|
Unidirectionality Hypothesis
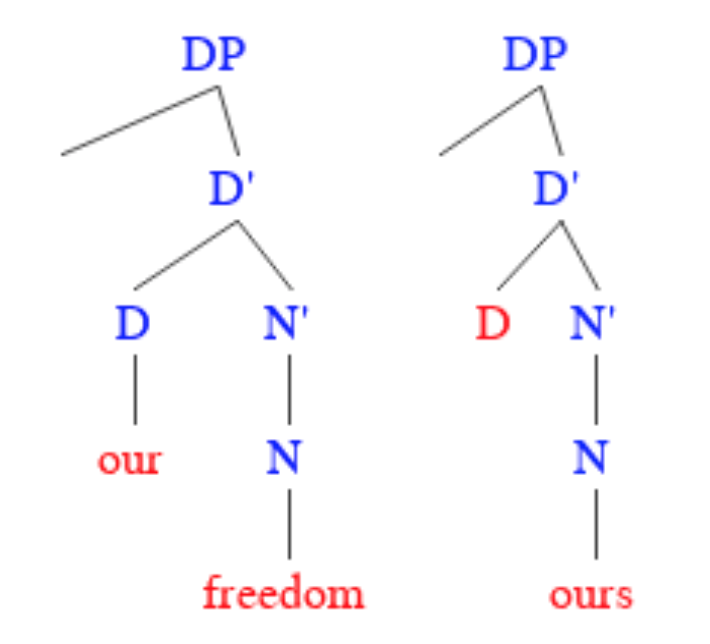
In linguistics, the unidirectionality hypothesis proposes that grammaticalisation works in a single direction. That is, pronouns and prepositions may fuse with verbs or nouns to create new inflectional systems, but inflectional endings do not break off to create new pronouns or prepositions. The hypothesis is not universally applicable, with some rare counterexamples appearing in unusual circumstances. The unidirectionality hypothesis does not claim that linguistic change ''will'' occur in any particular instance, only that if it ''does'' occur, it will be in the direction of lexical word to grammatical word and not the other way around. It should not be confused with a denial of lexicalisation In linguistics, lexicalization is the process of adding words, set phrases, or word patterns to a language's lexicon. Whether ''word formation'' and ''lexicalization'' refer to the same process is controversial within the field of linguistics. Mo ..., which is more general addition of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistics
Linguistics is the scientific study of language. The areas of linguistic analysis are syntax (rules governing the structure of sentences), semantics (meaning), Morphology (linguistics), morphology (structure of words), phonetics (speech sounds and equivalent gestures in sign languages), phonology (the abstract sound system of a particular language, and analogous systems of sign languages), and pragmatics (how the context of use contributes to meaning). Subdisciplines such as biolinguistics (the study of the biological variables and evolution of language) and psycholinguistics (the study of psychological factors in human language) bridge many of these divisions. Linguistics encompasses Outline of linguistics, many branches and subfields that span both theoretical and practical applications. Theoretical linguistics is concerned with understanding the universal grammar, universal and Philosophy of language#Nature of language, fundamental nature of language and developing a general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammaticalisation
Grammaticalization (also known as grammatization or grammaticization) is a linguistic process in which words change from representing objects or actions to serving grammatical functions. Grammaticalization can involve content words, such as nouns and verbs, developing into new function words that express grammatical relationships among other words in a sentence. This may happen rather than speakers deriving such new function words from (for example) existing bound, inflectional constructions. For example, the Old English verb 'to want', 'to wish' has become the Modern English auxiliary verb ''will'', which expresses intention or simply futurity. Some concepts are often grammaticalized; others, such as evidentiality, less frequently. In explaining this process, linguistics distinguishes between two types of linguistic items: * lexical items or content words, which carry specific lexical meaning * grammatical items or function words, which serve mainly to express grammatical re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronoun
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (Interlinear gloss, glossed ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the part of speech, parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Sub-types include personal pronoun, personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive pronoun, reflexive and reciprocal pronoun, reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative pronoun, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora (linguistics), anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent (grammar), antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Preposition
Adpositions are a part of speech, class of words used to express spatial or temporal relations (''in, under, towards, behind, ago'', etc.) or mark various thematic relations, semantic roles (''of, for''). The most common adpositions are prepositions (which precede their complement) and postpositions (which follow their complement). An adposition typically combines with a noun phrase, this being called its complement (grammar), complement, or sometimes object (grammar), object. English language, English generally has prepositions rather than postpositions – words such as ''in, under'' and ''of'' precede their objects, such as "in England", "under the table", "of Jane" – although there are a few exceptions including ''ago'' and ''notwithstanding'', as in "three days ago" and "financial limitations notwithstanding". Some languages that use a different word order have postpositions instead (like Turkic languages) or have both types (like Finnish language, Finnish). The phrase form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflection
In linguistic Morphology (linguistics), morphology, inflection (less commonly, inflexion) is a process of word formation in which a word is modified to express different grammatical category, grammatical categories such as grammatical tense, tense, grammatical case, case, grammatical voice, voice, grammatical aspect, aspect, grammatical person, person, grammatical number, number, grammatical gender, gender, grammatical mood, mood, animacy, and definiteness. The inflection of verbs is called ''grammatical conjugation, conjugation'', while the inflection of nouns, adjectives, adverbs, etc. can be called ''declension''. An inflection expresses grammatical categories with affixation (such as prefix, suffix, infix, circumfix, and transfix), apophony (as Indo-European ablaut), or other modifications. For example, the Latin verb ', meaning "I will lead", includes the suffix ', expressing person (first), number (singular), and tense-mood (future indicative or present subjunctive). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Word
In grammar, a part of speech or part-of-speech (Abbreviation, abbreviated as POS or PoS, also known as word class or grammatical category) is a category of words (or, more generally, of lexical items) that have similar grammar, grammatical properties. Words that are assigned to the same part of speech generally display similar syntax, syntactic behavior (they play similar roles within the grammatical structure of sentences), sometimes similar morphology (linguistics), morphological behavior in that they undergo inflection for similar properties and even similar semantic behavior. Commonly listed English language, English parts of speech are noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, preposition, conjunction (grammar), conjunction, interjection, Numeral (linguistics), numeral, article (grammar), article, and determiner. Other terms than ''part of speech''—particularly in modern linguistics, linguistic classifications, which often make more precise distinctions than the traditional sc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Word
In linguistics, function words (also called functors) are words that have little lexical meaning or have ambiguous meaning and express grammatical relationships among other words within a sentence, or specify the attitude or mood of the speaker. They signal the structural relationships that words have to one another and are the glue that holds sentences together. Thus they form important elements in the structures of sentences. Words that are not function words are called ''content words'' (or open class words, ''lexical words,'' or ''autosemantic words'') and include nouns, most verbs, adjectives, and most adverbs, although some adverbs are function words (like ''then'' and ''why''). Dictionaries define the specific meanings of content words but can describe only the general usages of function words. By contrast, grammars describe the use of function words in detail but treat lexical words only in general terms. Since it was first proposed in 1952 by C. C. Fries, the distinguis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexicalisation
In linguistics, lexicalization is the process of adding words, set phrases, or word patterns to a language's lexicon. Whether ''word formation'' and ''lexicalization'' refer to the same process is controversial within the field of linguistics. Most linguists agree that there is a distinction, but there are many ideas of what the distinction is. Lexicalization may be simple, for example borrowing a word from another language, or more involved, as in calque or loan translation, wherein a foreign phrase is translated literally, as in ''marché aux puces'', or in English, flea market. Other mechanisms include compounding, abbreviation, and blending. Particularly interesting from the perspective of historical linguistics is the process by which ''ad hoc'' phrases become set in the language, and eventually become new words (see lexicon). Lexicalization contrasts with grammaticalization, and the relationship between the two processes is subject to some debate. In psycholinguistics I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |