደባርቅ) which is a town in northern Ethiopia, 90 kilometers north of Gondar on the highway between Gondar and Axum and in the Semien Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region The Amhara Region (), officially the Amhara National Regional State (), is a Regions of Ethiopia, regional state in northern Ethiopia and the homeland of the Amhara people, Amhara, Awi people, Awi, Xamir people, Xamir, Argobba people, Argobba, a .... It has a latitude and longitude of 13°08′N 37°54′E and an elevation of 2850 meters above sea le ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
East African Campaign (World War II)
The East African campaign (also known as the Abyssinian campaign) was fought in East Africa during the Second World War by Allies of World War II, mainly from the British Empire, against Kingdom of Italy, Italy and its colony of Italian East Africa, between June 1940 and November 1941. The British Middle East Command with troops from the United Kingdom, Union of South Africa, South Africa, British Raj, British India, Uganda Protectorate, British Kenya, Kenya, British Somaliland, Somaliland, British West Africa, West Africa, Northern Rhodesia, Northern and Southern Rhodesia, Anglo-Egyptian Sudan, Sudan and Nyasaland participated in the campaign. These were joined by the Allied of Belgian Congo, Ethiopian Empire, Imperial Ethiopian Arbegnoch (resistance forces) and a small unit of Free French Forces. Italian East Africa was defended by the (Italian East African Armed Forces Command), with units from the (Royal Army), (Royal Air Force) and (Royal Navy). The Italian forces inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amhara Region
The Amhara Region (), officially the Amhara National Regional State (), is a Regions of Ethiopia, regional state in northern Ethiopia and the homeland of the Amhara people, Amhara, Awi people, Awi, Xamir people, Xamir, Argobba people, Argobba, and Qemant people, Qemant people. Its capital is Bahir Dar which is the seat of the Government of Amhara Region, Regional Government of Amhara. Amhara is the site of the largest inland body of water in Ethiopia, Lake Tana (which is the source of the Blue Nile), and Semien Mountains National Park (which includes Ras Dashan, the highest point in Ethiopia). Amhara is bordered by Sudan to the west and northwest and by other the regions of Ethiopia: Tigray Region, Tigray to the north, Afar Region, Afar to the east, Benishangul-Gumuz Region, Benishangul-Gumuz to the west and southwest, and Oromia to the south. Towns and cities in Amhara include: Bahir Dar, Dessie, Gondar, Gonder, Debre Birhan, Debre Tabor, Kombolcha, Weldiya, Debre Markos, Soqota, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
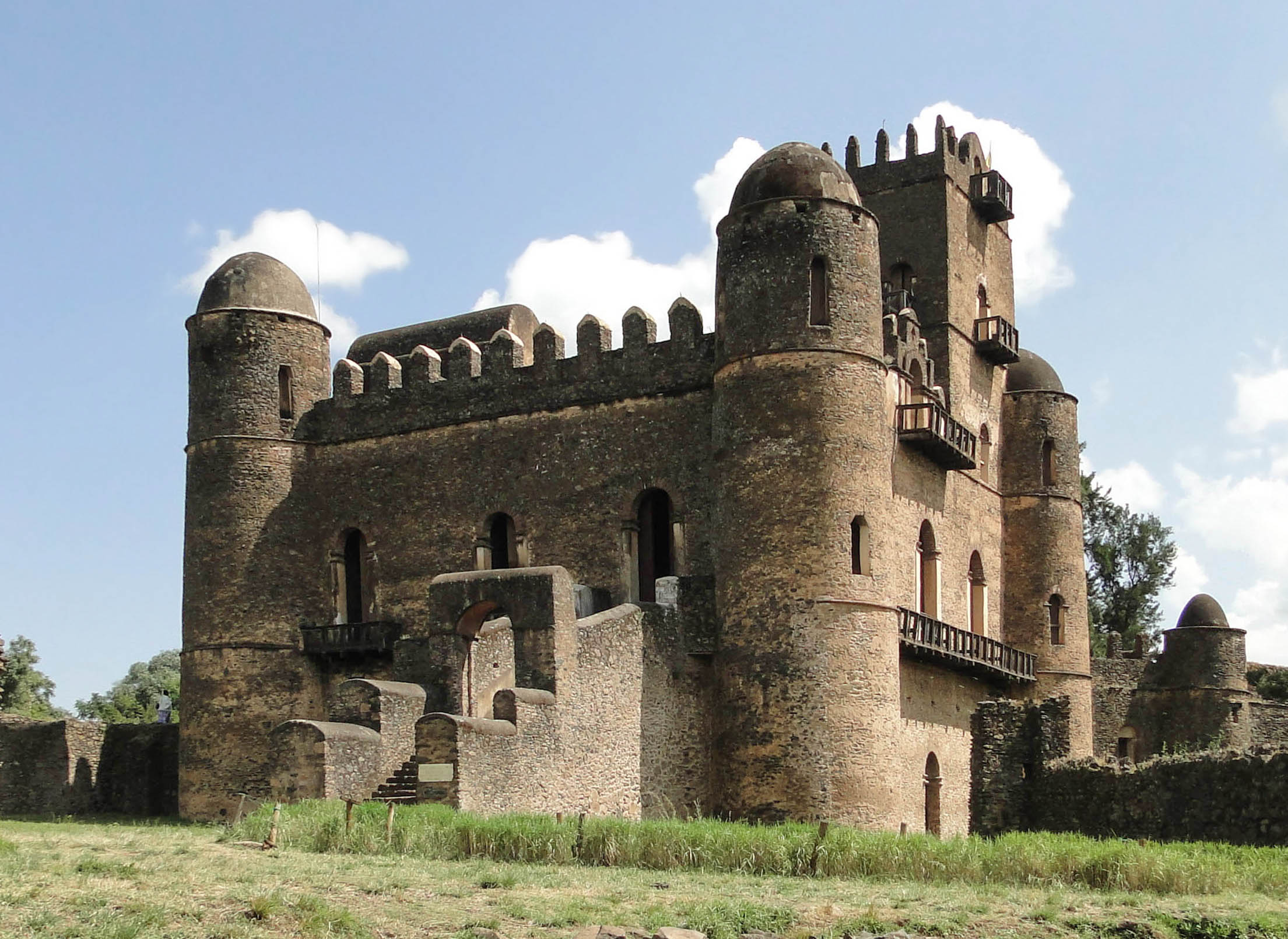
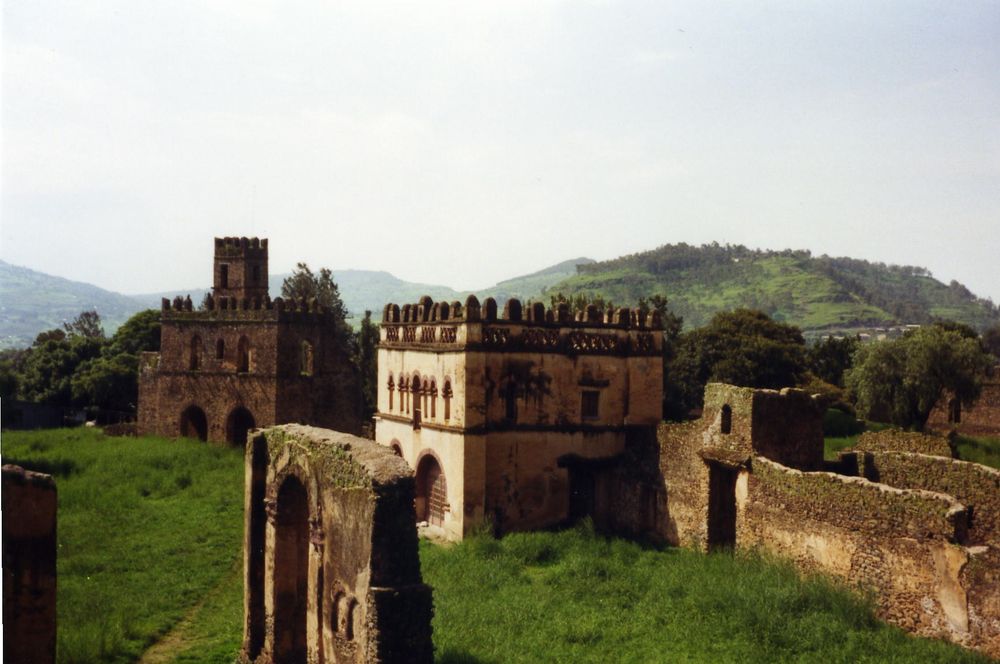
GONDAR 01
Gondar, also spelled Gonder (Amharic language, Amharic: ጎንደር, ''Gonder'' or ''Gondär''; formerly , ''Gʷandar'' or ''Gʷender''), is a city and Districts of Ethiopia, woreda in Ethiopia. Located in the North Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Gondar is north of Lake Tana on the Lesser Angereb River and southwest of the Simien Mountains. , Gondar has an estimated population of 443,156. Gondar previously served as the capital of both the Ethiopian Empire and the subsequent Begemder, Begemder Province. The city holds the remains of several royal castles, including those in the Fasil Ghebbi UNESCO World Heritage Site for which Gondar has been called the "Camelot of Africa". History Origins The term Gondar was first mentioned during the reign of Amda Seyon I as the name of a regiment of soldiers stationed (likely in Wegera (woreda), Wegera) to guard nearby trade routes and control a restive population. In 1636, Emperor Fasilides of Ethiopia, Fasilides selected Gondar a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GONDAR 02
Gondar, also spelled Gonder (Amharic: ጎንደር, ''Gonder'' or ''Gondär''; formerly , ''Gʷandar'' or ''Gʷender''), is a city and woreda in Ethiopia. Located in the North Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Gondar is north of Lake Tana on the Lesser Angereb River and southwest of the Simien Mountains. , Gondar has an estimated population of 443,156. Gondar previously served as the capital of both the Ethiopian Empire and the subsequent Begemder Province. The city holds the remains of several royal castles, including those in the Fasil Ghebbi UNESCO World Heritage Site for which Gondar has been called the "Camelot of Africa". History Origins The term Gondar was first mentioned during the reign of Amda Seyon I as the name of a regiment of soldiers stationed (likely in Wegera) to guard nearby trade routes and control a restive population. In 1636, Emperor Fasilides selected Gondar as his ''katama'' (royal camp). Situated about 35 km due north of Lake Tana in the midst of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KAR Soldiers Collecting Arms At Wolchefit Pass
Kar or KAR may refer to: * .kar, a file format for karaoke files * Kar, Iran Qar (, also Romanized as Qār; also known as Kār and Qāv) is a village in Howmeh Rural District, in the Central District of Sanandaj County, Kurdistan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 805, in 190 families. The village is ..., in Kurdistan Province * ''Kar'' (beetle), a genus of beetles * Car (Greek myth) * Kar (novel), ''Kar'' (novel), 2002, by Orhan Pamuk * Kar (political group), a former faction in Afghanistan * Kar (Turkish music), a genre in Ottoman classical music * Kar (suffix), surname suffix in India * Kainic acid receptor, ion channels that respond to neurotransmitters * Karair, a Finnish airline, by ICAO code * Killer activation receptor * King's African Rifles, British regiment, 1902-1960s * Keilschrifttexte aus Assur religiösen Inhalts, the title of a two-volume German work often abbreviated as KAR * ISO 639-5 code for Karenic languages * Kar Nataka or Karnataka, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Addis Ababa
Addis Ababa (; ,) is the capital city of Ethiopia, as well as the regional state of Oromia. With an estimated population of 2,739,551 inhabitants as of the 2007 census, it is the largest city in the country and the List of cities in Africa by population, eleventh-largest in Africa. Addis Ababa is a highly developed and important cultural, artistic, financial and administrative center of Ethiopia. It is widely known as one of Africa's major capitals. The founding history of Addis Ababa dates back to the late 19th century by Menelik II, Negus of Shewa, in 1886 after finding Mount Entoto unpleasant two years prior. At the time, the city was a resort town; its large mineral spring abundance attracted nobilities of the empire and led them to establish permanent settlement. It also attracted many members of the working classes – including artisans and merchants – and foreign visitors. Menelik II then formed his Menelik Palace, imperial palace in 1887. Addis Ababa became the em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
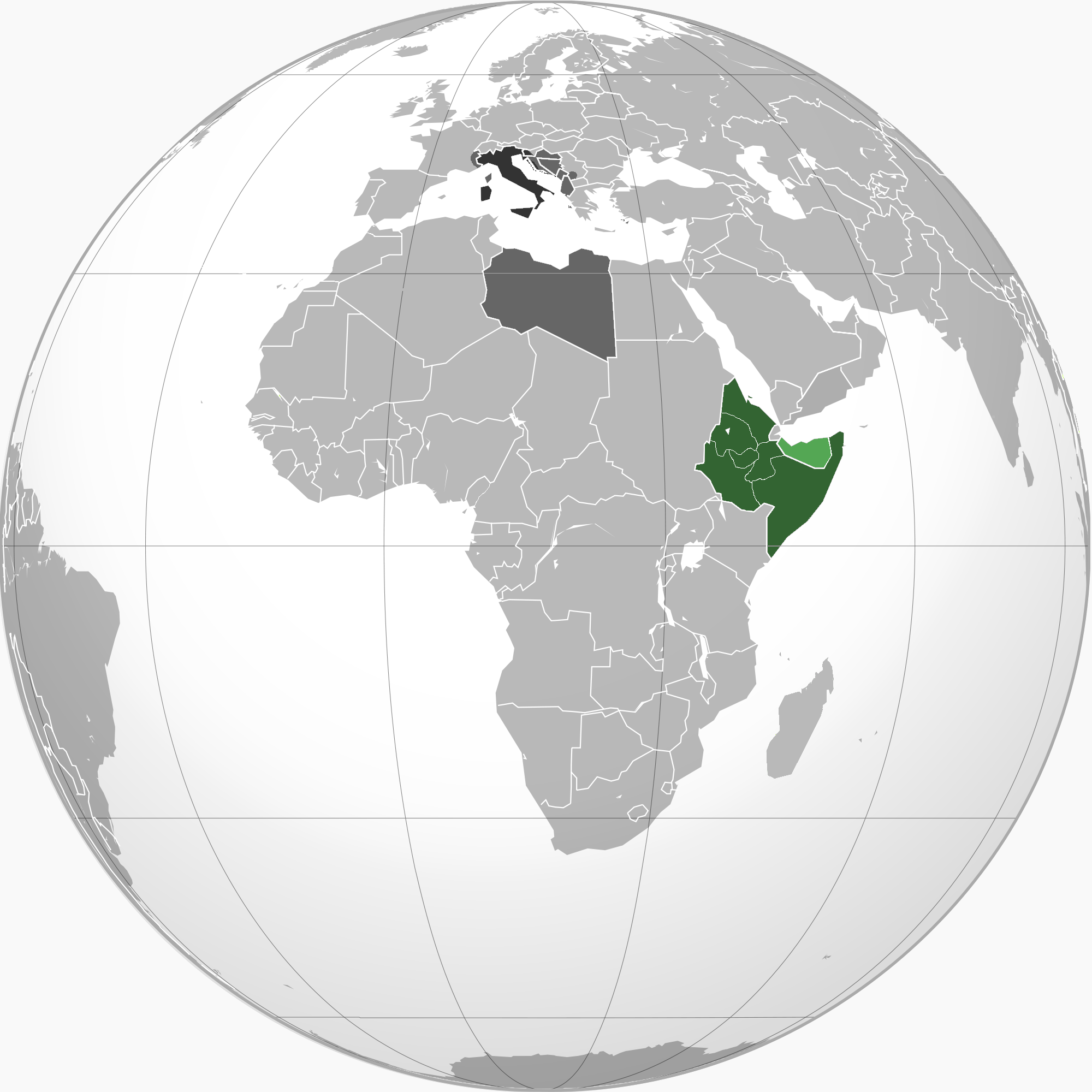
Italian East Africa
Italian East Africa (, A.O.I.) was a short-lived colonial possession of Fascist Italy from 1936 to 1941 in the Horn of Africa. It was established following the Second Italo-Ethiopian War, which led to the military occupation of the Ethiopian Empire (Abyssinia). It encompassed Italian Somaliland, Italian Eritrea and the acquired Ethiopian territories, all governed by a single administrative unit, the Governo Generale dell'Africa Orientale Italiana. Its establishment contributed to the outbreak of the Second World War by exposing the weaknesses of the League of Nations. Italian East Africa was divided into six governorates. Eritrea and Somalia, Italian possessions since the 1880s, were enlarged with captured Ethiopian territory and became the Eritrea and Somalia Governorates. The remainder of the occupied Ethiopian territories comprised the Harar, Galla-Sidamo, Amhara, and Scioa Governorates. At its largest extent, Italian East Africa occupied territories in British Som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gondar
Gondar, also spelled Gonder (Amharic: ጎንደር, ''Gonder'' or ''Gondär''; formerly , ''Gʷandar'' or ''Gʷender''), is a city and woreda in Ethiopia. Located in the North Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region, Gondar is north of Lake Tana on the Lesser Angereb River and southwest of the Simien Mountains. , Gondar has an estimated population of 443,156. Gondar previously served as the capital of both the Ethiopian Empire and the subsequent Begemder Province. The city holds the remains of several royal castles, including those in the Fasil Ghebbi UNESCO World Heritage Site for which Gondar has been called the " Camelot of Africa". History Origins The term Gondar was first mentioned during the reign of Amda Seyon I as the name of a regiment of soldiers stationed (likely in Wegera) to guard nearby trade routes and control a restive population. In 1636, Emperor Fasilides selected Gondar as his '' katama'' (royal camp). Situated about 35 km due north of Lake Tana in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Debarq
Debarq (Amharic: ደባርቅ) also spelled Dabareq and Debark, is a town in northern Ethiopia, 90 kilometers north-east of Gondar on the highway between Gondar and Axum, and is in the Semien Gondar Zone of the Amhara Region. It has a latitude and longitude of and an elevation of 2850 meters above sea level. Debarq is located on the western foothills of the Semien mountains, and nowadays serves as a starting point for hiking tours to the Semien Mountains National Park. History 17th century The earliest sourced mention of Debarq appears to date back to the late 17th century, serving as a stopover for replenishment to journeys and military campaigns that emperor Iyasu I undertook from Gondar to the north. 18th century In early 1770, explorer James Bruce was one of the earliest foreign sources to mention Debarq. Bruce noted in his journal, the contrasting and temperate climate as he passed through a market in Debarq. 19th century In 1814, Debarq appeared on a map by trave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early Middle Ages, medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the English Navy of the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the early 18th century until the World War II, Second World War, it was the world's most powerful navy. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superior ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HMSO
The Office of Public Sector Information (OPSI) is the body responsible for the operation of His Majesty's Stationery Office (HMSO) and of other public information services of the United Kingdom. The OPSI is part of the National Archives of the United Kingdom and is responsible for Crown copyright. The OPSI announced on 21 June 2006 that it was merging with the National Archives. The merger took place in October 2006. The OPSI continues to discharge its roles and responsibilities from within the structure of the National Archives. Controller of HMSO and Director of OPSI The Controller of HMSO is also the Director of OPSI. HMSO continues to operate from within the expanded remit of OPSI. The Controller of HMSO also holds the offices of Kings's Printer of Acts of Parliament, King's Printer for Scotland and Government Printer for Northern Ireland. By virtue of holding these offices OPSI publishes, through HMSO, the ''London Gazette'', '' Edinburgh Gazette'', '' Belfast Gazette'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |