|
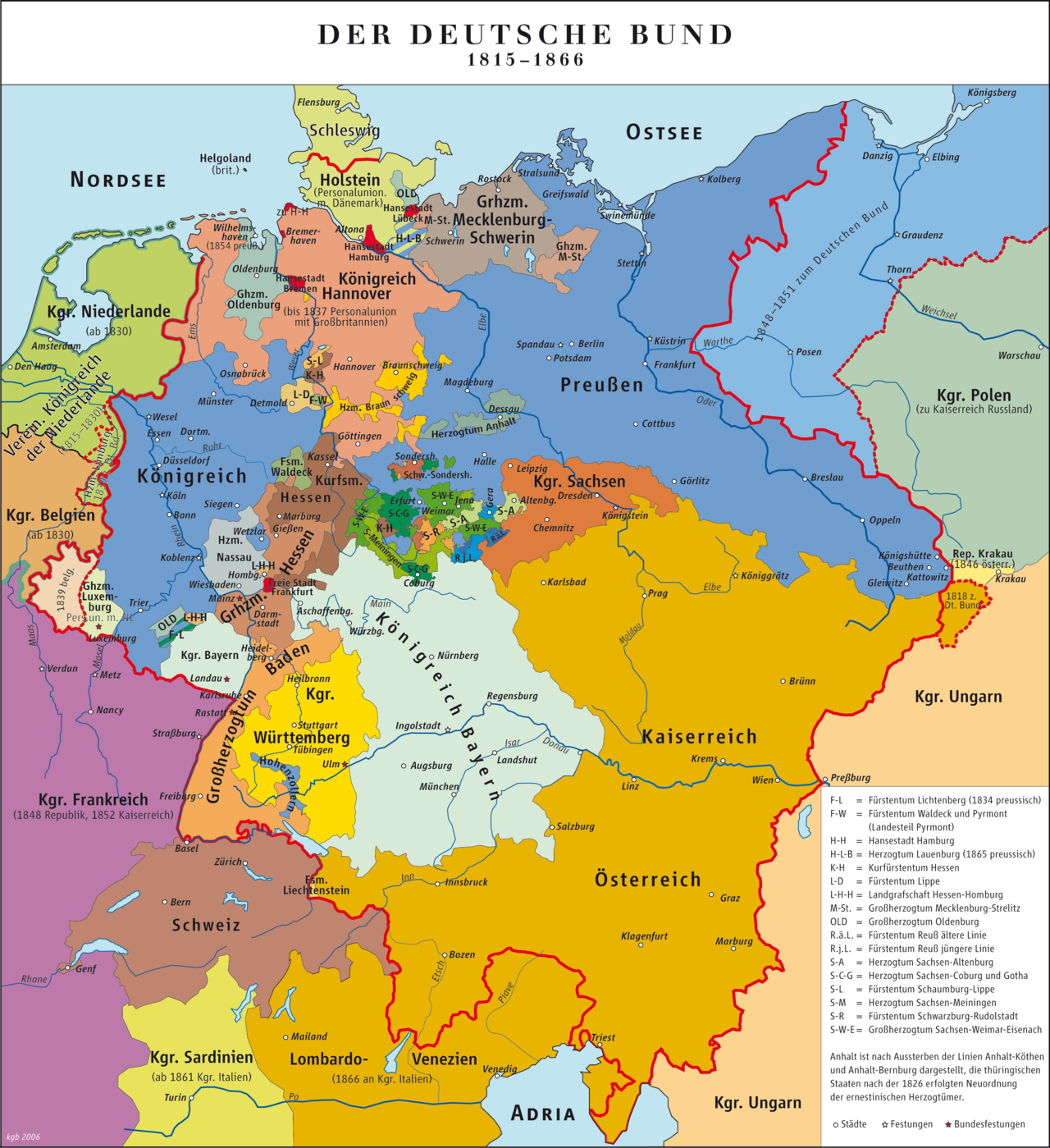
Unification Of Germany
The unification of Germany (, ) was a process of building the first nation-state for Germans with federalism, federal features based on the concept of Lesser Germany (one without Habsburgs' multi-ethnic Austria or its German-speaking part). It commenced on 18 August 1866 with the adoption of the North German Confederation Treaty establishing the North German Confederation, initially a military alliance ''de facto'' dominated by the Kingdom of Prussia which was subsequently deepened through adoption of the North German Constitution. The process symbolically concluded when most of the south German states joined the North German Confederation with the ceremonial proclamation of the German Empire (German Reich) having States of the German Empire, 25 member states and led by the Kingdom of Prussia of Hohenzollerns on 18 January 1871; the event was typically celebrated as the date of the German Empire's foundation, although the legally meaningful events relevant to the completion of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
States Of The German Empire
The German Empire consisted of 25 constituent states and an imperial territory, the largest of which was Prussia. These states, or ''Staaten'' (or ''Bundesstaaten'', i.e. federated states, a name derived from the previous North German Confederation; they became known as ''Länder'' during the Weimar Republic) each had votes in the Bundesrat, which gave them representation at a federal level. Several of these states had gained sovereignty following the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire. Others were created as sovereign states after the Congress of Vienna in 1815. Territories were not necessarily contiguous, such as Bavaria, or Oldenburg—many existed in several parts (enclaves and exclaves), as a result of historical acquisitions, or, in several cases, divisions of the ruling family trees. Kingdoms * Kingdom of Bavaria *Kingdom of Prussia (itself subdivided into provinces; including the Duchy of Saxe-Lauenburg ruled in personal union until annexed 1 July 1876) *Kingdom of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Reuss-Gera
The Principality of Reuss-Gera (), officially called the Principality of the Reuss Junior Line () after 1848, was a sovereign state in modern Germany, ruled by members of the House of Reuss. It was one of the successor states of the Imperial County of Reuss. The Counts Reuss, with their respective capitals and '' Residenzen'' at Gera, Schleiz, Lobenstein, Köstritz and Ebersdorf, were all elevated to the title of prince ('' Fürst'') in 1806. Their successor branch heads shared that title, while their cadets were also each titled prince (''Prinz''). Thus all males of the family were properly "Prince Heinrich (Roman numeral) Reuss, ''J.L.''", without use of a nobiliary particle, although for convenience their branch names remained in colloquial use (for example, "Prince Heinrich I Reuss of Köstritz"). Territory The territories of four separate branches of the Junior Line amalgamated between 1824 and 1848, at which time the senior branch of Gera retained sovereignty over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lesser Germany
The term "Lesser Germany" ( German: , ) or "Lesser German solution" (German: {{Lang, de, Kleindeutsche Lösung) denoted essentially exclusion of the multinational Austria of the Habsburgs from the planned German unification as an option for solving the German question, in opposition to the one of ' Greater Germany'. In the 19th century, a part of the Austrian Empire belonged to the German Confederation. In the revolutionary era of 1848–1850, it was discussed whether Austria or a part of Austria could belong to a new German federal state. In 1867–1871, the 'Lesser Germany' became reality: a federal state under leadership of Prussia and without Austria. After that, the term lost its significance because since then 'Germany' is usually identified as this Lesser Germany. The other term, Greater Germany, remained in use for those who sought to incorporate Austria or the German-speaking parts of Austria into Germany. This became a political issue in the aftermath of World War On ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free And Hanseatic City Of Lübeck
Free may refer to: Concept * Freedom, the ability to act or change without constraint or restriction * Emancipate, attaining civil and political rights or equality * Free (''gratis''), free of charge * Gratis versus libre, the difference between the two common meanings of the adjective "free". Computing * Free (programming), a function that releases dynamically allocated memory for reuse * Free software, software usable and distributable with few restrictions and no payment *, an emoji in the Enclosed Alphanumeric Supplement block. Mathematics * Free object ** Free abelian group ** Free algebra ** Free group ** Free module ** Free semigroup * Free variable People * Free (surname) * Free (rapper) (born 1968), or Free Marie, American rapper and media personality * Free, a pseudonym for the activist and writer Abbie Hoffman * Free (active 2003–), American musician in the band FreeSol Arts and media Film and television * ''Free'' (film), a 2001 American dramedy * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free And Hanseatic City Of Hamburg
Hamburg (, ; ), officially the Free and Hanseatic City of Hamburg,. is the second-largest city in Germany after Berlin and 7th-largest in the European Union with a population of over 1.9 million. The Hamburg Metropolitan Region has a population of over 5.1 million and is the eighth-largest metropolitan region by GDP in the European Union. At the southern tip of the Jutland Peninsula, Hamburg stands on the branching River Elbe at the head of a estuary to the North Sea, on the mouth of the Alster and Bille. Hamburg is one of Germany's three city-states alongside Berlin and Bremen, and is surrounded by Schleswig-Holstein to the north and Lower Saxony to the south. The Port of Hamburg is Germany's largest and Europe's third-largest, after Rotterdam and Antwerp. The local dialect is a variant of Low Saxon. The official name reflects Hamburg's history as a member of the medieval Hanseatic League and a free imperial city of the Holy Roman Empire. Before the 1871 unifi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Free Hanseatic City Of Bremen
Bremen (), officially the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (; ), is the smallest and least populous of Germany's 16 states. It is informally called ('State of Bremen'), although the term is sometimes used in official contexts. The state consists of the city of Bremen and its seaport exclave, Bremerhaven, surrounded by the larger state of Lower Saxony in northern Germany. Geography The state of Bremen consists of two non-contiguous territories. These enclaves contain Bremen, officially the 'City' (''Stadtgemeinde Bremen'') which is the state capital, and the city of Bremerhaven (''Stadt Bremerhaven''). Both are located on the River Weser; Bremerhaven ("Bremen's harbour") is further downstream on the mouth of the Weser with open access to the North Sea. Both enclaves are completely surrounded by the neighbouring State of Lower Saxony (''Niedersachsen''). The highest point in the state is in Friedehorst Park (). History When the Holy Roman Empire was dissolved in 1806, what had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Hesse
The Grand Duchy of Hesse and by Rhine () was a grand duchy in western Germany that existed from 1806 to 1918. The grand duchy originally formed from the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt in 1806 as the Grand Duchy of Hesse (). It assumed the name Hesse und bei Rhein in 1816 to distinguish itself from the Electorate of Hesse, which had formed from the neighbouring Landgraviate of Hesse-Kassel. Colloquially, the grand duchy continued to be known by its former name of Hesse-Darmstadt. In 1806, the Landgraviate of Hesse-Darmstadt seceded from the Holy Roman Empire and joined Napoleon's new Confederation of the Rhine. The country was promoted to the status of grand duchy and received considerable new territories, principally the Duchy of Westphalia. After the French defeat in 1815, the grand duchy joined the new German Confederation. Westphalia was taken by Prussia, but Hesse received Rhenish Hesse in return. A constitution was proclaimed in 1820 and a long process of legal reforms was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grand Duchy Of Baden
The Grand Duchy of Baden () was a German polity on the east bank of the Rhine. It originally existed as a sovereign state from 1806 to 1871 and later as part of the German Empire until 1918. The duchy's 12th-century origins were as a Margraviate of Baden, margraviate that eventually split into two, Margraviate of Baden-Durlach, Baden-Durlach and Margraviate of Baden-Baden, Baden-Baden, before being reunified in 1771. The territory grew and assumed its ducal status after the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire but suffered a Baden Revolution, revolution in 1848, whose demands had been formulated in Offenburg the previous year at a meeting now considered the first-ever democratic program in Germany. With the collapse of the German Empire it became part of the Weimar Republic under the name Republic of Baden. The Grand Duchy of Baden was bordered to the north by the Kingdom of Bavaria and the Grand Duchy of Hesse, to the west by the Rhine, to the south by Switzerland, and to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Württemberg
The Kingdom of Württemberg ( ) was a German state that existed from 1806 to 1918, located within the area that is now Baden-Württemberg. The kingdom was a continuation of the Electorate of Württemberg, which existed from 1803 to 1806. Geography The borders of the Kingdom of Württemberg, as defined in 1813, lay between 47°34' and 49°35' north and 8°15' and 10°30' east. The greatest distance north to south was and the greatest east to west was . The border had a total length of and the total area of the state was . The kingdom had borders with Bavaria on the east and south, with Baden in the north, west, and south. The southern part surrounded the Prussian province of Hohenzollern on most of its sides and touched on Lake Constance. History Frederick I Frederick III, the Duke of Württemberg (1754–1816; succeeded: 1797), assumed the title of King Frederick I on 1 January 1806. He abrogated the constitution, and united Old and New Württemberg. Subsequently, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bavaria
The Kingdom of Bavaria ( ; ; spelled ''Baiern'' until 1825) was a German state that succeeded the former Electorate of Bavaria in 1806 and continued to exist until 1918. With the unification of Germany into the German Empire in 1871, the kingdom became a federated state of the new empire and was second in size, power, and wealth only to the leading state, the Kingdom of Prussia. The polity's foundation dates back to the ascension of Elector Maximilian IV Joseph of the House of Wittelsbach as King of Bavaria in 1806. The crown continued to be held by the Wittelsbachs until the kingdom came to an end in 1918. Most of the border of modern Germany's Free State of Bavaria was established after 1814 with the Treaty of Paris, in which the Kingdom of Bavaria ceded Tyrol and Vorarlberg to the Austrian Empire while receiving Aschaffenburg and Würzburg. In 1918, Bavaria became a republic after the German Revolution, and the kingdom was thus succeeded by the current Free State of Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Waldeck And Pyrmont
The County of Waldeck (later the Principality of Waldeck and Principality of Waldeck and Pyrmont) was a state of the Holy Roman Empire and its successors from the late 12th century until 1929. In 1349 the county gained Imperial immediacy and in 1712 was raised to the rank of principality. After the dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire in 1806 it was a constituent state of its successors: the Confederation of the Rhine, the German Confederation, the North German Confederation, and the German Empire. After the abolition of the monarchy in 1918, the renamed Free State of Waldeck-Pyrmont became a component of the Weimar Republic until divided between Hannover and other Prussian provinces in 1929. It comprised territories in present-day Hesse and Lower Saxony (Germany). History The noble family of the and the later Princes of Waldeck and Pyrmont were male line descendants of the (based at Schwalenberg Castle), ultimately descendent from (reigned 1127–1136/7). Waldeck Cas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Principality Of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen
Schwarzburg-Sondershausen was a small principality in Germany, in the present day state of Thuringia, with its capital at Sondershausen. History Schwarzburg-Sondershausen was a county (earldom) until 1697. In that year, it became a principality, which lasted until the fall of the German monarchies in 1918, during the German Revolution of 1918–1919. After the German Revolution, it became a republic and joined the Weimar Republic as a constituent state. In 1920, it joined with other small states in the area to form the new state of Thuringia. Schwarzburg-Sondershausen had an area of 862 km2 (333 sq. mi.) and a population of 85,000 (1905). Towns placed in the state were: Arnstadt, Sondershausen, Gehren, Langewiesen, Großbreitenbach, Ebeleben, Großenehrich, Greußen and Plaue. Rulers of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen, 1552–1918 Counts of Schwarzburg-Sondershausen * 1552–1586 John Günther I * 1586–1631 Günther XLII, ''with'' Anton Henry, John Günther II and C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |