|
University Of Community Health, Magway
The University of Community Health, Magway (UCH) (, ) is a Community Health University under the Ministry of Health (Myanmar), and located in Magway city , Myanmar. The university offers a four-year Bachelor of Community Health ( B.Comm.H) degree program. Students have to study how to perform community health. Also, they must take clinical subjects as integration for rural population whom can't get primary health care. Formally, the graduates are allowed to practice as Health Assistants (HA) in Department of Public Health and FDA of Myanmar, many of whom are the main providers of primary health care in rural Myanmar where access to regular physicians is difficult. First, it was established as Health Assistant’s training school in Yangon in 1951. Health Assistant’s training school and Aung San Health Demonstration Unit (Field Department) were combined and emerged as School of Health Science for Basic Health Workers in December 1991 that was upgraded up to University of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magway, Burma
Magway (, ) is the capital city of Magway Region (formerly Magway Division) of Myanmar, and situated on the banks of the Irrawaddy River. The Myathalun Pagoda is located at the north of the city. Magway Region is famous for the cultivation of sesame and many kinds of nuts. It is also the second largest city of Magway Region and it is home to Magway Airport. History During British Occupation, Magway was a township of Minbu Division (or) Minbu province. Minbu Region was established with 3 districts. They are Minbu District, Thayet District and Yenangyaung District. Magway was a township of Yenangyaung District until 1974. On 2 March 1962, the military led by General Ne Win took control of Burma through a coup d'état, and the government has been under direct or indirect control by the military. A new constitution of the Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma was adopted in 1974. By 1974, the name of Minbu region was changed to Magway Region and Yenangyaung District was abolish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
U Nu
Nu (; ; 25 May 1907 – 14 February 1995), commonly known as Burmese names#Honorifics, U Nu and also by the honorific name Thakin Nu, was a prominent Burmese people, Burmese statesman and the first Prime Minister of Union of Burma. He was educated at Rangoon University, where he developed his political ideas and became actively involved in the student movement. Nu's involvement in the nationalist movement deepened during his university years, and he quickly emerged as a leading figure advocating for Burma's independence from British rule in Burma, British colonial rule. He played a crucial role in the Anti-Fascist People's Freedom League (AFPFL), the primary political organization leading the fight for independence. Following Burma's independence in 1948, Nu became the country's first Prime Minister under the provisions of the 1947 Constitution of Myanmar, Constitution of the Union of Burma. His tenure was marked by efforts to rebuild the war-torn nation, establish democrat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Technology
Educational technology (commonly abbreviated as edutech, or edtech) is the combined use of computer hardware, software, and educational theory and practice to facilitate learning and teaching. When referred to with its abbreviation, "EdTech", it often refers to the industry of companies that create educational technology. In ''EdTech Inc.: Selling, Automating and Globalizing Higher Education in the Digital Age'', Tanner Mirrlees and Shahid Alvi (2019) argue "EdTech is no exception to industry ownership and market rules" and "define the EdTech industries as all the privately owned companies currently involved in the financing, production and distribution of commercial hardware, software, cultural goods, services and platforms for the educational market with the goal of turning a profit. Many of these companies are US-based and rapidly expanding into educational markets across North America, and increasingly growing all over the world." In addition to the practical educational ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Health
Environmental health is the branch of public health concerned with all aspects of the natural environment, natural and built environment affecting human health. To effectively control factors that may affect health, the requirements for a healthy environment must be determined. The major sub-disciplines of environmental health are environmental science, toxicology, environmental epidemiology, and Environmental medicine, environmental and occupational medicine. Definitions WHO definitions Environmental health was defined in a 1989 document by the World Health Organization (WHO) as: Those aspects of human health and disease that are determined by factors in the environment. It is also referred to as the theory and practice of accessing and controlling factors in the environment that can potentially affect health. A 1990 WHO document states that environmental health, as used by the WHO Regional Office for Europe, "includes both the direct pathological effects of chemicals, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
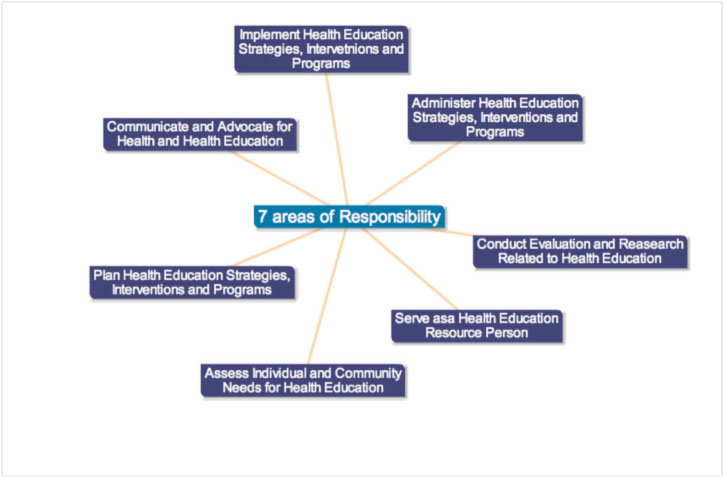
Health Education
Health education is a profession of educating people about health. Areas within this profession encompass environmental health, physical health, social health, emotional health, intellectual health, and spiritual health, as well as sexual and reproductive health education. It can also be defined as any combination of learning activities that aim to assist individuals and communities improve their health by expanding knowledge or altering attitudes. Health education has been defined differently by various sources. The National Conference on Preventive Medicine in 1975 defined it as "a process that informs, motivates, and helps people to adopt and maintain healthy practices and lifestyles, advocates environmental changes as needed to facilitate this goal, and conducts professional training and research to the same end." The Joint Committee on Health Education and Promotion Terminology of 2001 defined Health Education as "any combination of planned learning experiences based on sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemiology
Epidemiology is the study and analysis of the distribution (who, when, and where), patterns and Risk factor (epidemiology), determinants of health and disease conditions in a defined population, and application of this knowledge to prevent diseases. It is a cornerstone of public health, and shapes policy decisions and evidence-based practice by identifying Risk factor (epidemiology), risk factors for disease and targets for preventive healthcare. Epidemiologists help with study design, collection, and statistical analysis of data, amend interpretation and dissemination of results (including peer review and occasional systematic review). Epidemiology has helped develop methodology used in clinical research, public health studies, and, to a lesser extent, basic research in the biological sciences. Major areas of epidemiological study include disease causation, transmission (medicine), transmission, outbreak investigation, disease surveillance, environmental epidemiology, forensic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Community Health
Community health refers to non-treatment based health services that are delivered outside Hospital, hospitals and Clinic, clinics. Community health is a subset of public health that is taught to and practiced by Clinician, clinicians as part of their normal duties. Community health volunteers and community health workers work with Primary care provider, primary care providers to facilitate entry into, exit from and utilization of the formal health system by community members as well as providing supplementary services such as support groups or wellness events that are not offered by medical institutions. Community health is a major field of study within the Medical sciences, medical and Clinical science, clinical sciences which focuses on the maintenance, protection, and improvement of the health status of population groups and communities, in particular those who are a part of disadvantaged communities. It is a distinct field of study that may be taught within a separate school of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomedical Science
Biomedical sciences are a set of sciences applying portions of natural science or formal science, or both, to develop knowledge, interventions, or technology that are of use in healthcare or public health. Such disciplines as medical microbiology, clinical virology, clinical epidemiology, genetic epidemiology, and biomedical engineering are medical sciences. In explaining physiological mechanisms operating in pathological processes, however, pathophysiology can be regarded as basic science. Biomedical Sciences, as defined by the UK Quality Assurance Agency for Higher Education Benchmark Statement in 2015, includes those science disciplines whose primary focus is the biology of human health and disease and ranges from the generic study of biomedical sciences and human biology to more specialised subject areas such as pharmacology, human physiology and human nutrition. It is underpinned by relevant basic sciences including anatomy and physiology, cell biology, biochemistry, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Upper Myanmar
Upper Myanmar ( or , also called Upper Burma) is one of two geographic regions in Myanmar, the other being Lower Myanmar. Located in the country's centre and north stretches, Upper Myanmar encompasses six inland states and regions, including Mandalay Region, Mandalay, Sagaing Region, Sagaing, Magway Regions, and Chin State, Chin, Kachin State, Kachin and Shan States. By contrast, Lower Myanmar encompasses the southern and coastal-facing regions of Myanmar. Upper Myanmar is home to several distinct cultural regions, including the homeland of the Bamar people, Bamar in the low-lying central plains, and those of the Chin people, Chin, Kachin people, Kachin, and Shan people, Shan peoples in the highlands. Home to over 23 million people, the region's agricultural sector, natural resources, and shared borders with India, China, and Thailand have made Upper Myanmar a major economic hub. Four of List of cities and largest towns in Myanmar, Myanmar's ten largest cities—Mandalay, Taungg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yangon Division
Yangon Region (, ; formerly Rangoon Division and Yangon Division) is an administrative region of Myanmar. Located in central Myanmar, the region is bordered by Bago Region to the north and east, the Gulf of Martaban to the south, and Ayeyarwady Region to the west. Yangon Region is dominated by its capital city of Yangon, the former national capital and the largest city in the country. Other important cities are Thanlyin and Twante. The division is the most developed region of the country and the main international gateway. The division measures . History The region was historically populated by the Mon people, Mon. Politically, the area was controlled by Mon kingdoms prior to 1057, and after 1057, with few exceptions, by Bamar people, Burman kingdoms from the north. The control of the region reverted to Bago, Myanmar, Pegu-based Mon kingdoms in the 13th to 16th centuries (1287–1539) and briefly in the 18th century (1740–57). The Portuguese Empire, Portuguese were in contr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Peace And Development Council
The State Peace and Development Council ( ; abbreviated SPDC or , ) was the official name of the Military dictatorship, military government of Burma (Myanmar) which, in 1997, succeeded the State Law and Order Restoration Council (; abbreviated SLORC or ) that had seized power under the rule of Saw Maung in 1988. On 30 March 2011, Senior general (Myanmar), Senior General and Council Chairman Than Shwe signed a decree that officially dissolved the council. SLORC succeeded the People's Assembly (Burma), Pyithu Hluttaw as a legislature and the Council of State (Myanmar), Council of State as a ruling council, after dissolving the state organs of the Socialist Republic of the Union of Burma. In 1997, SLORC was abolished and reconstituted as the State Peace and Development Council (SPDC). The powerful regional military commanders, who were members of SLORC, were promoted to new positions and transferred to the capital of Rangoon (now Yangon). The new regional military commanders w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hlegu
Hlegu (, ) is the capital of Hlegu District in northern Yangon Region, Myanmar about 45 km north-east of Yangon Yangon, formerly romanized as Rangoon, is the capital of the Yangon Region and the largest city of Myanmar. Yangon was the List of capitals of Myanmar, capital of Myanmar until 2005 and served as such until 2006, when the State Peace and Dev ... city. It is located on both sides of the Ngamoyeik River. GeoNames.org Hlegu is also the administrative seat of Hlegu Township and has five urban wards. Notes {{Yangon Region[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |