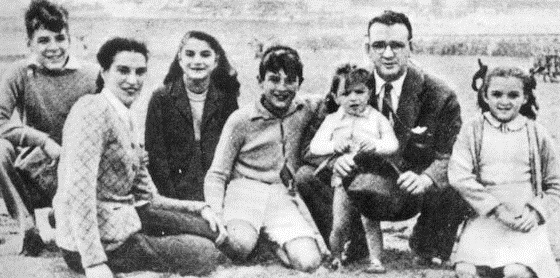|
United Action Party
The Progressive Action Party (, PAP) was a Cuban political party led by Fulgencio Batista. The party was founded on 1 April 1949, in the aftermath of the 1948 general elections, under the name of Unitary Action Party (, PAU). It presented its first manifesto a few months later, on 1 August. In 1952, certain to lose the election, Batista made a coup d'etat by seizing the Presidency. The party also ran in the elections of 1954 and 1958, winning due to the early withdrawal of opponents, as well as electoral fraud. The party was based on a combination of strong conservatism and economic liberalism on a large scale, to attract American capital in Cuba. This led to a high level of corruption and poverty plaguing the country. The other bulwark of the party was anti-communism, not only because of the alignment with the United States but also because most of the members of the anti-Batista left-wing nationalist 26th of July Movement could be branded as Communists, including Fidel Castr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fulgencio Batista
Fulgencio Batista y Zaldívar (born Rubén Zaldívar; January 16, 1901 – August 6, 1973) was a Cuban military officer and politician who played a dominant role in Cuban politics from his initial rise to power as part of the 1933 Revolt of the Sergeants. He ruled Cuba as a military dictator until his overthrow in the Cuban Revolution in 1959. He served as president of Cuba from 1940 to 1944, and again from 1952 to his 1959 resignation. Raised in humble circumstances, Batista first came to prominence in the Revolt of the Sergeants, which overthrew the provisional government of Carlos Manuel de Céspedes y Quesada. Batista then appointed himself chief of the armed forces, with the rank of colonel, and effectively controlled the five-member "pentarchy" that functioned as the collective head of state. He maintained control through a series of puppet presidents until 1940, when he was elected president on a populist platform. He then instated the 1940 Constitution of Cuba and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electoral Fraud
Electoral fraud, sometimes referred to as election manipulation, voter fraud, or vote rigging, involves illegal interference with the process of an election, either by increasing the vote share of a favored candidate, depressing the vote share of rival candidates, or both. It differs from but often goes hand-in-hand with voter suppression. What exactly constitutes electoral fraud varies from country to country, though the goal is often election subversion. Electoral legislation outlaws many kinds of election fraud, * also at but other practices violate general laws, such as those banning assault, harassment or libel. Although technically the term "electoral fraud" covers only those acts which are illegal, the term is sometimes used to describe acts which are legal, but considered morally unacceptable, outside the spirit of an election or in violation of the principles of democracy. Show elections, featuring only one candidate, are sometimes classified as electoral fraud, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuban Presidential Election, 1958
Cuban or Cubans may refer to: Related to Cuba * of or related to Cuba, a country in the Caribbean * Cubans, people from Cuba, or of Cuban descent ** Cuban exile, a person who left Cuba for political reasons, or a descendant thereof * Cuban Americans, citizens of the United States who are of Cuban descent * Cuban Spanish, the dialect of Cuba * Culture of Cuba * Cuban cigar * Cuban cuisine ** Cuban sandwich People with the surname * Brian Cuban (born 1961), American lawyer and activist * Mark Cuban (born 1958), American entrepreneur See also * * Kuban (other) * List of Cubans * Demographics of Cuba * Cuban Boys, a British music act * Cuban eight, a type of aerobatic maneuver * Cuban Missile Crisis * Cubane Cubane is a synthetic hydrocarbon compound with the Chemical formula, formula . It consists of eight carbon atoms arranged at the corners of a Cube (geometry), cube, with one hydrogen atom attached to each carbon atom. A solid crystalline substanc ..., a synthetic hyd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
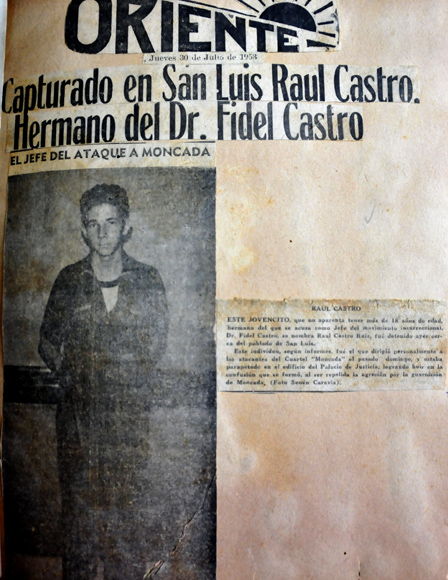
Cuban Revolution
The Cuban Revolution () was the military and political movement that overthrew the dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista, who had ruled Cuba from 1952 to 1959. The revolution began after the 1952 Cuban coup d'état, in which Batista overthrew the emerging Cuban democracy and consolidated power. Among those who opposed the coup was Fidel Castro, then a young lawyer, who initially tried to challenge the takeover through legal means in the Cuban courts. When these efforts failed, Fidel Castro and his brother Raúl Castro, Raúl led an armed Attack on the Moncada Barracks, assault on the Moncada Barracks, a Cuban military post, on 26 July 1953. Following the attack's failure, Fidel Castro and his co-conspirators were arrested and formed the 26th of July Movement (M-26-7) in detention. At his trial, Fidel Castro launched into a History Will Absolve Me, two-hour speech that won him national fame as he laid out his grievances against the Batista dictatorship. In an attempt to win pub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extrajudicial Killing
An extrajudicial killing (also known as an extrajudicial execution or an extralegal killing) is the deliberate killing of a person without the lawful authority granted by a judicial proceeding. It typically refers to government authorities, whether lawfully or unlawfully, targeting specific people for death, which in authoritarian regimes often involves political, trade union, dissident, religious and social figures. The term is typically used in situations that imply the human rights of the victims have been violated. Deaths caused by legal police actions (such as self defense) or legal warfighting on a battlefield are generally not included, even though military and police forces are often used for killings seen by critics as illegitimate. The label "extrajudicial killing" has also been applied to organized, lethal enforcement of extralegal social norms by non-government actors, including lynchings and honor killings. United Nations Morris Tidball-Binz was appointed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Che Guevara
Ernesto "Che" Guevara (14th May 1928 – 9 October 1967) was an Argentines, Argentine Communist revolution, Marxist revolutionary, physician, author, Guerrilla warfare, guerrilla leader, diplomat, and Military theory, military theorist. A major figure of the Cuban Revolution, his stylized visage has become a ubiquitous Counterculture of the 1960s, countercultural symbol of rebellion and global insignia Che Guevara in popular culture, in popular culture. As a young medical student, Guevara travelled throughout South America and was appalled by the poverty, hunger, and disease he witnessed.On Revolutionary Medicine Speech by Che Guevara to the Cuban Militia on 19 August 1960. "Because of the circumstances in which I traveled, first as a student and later as a doctor, I came into close contact with poverty, hunger a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raúl Castro
Raúl Modesto Castro Ruz ( ; ; born 3 June 1931) is a Cuban retired politician and general who served as the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba, first secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba, the most senior position in the One-party state, one-party communist state, from 2011 to 2021, and President of Cuba between 2008 and 2018, succeeding his brother Fidel Castro. One of the military leaders of the Cuban Revolution, Castro served as the minister of the Cuban Revolutionary Armed Forces, Armed Forces from 1959 to 2008. His ministerial tenure made him the longest-serving minister of the armed forces. Castro was also a member of the Politburo of the Communist Party of Cuba, the highest decision-making body, from 1965 until 2021. Because of his brother's illness, Castro became the acting (law), acting President of Cuba, president of the Council of State (Cuba), Council of State in a temporary 2006 Cuban transfer of power, transfer of power from 31 July 2006. Castro wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camilo Cienfuegos
Camilo Cienfuegos Gorriarán (; 6 February 1932 – 28 October 1959) was a Cuban revolutionary. One of the major figures of the Cuban Revolution, he was considered second only to Fidel Castro among the revolutionary leadership. The son of Anarchism in Spain, Spanish anarchists, Cienfuegos engaged with left-wing politics from an early age, going on to join the opposition movement against the dictatorship of Fulgencio Batista. He joined Castro's 26th of July Movement on its expedition to Cuba and was one of the few survivors of the Landing of the Granma. He quickly distinguished himself as one of the top commanders of the Cuban Revolutionary Armed Forces and a popular leading figure of the revolution, becoming close friends with Che Guevara during their guerrilla campaign in Santa Clara Province, Las Villas. After winning the Battle of Yaguajay in December 1958, Cienfuegos led the capture of Matanzas and Havana, where he was appointed as commander-in-chief of the armed forces by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fidel Castro
Fidel Alejandro Castro Ruz (13 August 1926 – 25 November 2016) was a Cuban politician and revolutionary who was the leader of Cuba from 1959 to 2008, serving as the prime minister of Cuba from 1959 to 1976 and President of Cuba, president from 1976 to 2008. Ideologically a Marxist–Leninist and Cuban nationalist, he also served as the First Secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba, first secretary of the Communist Party of Cuba from 1965 until 2011. Under his administration, Cuba became a One-party state, one-party communist state; industry and business were nationalized, and socialist reforms were implemented throughout society. Born in Birán, the son of a wealthy Spanish farmer, Castro adopted leftist and anti-imperialist ideas while studying law at the University of Havana. After participating in rebellions against right-wing governments in the Dominican Republic#Trujillo Era (1930–61), Dominican Republic and La Violencia, Colombia, he planned the overthrow of Cuban ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communism
Communism () is a political sociology, sociopolitical, political philosophy, philosophical, and economic ideology, economic ideology within the history of socialism, socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a socioeconomic order centered on common ownership of the means of production, distribution, and exchange that allocates products in society based on need.: "One widespread distinction was that socialism socialised production only while communism socialised production and consumption." A communist society entails the absence of private property and social classes, and ultimately money and the State (polity), state. Communists often seek a voluntary state of self-governance but disagree on the means to this end. This reflects a distinction between a Libertarian socialism, libertarian socialist approach of communization, revolutionary spontaneity, and workers' self-management, and an authoritarian socialism, authoritarian socialist, vanguardis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
26th Of July Movement
The 26 July Movement (; M-26-7) was a Cuban vanguard revolutionary organization and later a political party led by Fidel Castro. The movement's name commemorates the failed 1953 attack on the Moncada Barracks in Santiago de Cuba, part of an attempt to overthrow the dictator Fulgencio Batista. M-26-7 is considered the leading organization of the Cuban Revolution. At the end of 1956, Castro established a guerrilla base in the Sierra Maestra. This base defeated the troops of Batista on 31 December 1958, setting into motion the Cuban Revolution and installing a government led by Manuel Urrutia Lleó. The Movement fought the Batista regime on both rural and urban fronts. The movement's main objectives were distribution of land to peasants, nationalization of public services, industrialization, honest elections, and large-scale education reform. In July 1961, the 26th of July Movement was one of the parties that integrated into the Integrated Revolutionary Organization (ORI) as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Left-wing Nationalism
Left-wing nationalism or leftist nationalism (in certain contexts also called popular nationalism by those who do not adhere to the left-right plane, or in contrast to conservative nationalism) is a form of nationalism which is based upon national self-determination, popular sovereignty, and left-wing political positions such as social equality. Left-wing nationalism can also include anti-imperialism and national liberation movements.Smith 1999, 30. Left-wing nationalism often stands in contrast to right-wing politics and right-wing nationalism. Overview Some left-wing nationalist groups have historically used the term '' national socialism'' for themselves, but only before the rise of the Nazis or outside Europe. Since the Nazis' rise to prominence, ''national socialism'' has become associated almost exclusively with their ideas and it is rarely used in relation to left-wing nationalism in Europe, with ''nationalist socialism'' or ''socialist nationalism'' being pre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |