|
Unpromising Villages
Unpromising, or literally perspectiveless villages () was a term used by the Soviet Union, Soviet government in 1960s–80s referring to the small rural settlements, which were considered to be not suitable for a Economy of the Soviet Union, planned economy. The policy of unpromising villages' liquidation included the resettlement of the residents to larger rural settlements with concentration of the bulk of the rural population, production and social facilities. The most negative social impact of this policy was the significant damage done to rural infrastructure. Planning For the first time, the concept of "unpromising villages" was used in recommendations for the design of rural settlements. The recommendations were drawn up in 1960 by the Russian Academy of Architecture and Construction Sciences, Academy of Civil Engineering and Architecture of the USSR in accordance with the decisions of the Plenum of the Central Committee of the CPSU of December 1959 on the development o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet Union, it dissolved in 1991. During its existence, it was the list of countries and dependencies by area, largest country by area, extending across Time in Russia, eleven time zones and sharing Geography of the Soviet Union#Borders and neighbors, borders with twelve countries, and the List of countries and dependencies by population, third-most populous country. An overall successor to the Russian Empire, it was nominally organized as a federal union of Republics of the Soviet Union, national republics, the largest and most populous of which was the Russian SFSR. In practice, Government of the Soviet Union, its government and Economy of the Soviet Union, economy were Soviet-type economic planning, highly centralized. As a one-party state go ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fyodor Abramov
Fyodor Aleksandrovich Abramov () (29 February 192014 May 1983) was a Russian novelist and literary critic. His work focused on the challenging lives of the Russian peasant class, often depicting their struggles and hardships. Although his writing was critically acclaimed, he frequently faced reprimands for deviating from Soviet policy on writing. Biography Abramov was from a peasant background. He studied at Leningrad State University, but interrupted his studies to serve as a soldier in World War II. In 1951, he finished his schooling at the university, then remained a teacher until 1960. After leaving teaching in 1960, he became a full-time writer. His 1954 essay, "People in the Kolkhoz Village in Postwar Prose", which critiqued the glorified portrayal of life in Communist Soviet Villages, was denounced by the Writers' Union and the Central Committee. In a later essay, Abramov argued for the repeal of the law denying peasants internal passports and recommended granting them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Era Of Stagnation
The "Era of Stagnation" (, or ) is a term coined by Mikhail Gorbachev in order to describe the negative way in which he viewed the economic, political, and social policies of the Soviet Union that began during the rule of Leonid Brezhnev (1964–1982) and continued under Yuri Andropov (1982–1984) and Konstantin Chernenko (1984–1985). It is sometimes called the "Brezhnevian Stagnation" in English. Terminology During the period of Brezhnev's leadership, the term "Era of Stagnation" was not used. Instead in Soviet ideology the term "period of developed socialism" () was used for the period that started in 1967. This Soviet concept was officially declared at the 24th Congress of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union in 1971. It stemmed from the failure of Khrushchev's promise in 1961 of reaching communism in 20 years and was a replacement for the concept "period of the extensive construction of communism" (). It was in the 1980s that the Soviet leader Mikhail Gorbache ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Phraseology
Soviet phraseology, or Sovietisms, i.e. the neologisms and cliches in the Russian language of the epoch of the Soviet Union, has a number of distinct traits that reflect the Soviet way of life and Soviet culture and politics. Most of these distinctions are ultimately traced (directly or indirectly, as a cause-effect chain) to the utopic goal of creating a new society, the ways of the implementation of this goal and what was actually implemented. The topic of this article is not limited to the Russian language, since this phraseology also permeated regional languages in the Soviet Union. Nevertheless, Russian was the official language of inter-nationality communication in the Soviet Union, and was declared official language of the state in 1990, therefore it was the major source of Soviet phraseology. Taxonomy The following main types of Sovietism coinage may be recognized: * Semantic shift: for example, "to throw out" acquired the colloquial meaning of "to put goods for sale". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
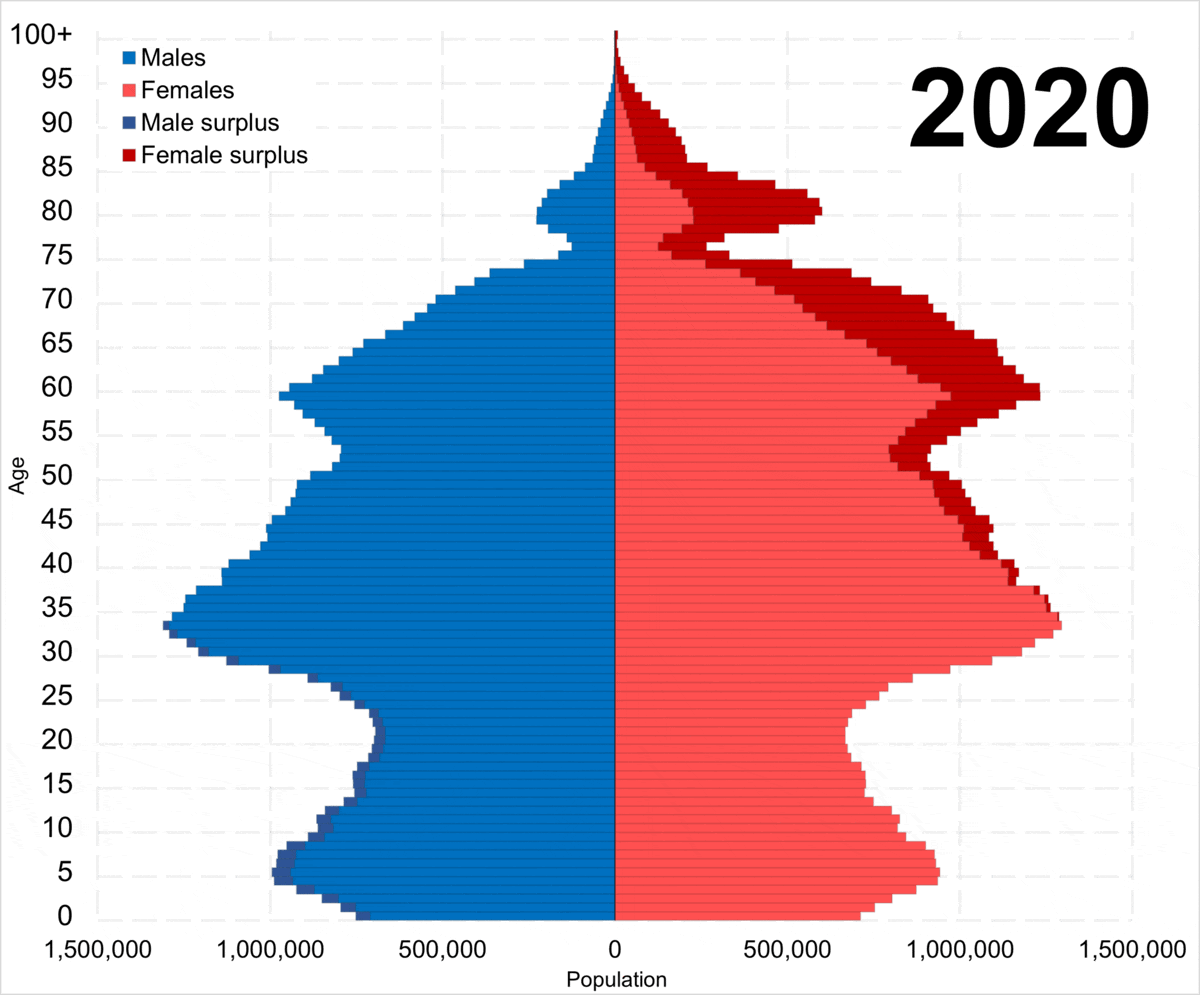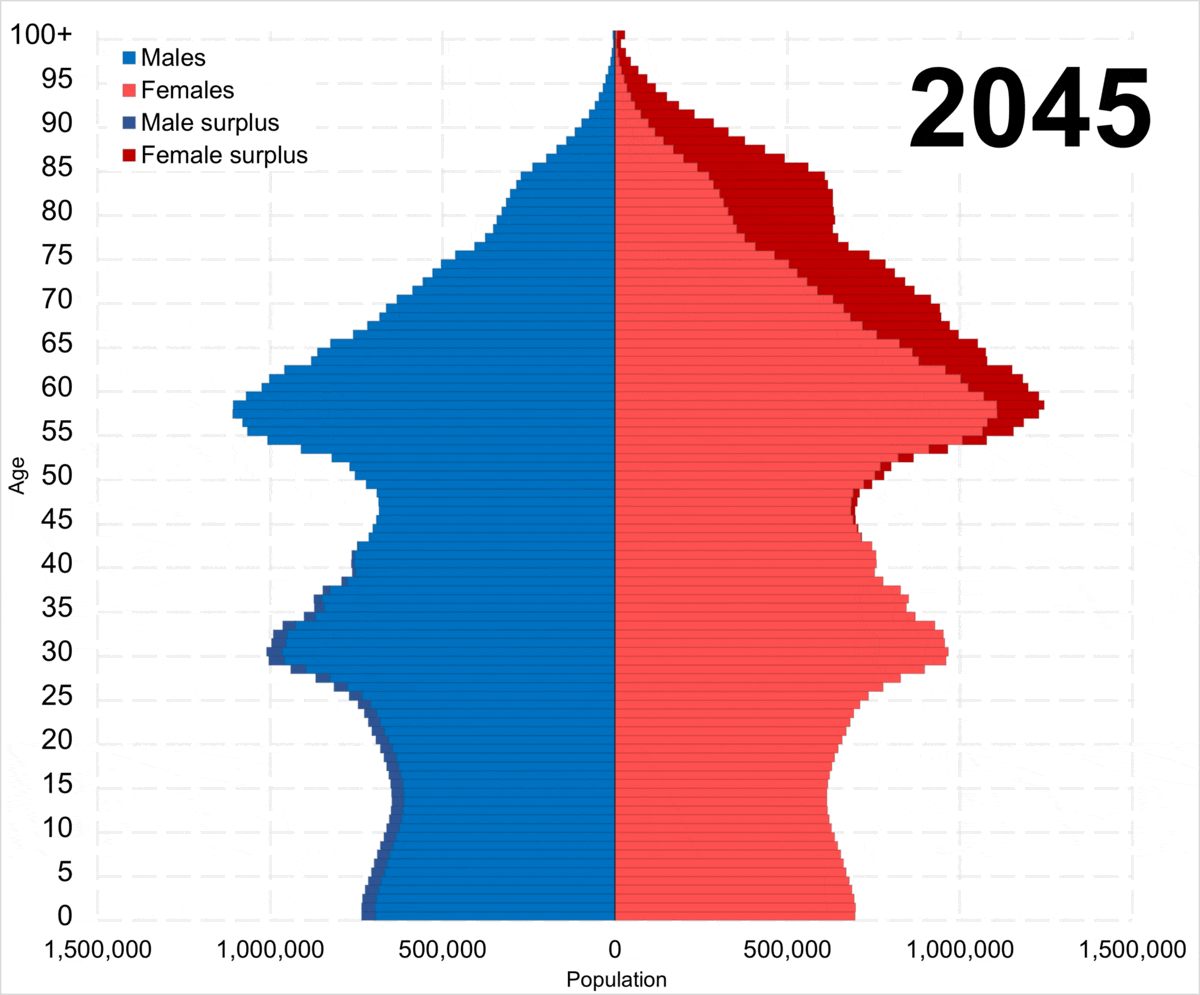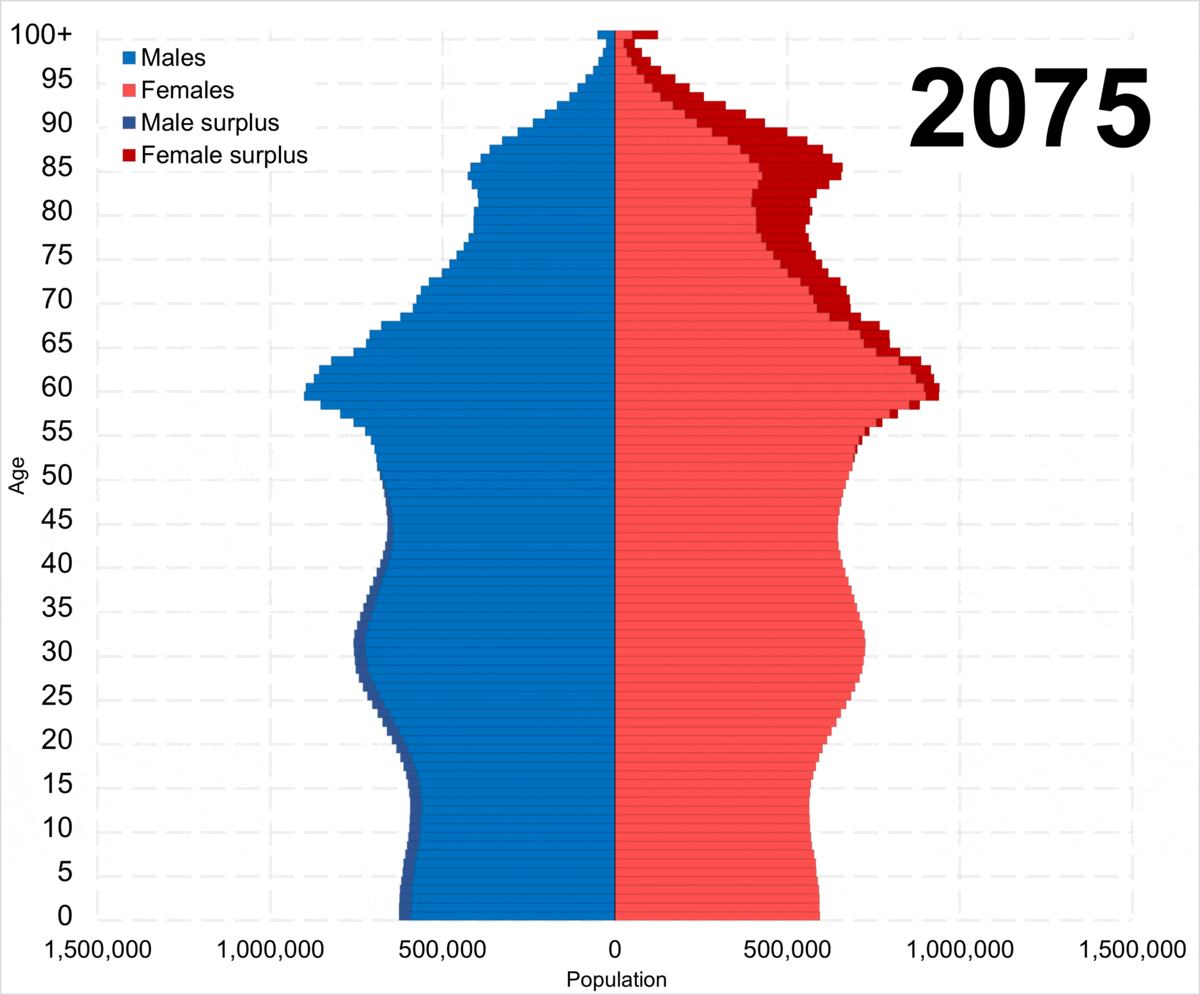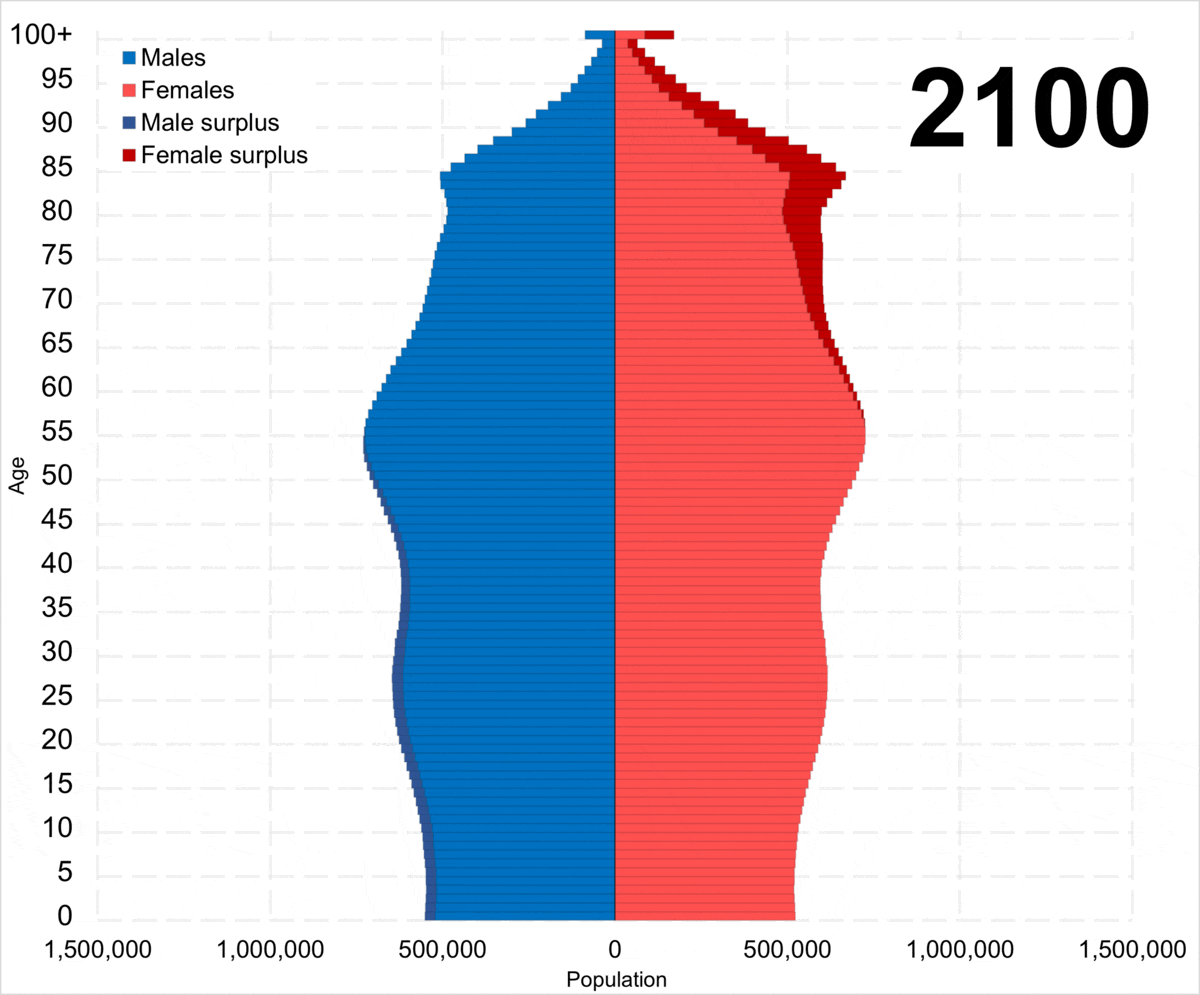
Demographics Of Russia
Russia has an estimated population of 146.0 million as of 1 January 2025, down from 147.2 million recorded in the 2021 census. It is the most populous country in Europe, and the ninth-most populous country in the world. Russia has a population density of , with its overall life expectancy being 73 years (68 years for males and 79 years for females) . The total fertility rate across Russia was estimated to be 1.41 children born per woman , which is in line with the European average. It has one of the oldest populations in the world, with a median age of 41.9 years. By the end of 2024, the natural decline of the Russian population amounted to 596.2 thousand people, according to published data from Rosstat. Compared to the end of 2023, the indicator increased by 20.4% (from 495.3 thousand). From 1992 to 2012, and again since 2016, Russia's death rate has exceeded its birth rate, which has been called a demographic crisis by analysts. In 2009, Russia recorded annual populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographics Of The Soviet Union
Demographic features of the population of the Soviet Union include vital statistics, ethnicity, religious affiliations, education level, health of the populace, and other aspects of the population. During its existence from 1922 until 1991, the Soviet Union had one of the largest populations in the world. When the last census was taken in 1989, the USSR had the third largest in the world with over 285 million citizens, behind China and India. The former nation was a federal union of national republics, home to hundreds of different ethnicities. By the time the Soviet Union dissolved, Russians were the largest ethnic group by making up nearly 51% of the country. The remaining 49% of Soviet citizens identified with a variety of groups, including Ukrainians, Belarusians, Uzbeks, Kazakhs, Georgians, Jews, etc. History Revolution and Civil war, 1917–1923 During the Russian Revolution and Civil War period, Russia lost former territories of the Russian Empire w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urban Planning In Russia
Urban planning in Russia is the practice of urban planning according to the legislation and is influenced by various factors such as historical legacy, traditions, geography and climate and involves various actors including the federal as well as regional and local governments. The direct translation to Russian is ''Gradoplanirovaniye'' () but also common is the term ''Gradostraitelstvo'' () which literally translated as urban construction. History During the Kievan Rus' period, settlements which were located in strategic places, such as confluence of rivers or sitting on important routes grew in importance and transformed into towns. Concurrently they became gravity center of political, economic and military power. From the 10th century markets and handicraft trade developed, a process which contributed to the growth of towns and around them grew settlements which were suburbs of the core town, gravitated towards them and were called (''Posad''). In some cases, cities of Kievan R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture In The Soviet Union
Agriculture in the Soviet Union was mostly collectivized, with some limited cultivation of private plots. It is often viewed as one of the more inefficient sectors of the economy of the Soviet Union. A number of food taxes ( prodrazverstka, prodnalog, and others) were introduced in the early Soviet period despite the Decree on Land that immediately followed the October Revolution. The forced collectivization and class war against (vaguely defined) " kulaks" under Stalinism greatly disrupted farm output in the 1920s and 1930s, contributing to the Soviet famine of 1932–33 (most especially the Holodomor in Ukraine). A system of state and collective farms, known as sovkhozes and kolkhozes, respectively, placed the rural population in a system intended to be unprecedentedly productive and fair but which turned out to be chronically inefficient and lacking in fairness. Under the administrations of Nikita Khrushchev, Leonid Brezhnev, and Mikhail Gorbachev, many reforms (su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demographic Crisis Of Russia
The demographic crisis of Russia is the aging and decline of the Russian population caused by demographic transition. Although most high-income and middle-income countries experience demographic transition, Russia does differ in that it has a high mortality rate and relatively low life expectancy. From 1992 to 2008 and again since 2020, Russia has experienced net population loss; the natural population decline has no longer been offset by a positive migration balance. The demographic decline of Russia is likely to continue in the future, with the UN projecting Russia's population to shrink from 146 million in 2022 to 135.8 million by 2050. The median age risen significantly as a result of the demographic crisis, increasing from 32.2 in 1990 to 40.3 in 2025, in what has been the aging of Russia. History In the economic sphere The demographic crisis has a positive economic effect on the second stage of the changing age structure of the population (the fraction of the av ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Committee For Construction
The Gosstroy () or State Committee for Construction in the Soviet Union (Gosstroy) was the government body for the implementation of national planning, monitoring and management in the construction sector of the USSR. It handled numerous construction projects (with the exception of military and nuclear power generation). According to the Soviet Constitution the committee was under the Union-Republican body. The committee had a seal with the coat of arms of the Soviet Union and emblems of the Union and autonomous republics. History It was formed on 9 May 1950. After January 1952 construction of residential and civil buildings and structures were carried out on projects and budgets, in accordance with instructions from the committee.Инструкция по составлению проектов и смет по промышленному и жилищно-гражданскому строительству (Утв. Постановлением СМ СССР от 26 ян� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Village Prose
Village prose (, or Деревенская литература) was a movement in Soviet literature beginning during the Khrushchev Thaw, which included works that focused on the Soviet rural communities. Some point to the critical essays on collectivization in Novyi mir by Valentin Ovechkin as the starting point of village prose, though most of the subsequent works associated with the genre are fictional novels and short stories. Authors associated with village prose include Aleksander Yashin, Fyodor Abramov, Boris Mozhayev, Vasily Belov, Viktor Astafyev, Vladimir Soloukhin, Vasily Shukshin, and Valentin Rasputin. Some critics also count Aleksandr Solzhenitsyn among the village prose writers for his short novel '' Matryona's Place''. Many village prose works espoused an idealized picture of traditional Russian village life and became increasingly associated with Russian nationalism in the 1970s and 1980s. Some have argued that the nationalist subtext of village prose is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |