|
Unified Social Credit Code
A Unified Social Credit Identifier (USCC) is issued to registered companies and other types of organization by the Chinese government. It is "unified" in the sense that it is used both as the business registration number with the State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR) and as the taxpayer identifier with the State Taxation Administration (STA). These identifiers are now used widely as the only organization Identity document, ID within and outside of the government. An identifier must be obtained before one can operate a business in China. History Previously, business owners in China had to obtain a business permit with a unique id from the State Administration for Industry and Commerce (SAIC), a taxpayer identifier from the STA, and an organization code from Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ) until reforms in 2015 introduced the USCC. SAIC and AQSIQ were merged into the newly founded SAMR following an organizational reform by the Sta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Business Licence In A Tea Shop In Suzhou
Business is the practice of making one's living or making money by producing or buying and selling products (such as goods and services). It is also "any activity or enterprise entered into for profit." A business entity is not necessarily separate from the owner and the creditors can hold the owner liable for debts the business has acquired except for limited liability company. The taxation system for businesses is different from that of the corporates. A business structure does not allow for corporate tax rates. The proprietor is personally taxed on all income from the business. A distinction is made in law and public offices between the term business and a company (such as a corporation or cooperative). Colloquially, the terms are used interchangeably. Corporations are distinct from sole proprietors and partnerships. Corporations are separate and unique legal entities from their shareholders; as such they provide limited liability for their owners and members. Corporat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
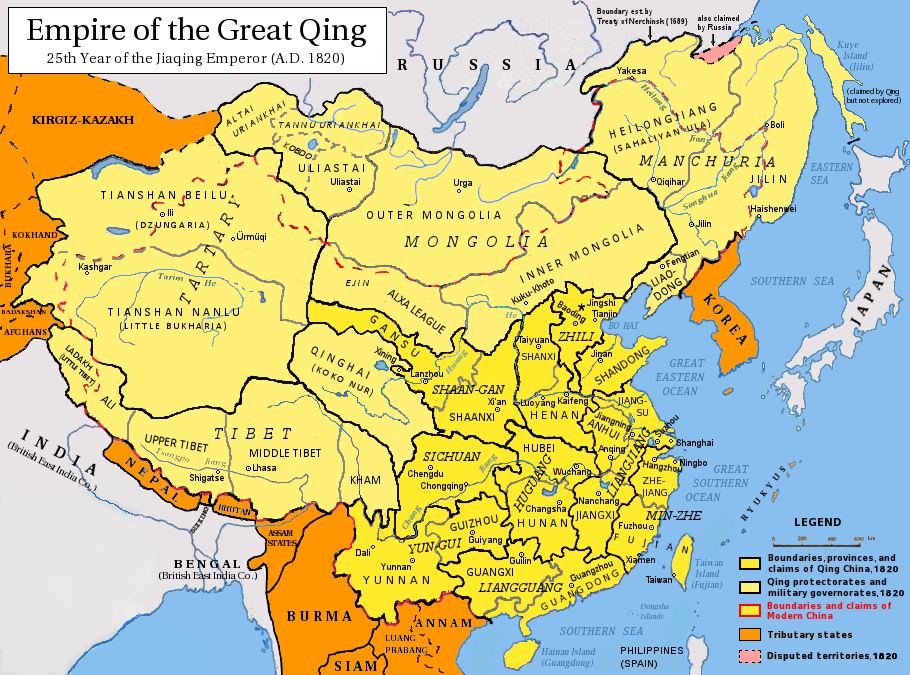
Administrative Divisions Of The People's Republic Of China
The administrative divisions of China have consisted of several levels since 1412, due to mainland China's large population and geographical area. In the People's Republic of China, the constitution provides for three levels of government. However in practice, there are five levels of local government; the provincial (province, autonomous region, municipality, and special administrative region), prefecture, county, township, and village. Since the 17th century, provincial boundaries in mainland China have remained largely static. Major changes since then have been the reorganization of provinces in the northeast after the establishment of the People's Republic of China in 1949 and the formation of autonomous regions, based on Soviet ethnic policies. The provinces serve an important cultural role in China, as people tend to identify with their native province. Levels The Constitution of the People's Republic of China provides for three levels: the provincial, the county l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modulus (algebraic Number Theory)
In mathematics, in the field of algebraic number theory, a modulus (plural moduli) (or cycle, or extended ideal) is a formal product of places of a global field (i.e. an algebraic number field or a global function field). It is used to encode ramification data for abelian extensions of a global field. Definition Let ''K'' be a global field with ring of integers ''R''. A modulus is a formal product :\mathbf = \prod_ \mathbf^,\,\,\nu(\mathbf)\geq0 where p runs over all places of ''K'', finite or infinite, the exponents ν(p) are zero except for finitely many p. If ''K'' is a number field, ν(p) = 0 or 1 for real places and ν(p) = 0 for complex places. If ''K'' is a function field, ν(p) = 0 for all infinite places. In the function field case, a modulus is the same thing as an effective divisor, and in the number field case, a modulus can be considered as special form of Arakelov divisor. The notion of congruence can be extended to the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ISO/IEC 7064
ISO/IEC 7064 is a standard promulgated by the International Standards Organization (ISO) and International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) that defines algorithms for calculating check digit characters. The checks should be applicable to alphanumeric strings and should be able to detect all single substitution errors, all or nearly all single local transposition errors, all or nearly all circular shift errors, a high proportion of double substitution errors, a high proportion of all other errors. Standards * Status: Published - ISO/IEC 7064:2003 Information technology -- Security techniques -- Check character systems * Status: Withdrawn - ISO 7064:1983 Data processing -- Check character systems Usage It is referred to by other ISO standards: * International Bank Account Number (IBAN) * International Standard Text Code (ISTC) * International Standard Name Identifier (ISNI) * Legal Entity Identifier (LEI) and by other systems: * Personal identification number (Croatia) * Resi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Checksum
A checksum is a small-sized block of data derived from another block of digital data for the purpose of detecting errors that may have been introduced during its transmission or storage. By themselves, checksums are often used to verify data integrity but are not relied upon to verify data authenticity. The procedure which generates this checksum is called a checksum function or checksum algorithm. Depending on its design goals, a good checksum algorithm usually outputs a significantly different value, even for small changes made to the input. This is especially true of cryptographic hash functions, which may be used to detect many data corruption errors and verify overall data integrity; if the computed checksum for the current data input matches the stored value of a previously computed checksum, there is a very high probability the data has not been accidentally altered or corrupted. Checksum functions are related to hash functions, fingerprints, randomization functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
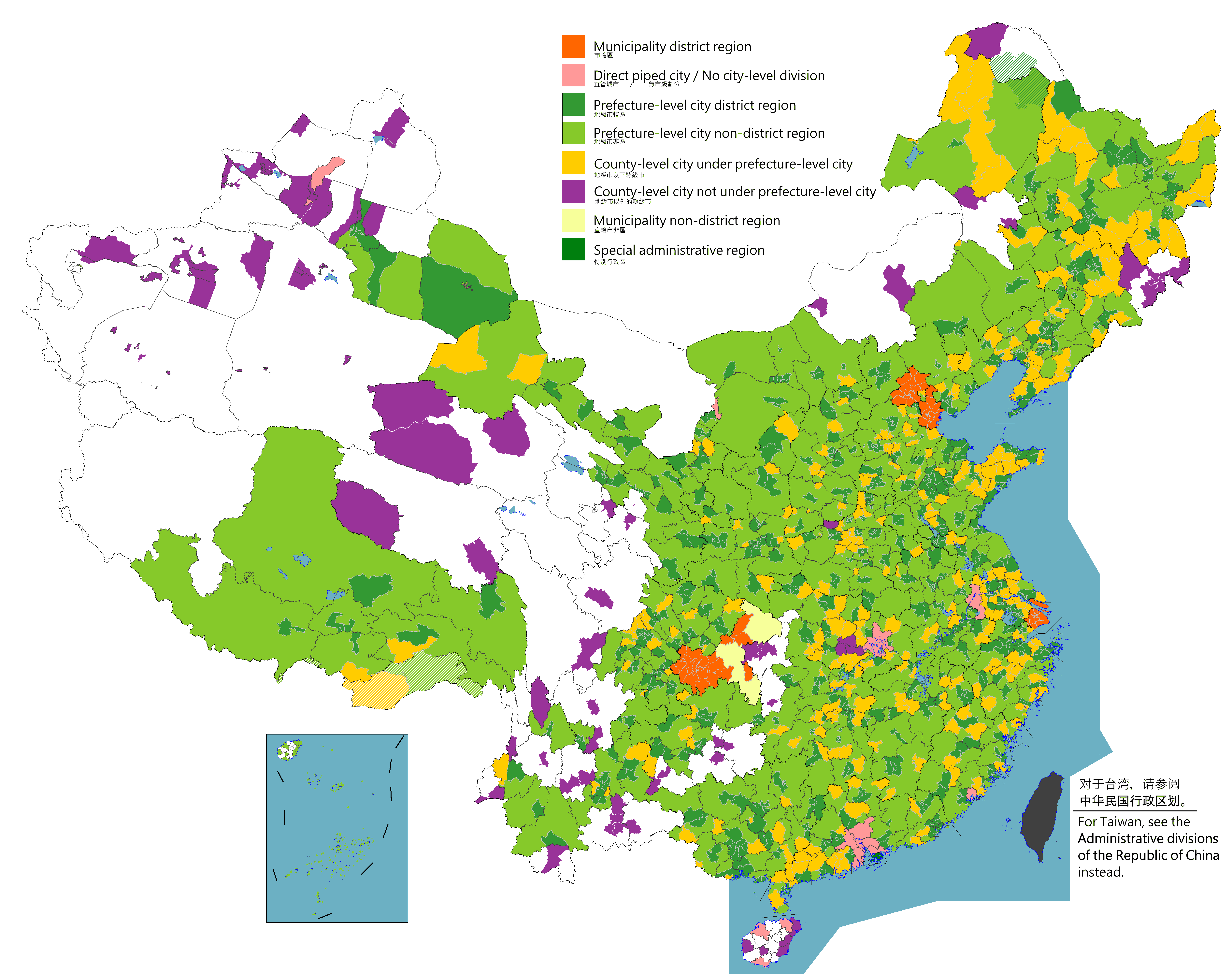
District (PRC)
The term ''district'', in the context of China, is used to refer to several unrelated political divisions in both ancient and modern China. In the modern context, district ( zh, s=区, labels=no), formally city-governed district, city-controlled district, or municipal district ( zh, s=市辖区, links=no, labels=no), are subdivisions of a municipality or a prefecture-level city. The rank of a district derives from the rank of its city. Districts of a municipality are prefecture-level; districts of a sub-provincial city are sub-prefecture-level; and districts of a prefecture-level city are county-level. The term was also formerly used to refer to obsolete county-controlled districts (also known as district public office). However, if the word ''district'' is encountered in the context of ancient Chinese history, then it is a translation for ''xian'', another type of administrative division in China. Before the 1980s, cities in China were administrative divisions contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banner (Inner Mongolia)
A banner (; ) is an administrative divisions of China, administrative division of the Inner Mongolia, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region in China, equivalent to a county-level administrative division. Banners were first used during the Qing dynasty, which organized the Mongols into banners, except those who belonged to the Eight Banners. Each banner had Sum (administrative division), sums as nominal subdivisions. In Inner Mongolia, several banners made up a Leagues of China, league. In the rest, including Outer Mongolia, northern Xinjiang, and Qinghai, Aimag (Аймаг) was the largest administrative division. While it restricted the Mongols from crossing banner borders, the dynasty protected Mongolia from population pressure from China proper. After the Mongolian Revolution of 1921, Mongolian People's Revolution, the banners of Outer Mongolia were abolished in 1923. There were 49 banners and 24 tribes in Inner Mongolia during the Republic of China. Today, banners are a Ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cities In The People's Republic Of China
According to the administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China, there are three levels of cities: provincial-level cities (consisting of directly-administered municipalities and the special administrative regions of Hong Kong and Macau), prefecture-level cities, and county-level cities. As of January 2024, the PRC has a total of 707 cities: 4 municipalities, 2 SARs, 293 prefecture-level cities (including the 15 sub-provincial cities) and 408 county-level cities (including the 38 sub-prefectural cities and 12 XXPC cities). This list does not include any cities in the disputed Taiwan Province and portions of Fujian Province, which are claimed by the PRC under the One China Policy, as these areas are controlled by the Republic of China (see the List of cities in Taiwan). Prefecture-level cities nearly always contain multiple counties (县), county-level cities, and other such sub-divisions. Because of this, prefecture-level cities often overlap in area wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Alphabet
Modern English is written with a Latin-script alphabet consisting of 26 Letter (alphabet), letters, with each having both uppercase and lowercase forms. The word ''alphabet'' is a Compound (linguistics), compound of ''alpha'' and ''beta'', the names of the first two letters in the Greek alphabet. The earliest Old English writing during the 5th century used a runic alphabet known as the Anglo-Saxon futhorc, futhorc. The Old English Latin alphabet was adopted from the 7th century onward—and over the following centuries, various letters entered and fell out of use. By the 16th century, the present set of 26 letters had largely stabilised: There are 5 vowel letters and 19 consonant letters—as well as Y and W, which may function as either type. Written English has a large number of Digraph (orthography), digraphs, such as , , , , and . Diacritics are generally not used to write native English words, which is unusual among orthographies used to write the languages of Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Administration For Market Regulation
The State Administration for Market Regulation (SAMR; ) is a ministerial-level agency directly under the State Council of the People's Republic of China responsible for market supervision and management. SAMR was established in 2018. It is China's primary antitrust regulator. History The Administration was created as part of the deepening the reform of the Party and state institutions, and merged or abolished a number of previous agencies, such as the State Intellectual Property Office. SAMR was created under the banner of the Central Comprehensively Deepening Reforms Commission under Xi Jinping, current General Secretary of the Chinese Communist Party. The Administration consolidates in one ministry the market regulation functions previously shared by three separate agencies, the General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine (AQSIQ), the China Food and Drug Administration (CFDA), and the State Administration of Industry and Commerce (SAIC). In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uppercase
Letter case is the distinction between the letters that are in larger uppercase or capitals (more formally ''#Majuscule, majuscule'') and smaller lowercase (more formally ''#Minuscule, minuscule'') in the written representation of certain languages. The writing systems that distinguish between the upper- and lowercase have two parallel sets of letters: each in the majuscule set has a counterpart in the minuscule set. Some counterpart letters have the same shape, and differ only in size (e.g. ), but for others the shapes are different (e.g., ). The two case variants are alternative representations of the same letter: they have the same name and pronunciation and are typically treated identically when sorting in alphabetical order. Letter case is generally applied in a mixed-case fashion, with both upper and lowercase letters appearing in a given piece of text for legibility. The choice of case is often denoted by the grammar of a language or by the conventions of a particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabic Numerals
The ten Arabic numerals (0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and 9) are the most commonly used symbols for writing numbers. The term often also implies a positional notation number with a decimal base, in particular when contrasted with Roman numerals. However the symbols are also used to write numbers in other bases, such as octal, as well as non-numerical information such as trademarks or license plate identifiers. They are also called Western Arabic numerals, Western digits, European digits, Ghubār numerals, or Hindu–Arabic numerals due to positional notation (but not these digits) originating in India. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' uses lowercase ''Arabic numerals'' while using the fully capitalized term ''Arabic Numerals'' for Eastern Arabic numerals. In contemporary society, the terms ''digits'', ''numbers'', and ''numerals'' often implies only these symbols, although it can only be inferred from context. Europeans first learned of Arabic numerals , though their spread ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |