|
Unstructured Data
Unstructured data (or unstructured information) is information that either does not have a pre-defined data model or is not organized in a pre-defined manner. Unstructured information is typically plain text, text-heavy, but may contain data such as dates, numbers, and facts as well. This results in irregularities and ambiguities that make it difficult to understand using traditional programs as compared to data stored in fielded form in databases or annotation, annotated (Tag (metadata), semantically tagged) in documents. In 1998, Merrill Lynch said "unstructured data comprises the vast majority of data found in an organization, some estimates run as high as 80%." It is unclear what the source of this number is, but nonetheless it is accepted by some. Other sources have reported similar or higher percentages of unstructured data. , International Data Corporation, IDC and Dell EMC project that data will grow to 40 zettabytes by 2020, resulting in a 50-fold growth from the beginnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Photograph Of Departmental Records Branch Military Records Center In Alexandria, Virginia - NARA - 23855327
A photograph (also known as a photo, or more generically referred to as an ''image'' or ''picture'') is an image created by light falling on a photosensitive surface, usually photographic film or an electronic image sensor. The process and practice of creating such images is called photography. Most photographs are now created using a smartphone or camera, which uses a lens to focus the scene's visible wavelengths of light into a reproduction of what the human eye would perceive. Etymology The word ''photograph'' was coined in 1839 by Sir John Herschel and is based on the Greek φῶς (''phos''), meaning "light", and γραφή (''graphê''), meaning "drawing, writing", together meaning "drawing with light". History The first permanent photograph, a contact-exposed copy of an engraving, was made in 1822 using the bitumen-based "heliography" process developed by Nicéphore Niépce. The first photographs of a real-world scene, made using a camera obscura, followed a few year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
SAS (software)
SAS (previously "Statistical Analysis System") is a statistical software suite developed by SAS Institute for data management, advanced analytics, multivariate analysis, business intelligence, and predictive analytics. SAS was developed at North Carolina State University from 1966 until 1976, when SAS Institute was incorporated. SAS was further developed in the 1980s and 1990s with the addition of new statistical procedures, additional components and the introduction of JMP. A point-and-click interface was added in version 9 in 2004. A social media analytics product was added in 2010. SAS Viya, a suite of analytics and artificial intelligence software, was introduced in 2016. Technical overview and terminology SAS is a software suite that can mine, alter, manage and retrieve data from a variety of sources and perform statistical analysis on it. SAS provides a graphical point-and-click user interface for non-technical users and more through the SAS language. SAS programs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Natural Language Processing
Natural language processing (NLP) is a subfield of computer science and especially artificial intelligence. It is primarily concerned with providing computers with the ability to process data encoded in natural language and is thus closely related to information retrieval, knowledge representation and computational linguistics, a subfield of linguistics. Major tasks in natural language processing are speech recognition, text classification, natural-language understanding, natural language understanding, and natural language generation. History Natural language processing has its roots in the 1950s. Already in 1950, Alan Turing published an article titled "Computing Machinery and Intelligence" which proposed what is now called the Turing test as a criterion of intelligence, though at the time that was not articulated as a problem separate from artificial intelligence. The proposed test includes a task that involves the automated interpretation and generation of natural language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Data Mining
Data mining is the process of extracting and finding patterns in massive data sets involving methods at the intersection of machine learning, statistics, and database systems. Data mining is an interdisciplinary subfield of computer science and statistics with an overall goal of extracting information (with intelligent methods) from a data set and transforming the information into a comprehensible structure for further use. Data mining is the analysis step of the " knowledge discovery in databases" process, or KDD. Aside from the raw analysis step, it also involves database and data management aspects, data pre-processing, model and inference considerations, interestingness metrics, complexity considerations, post-processing of discovered structures, visualization, and online updating. The term "data mining" is a misnomer because the goal is the extraction of patterns and knowledge from large amounts of data, not the extraction (''mining'') of data itself. It also is a buzzwo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Semi-structured Data
Semi-structured data is a form of structured data that does not obey the tabular structure of data models associated with relational databases or other forms of data tables, but nonetheless contains tags or other markers to separate semantic elements and enforce hierarchies of records and fields within the data. Therefore, it is also known as self-describing structure. In semi-structured data, the entities belonging to the same class may have different attributes even though they are grouped together, and the attributes' order is not important. Semi-structured data are increasingly occurring since the advent of the Internet where full-text documents and databases are not the only forms of data anymore, and different applications need a medium for exchanging information. In object-oriented databases, one often finds semi-structured data. Types XML XML, other markup languages, email, and EDI are all forms of semi-structured data. OEM (Object Exchange Model) was created prio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such as biological organisms, minerals and chemicals. Abstract structures include data structures in computer science and musical form. Types of structure include a hierarchy (a cascade of one-to-many relationships), a network featuring many-to-many links, or a lattice featuring connections between components that are neighbors in space. Load-bearing Buildings, aircraft, skeletons, anthills, beaver dams, bridges and salt domes are all examples of load-bearing structures. The results of construction are divided into buildings and non-building structures, and make up the infrastructure of a human society. Built structures are broadly divided by their varying design approaches and standards, into categories including building struct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Root Cause Analysis
In science and engineering, root cause analysis (RCA) is a method of problem solving used for identifying the root causes of faults or problems. It is widely used in IT operations, manufacturing, telecommunications, industrial process control, accident analysis (e.g., in aviation, rail transport, or nuclear plants), medical diagnosis, the healthcare industry (e.g., for epidemiology), etc. Root cause analysis is a form of inductive inference (first create a theory, or ''root'', based on empirical evidence, or ''causes'') and deductive inference (test the theory, i.e., the underlying causal mechanisms, with empirical data). RCA can be decomposed into four steps: # Identify and describe the problem clearly # Establish a timeline from the normal situation until the problem occurrence # Distinguish between the root cause and other causal factors (e.g., via event correlation) # Establish a causal graph between the root cause and the problem. RCA generally serves as input to a r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics encompasses a variety of Statistics, statistical techniques from data mining, Predictive modelling, predictive modeling, and machine learning that analyze current and historical facts to make predictions about future or otherwise unknown events. In business, predictive models exploit Pattern detection, patterns found in historical and transactional data to identify risks and opportunities. Models capture relationships among many factors to allow assessment of risk or potential associated with a particular set of conditions, guiding decision-making for candidate transactions. The defining functional effect of these technical approaches is that predictive analytics provides a predictive score (probability) for each individual (customer, employee, healthcare patient, product SKU, vehicle, component, machine, or other organizational unit) in order to determine, inform, or influence organizational processes that pertain across large numbers of individuals, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
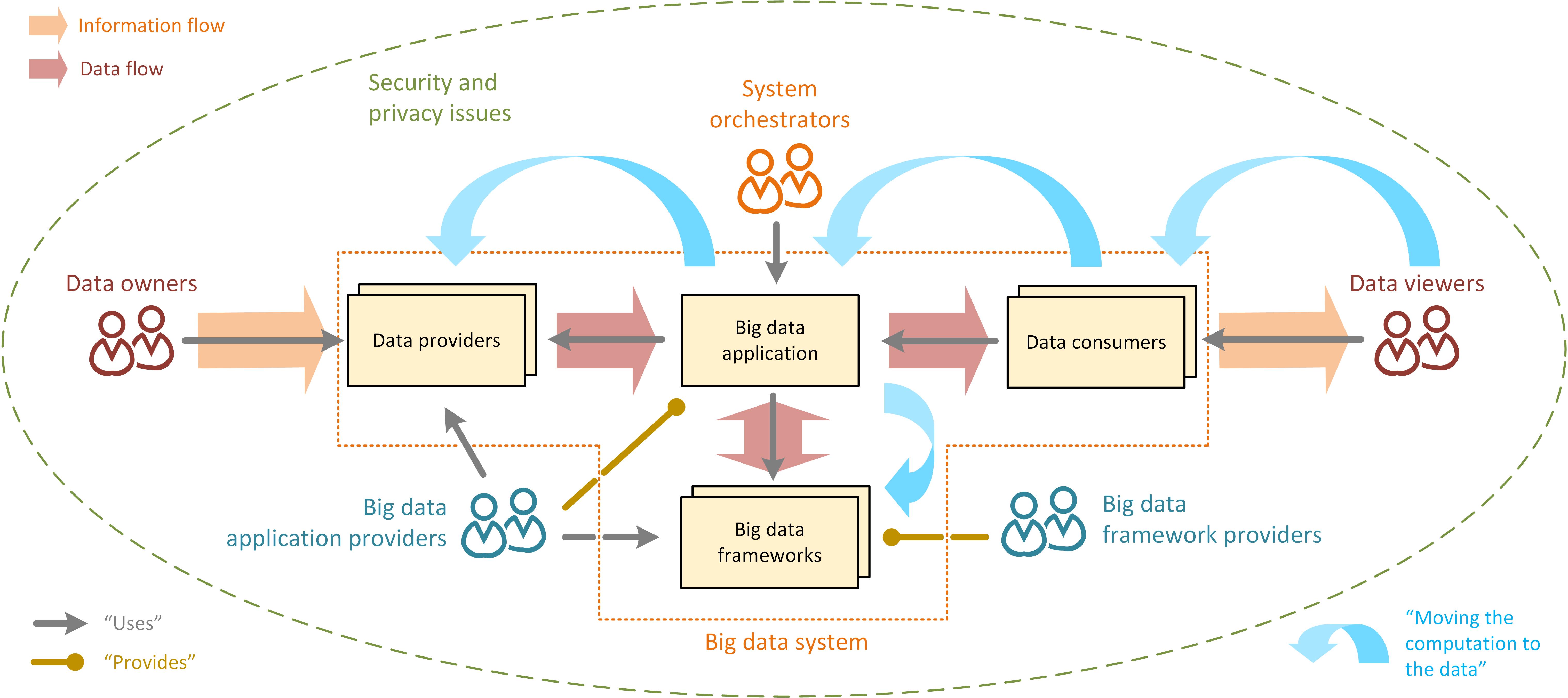 |
Big Data
Big data primarily refers to data sets that are too large or complex to be dealt with by traditional data processing, data-processing application software, software. Data with many entries (rows) offer greater statistical power, while data with higher complexity (more attributes or columns) may lead to a higher false discovery rate. Big data analysis challenges include Automatic identification and data capture, capturing data, Computer data storage, data storage, data analysis, search, Data sharing, sharing, Data transmission, transfer, Data visualization, visualization, Query language, querying, updating, information privacy, and data source. Big data was originally associated with three key concepts: ''volume'', ''variety'', and ''velocity''. The analysis of big data presents challenges in sampling, and thus previously allowing for only observations and sampling. Thus a fourth concept, ''veracity,'' refers to the quality or insightfulness of the data. Without sufficient investm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Voice Of The Customer
In marketing and quality management, the voice of the customer (VOC) summarizes customers' expectations, preferences and aversions. A widely used form of customer's voice market research produces a detailed set of customer wants and needs, organized into a hierarchical structure, and then prioritized in terms of relative importance and satisfaction with current alternatives. VOC studies typically consist of both qualitative and quantitative research steps and are generally conducted at the start of any new product, process, or service design initiative in order to better understand the customer's wants and needs, and as the key input for new product definition, quality function deployment (QFD), and the setting of detailed design specifications. Data gathering Much has been written about this process, and there are many possible ways to gather the information – focus groups, individual interviews, contextual inquiry, ethnographic techniques, conjoint analysis, etc. All inv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Sentiment Analysis
Sentiment analysis (also known as opinion mining or emotion AI) is the use of natural language processing, text analysis, computational linguistics, and biometrics to systematically identify, extract, quantify, and study affective states and subjective information. Sentiment analysis is widely applied to voice of the customer materials such as reviews and survey responses, online and social media, and healthcare materials for applications that range from marketing to customer service to clinical medicine. With the rise of deep language models, such as RoBERTa, also more difficult data domains can be analyzed, e.g., news texts where authors typically express their opinion/sentiment less explicitly.Hamborg, Felix; Donnay, Karsten (2021)"NewsMTSC: A Dataset for (Multi-)Target-dependent Sentiment Classification in Political News Articles" "Proceedings of the 16th Conference of the European Chapter of the Association for Computational Linguistics: Main Volume" Simple cases * "Coron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |