|
Umpolung
In organic chemistry, umpolung () or polarity inversion is the chemical modification of a functional group with the aim of the reversal of Chemical polarity, polarity of that group. This modification allows secondary reactions of this functional group that would otherwise not be possible. The concept was introduced by D. Seebach (hence the German word for reversed polarity) and E.J. Corey. Polarity analysis during retrosynthetic analysis tells a chemist when umpolung tactics are required to synthesize a target molecule. Introduction The vast majority of important organic molecules contain heteroatoms, which polarize carbon skeletons by virtue of their electronegativity. Therefore, in standard organic reactions, the majority of new bonds are formed between atoms of opposite polarity. This can be considered to be the "normal" mode of reactivity. One consequence of this natural polarization of molecules is that 1,3- and 1,5- heteroatom substituted carbon skeletons are extremely eas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzoin Condensation
In organic chemistry, the benzoin addition is an addition reaction involving two aldehydes (). The reaction generally occurs between aromatic compound, aromatic aldehydes or glyoxals (), and results in formation of an acyloin (). In the classic example, benzaldehyde is converted to Benzoin (organic compound), benzoin (). The benzoin condensation was first reported in 1832 by Justus von Liebig and Friedrich Wöhler during their research on almond, bitter almond oil. The catalytic version of the reaction involving cyanide was developed by Nikolay Zinin in the late 1830s. Reaction mechanism The reaction is catalysis, catalyzed by nucleophile, nucleophiles such as a cyanide or an persistent carbene, N-heterocyclic carbene (usually Thiazolium salt, thiazolium salts). The reaction mechanism was proposed in 1903 by Arthur Lapworth, A. J. Lapworth. In the first step in this reaction, the cyanide anion (as sodium cyanide) reacts with the aldehyde in a nucleophilic addition. Rearrangemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
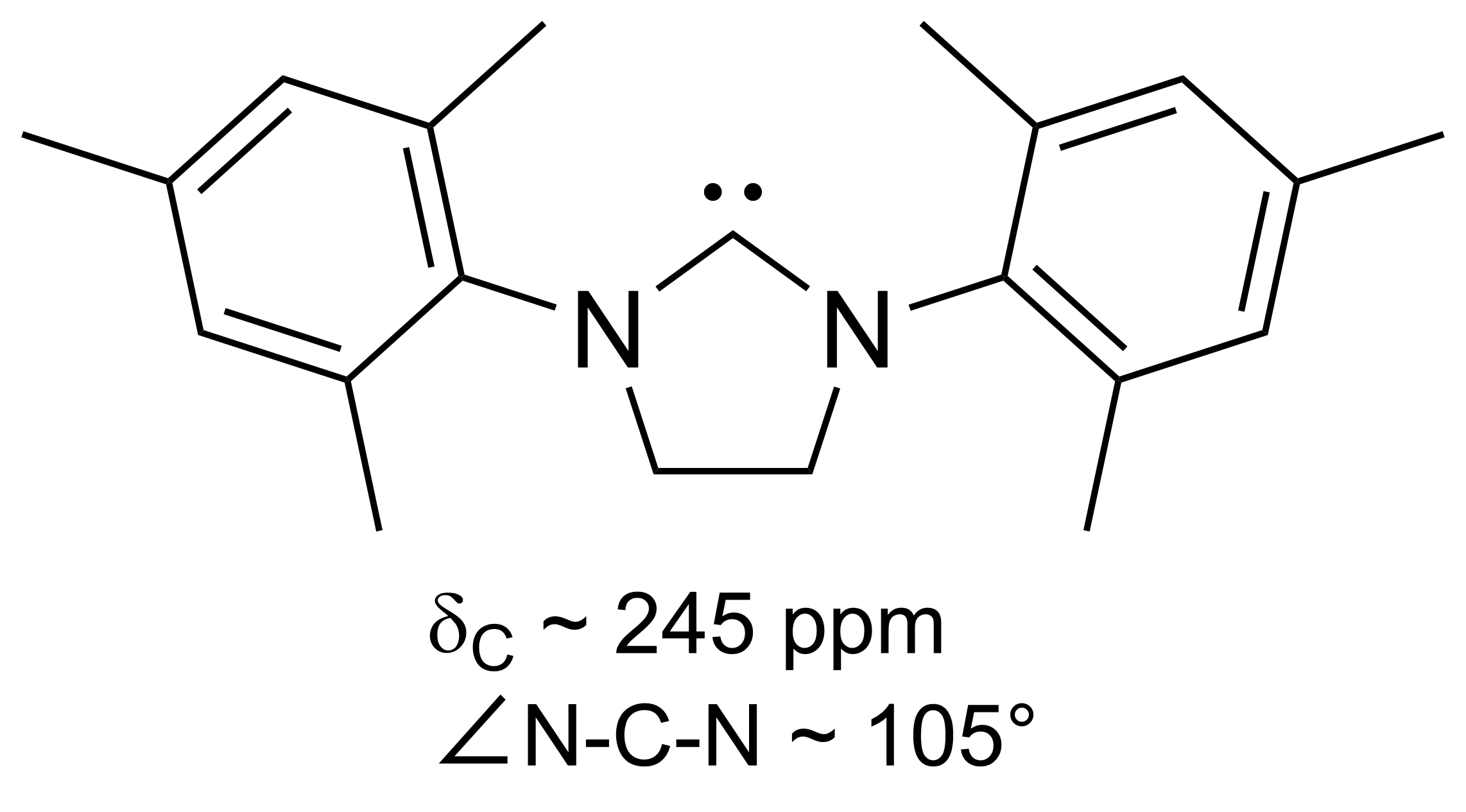
N-heterocyclic Carbene
A persistent carbene (also known as stable carbene) is an organic molecule whose natural resonance structure has a carbon atom with octet rule, incomplete octet (a carbene), but does not exhibit the tremendous instability typically associated with such moieties. The best-known examples and by far largest subgroup are the ''N''-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) (sometimes called Arduengo carbenes), in which nitrogen atoms flank the formal carbene. Modern theoretical analysis suggests that the term "persistent carbene" is in fact a misnomer. Persistent carbenes do not in fact have a carbene electronic structure in their ground state, but instead an ylide stabilized by Aromaticity, aromatic resonance or steric shielding. Excitation to a carbene structure then accounts for the carbene-like dimerization that some persistent carbenes undergo over the course of days. Persistent carbenes in general, and Arduengo carbenes in particular, are popular ligands in organometallic chemistry. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiamine
Thiamine, also known as thiamin and vitamin B1, is a vitamin – an Nutrient#Micronutrients, essential micronutrient for humans and animals. It is found in food and commercially synthesized to be a dietary supplement or medication. Phosphorylated forms of thiamine are required for some Metabolism, metabolic reactions, including the breakdown of Carbohydrate metabolism, glucose and amino acids. Food sources of thiamine include whole grains, legumes, and some meats and fish. Refined grain, Grain processing removes much of the vitamin content, so in many countries cereals and flours are food fortification, enriched with thiamine. Supplements and medications are available to treat and prevent thiamine deficiency and the disorders that result from it such as Thiamine deficiency#Dry beriberi, beriberi and Wernicke encephalopathy. They are also used to treat maple syrup urine disease and Leigh syndrome. Supplements and medications are typically taken Route of administration#Oral ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persistent Carbene
A persistent carbene (also known as stable carbene) is an organic molecule whose natural resonance structure has a carbon atom with octet rule, incomplete octet (a carbene), but does not exhibit the tremendous instability typically associated with such moieties. The best-known examples and by far largest subgroup are the ''N''-heterocyclic carbenes (NHC) (sometimes called Arduengo carbenes), in which nitrogen atoms flank the formal carbene. Modern theoretical analysis suggests that the term "persistent carbene" is in fact a misnomer. Persistent carbenes do not in fact have a carbene electronic structure in their ground state, but instead an ylide stabilized by Aromaticity, aromatic resonance or steric shielding. Excitation to a carbene structure then accounts for the carbene-like dimerization that some persistent carbenes undergo over the course of days. Persistent carbenes in general, and Arduengo carbenes in particular, are popular ligands in organometallic chemistry. Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the science, scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic matter, organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, J.; Greeves, N. and Warren, S. (2012) ''Organic Chemistry''. Oxford University Press. pp. 1–15. . Study of structure determines their structural formula. Study of properties includes Physical property, physical and Chemical property, chemical properties, and evaluation of Reactivity (chemistry), chemical reactivity to understand their behavior. The study of organic reactions includes the organic synthesis, chemical synthesis of natural products, drugs, and polymers, and study of individual organic molecules in the laboratory and via theoretical (in silico) study. The range of chemicals studied chemistry includes hydrocarbons (compounds containing only carbon and hydrogen) as well as compounds based on carbon, but a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
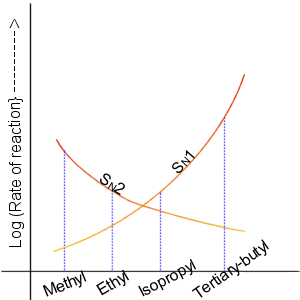
Nucleophilic Displacement
In chemistry, a nucleophilic substitution (SN) is a class of chemical reactions in which an electron-rich chemical species (known as a nucleophile) replaces a functional group within another electron-deficient molecule (known as the electrophile). The molecule that contains the electrophile and the leaving functional group is called the substrate. The most general form of the reaction may be given as the following: :\text\mathbf + \ce + \text\mathbf The electron pair (:) from the nucleophile (Nuc) attacks the substrate () and bonds with it. Simultaneously, the leaving group (LG) departs with an electron pair. The principal product in this case is . The nucleophile may be electrically neutral or negatively charged, whereas the substrate is typically neutral or positively charged. An example of nucleophilic substitution is the hydrolysis of an alkyl bromide, R-Br under basic conditions, where the attacking nucleophile is hydroxyl () and the leaving group is bromide (). :OH ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethylene Glycol
Ethylene glycol ( IUPAC name: ethane-1,2-diol) is an organic compound (a vicinal diol) with the formula . It is mainly used for two purposes: as a raw material in the manufacture of polyester fibers and for antifreeze formulations. It is an odorless, colorless, flammable, viscous liquid. It has a sweet taste but is toxic in high concentrations. This molecule has been observed in outer space. Production Industrial routes Ethylene glycol is produced from ethylene (ethene), via the intermediate ethylene oxide. Ethylene oxide reacts with water to produce ethylene glycol according to the chemical equation : This reaction can be catalyzed by either acids or bases or can occur at neutral pH under elevated temperatures. The highest yields of ethylene glycol occur at acidic or neutral pH with a large excess of water. Under these conditions, ethylene glycol yields of 90% can be achieved. The major byproducts are the oligomers diethylene glycol, triethylene glycol, and tetra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the publishing house of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world. Its first book was printed in Oxford in 1478, with the Press officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586. It is the second-oldest university press after Cambridge University Press, which was founded in 1534. It is a department of the University of Oxford. It is governed by a group of 15 academics, the Delegates of the Press, appointed by the Vice Chancellor, vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, Oxford, Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho, Oxford, Jericho. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halonium
A halonium ion is any onium ion containing a halogen atom carrying a positive charge. This cation has the general structure where X is any halogen and no restrictions on R, this structure can be cyclic or an open chain molecular structure. Halonium ions formed from fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine are called fluoronium, chloronium, bromonium, and iodonium, respectively. The 3-membered cyclic variety commonly proposed as intermediates in electrophilic halogenation may be called haliranium ions, using the Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature system. Structure The simplest halonium ions are of the structure (X = F, Cl, Br, I). Many halonium ions have a three-atom cyclic structure, similar to that of an epoxide, resulting from the formal addition of a halogenium ion to a C=C double bond, as when a halogen is added to an alkene. The formation of 5-membered halonium ions (e.g., chlorolanium, bromolanium ions) via neighboring group participation is also well studied. Diaryliodonium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxide
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether, where the ether forms a three-atom ring: two atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen. This triangular structure has substantial ring strain, making epoxides highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an ''epoxy''. However, few if any of the epoxy groups i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclopropane
Cyclopropane is the cycloalkane with the molecular formula (CH2)3, consisting of three methylene groups (CH2) linked to each other to form a triangular ring. The small size of the ring creates substantial ring strain in the structure. Cyclopropane itself is mainly of theoretical interest but many of its derivatives - cyclopropanes - are of commercial or biological significance. Cyclopropane was used as a clinical inhalational anesthetic from the 1930s through the 1980s. The substance's high flammability poses a risk of fire and explosions in operating rooms due to its tendency to accumulate in confined spaces, as its density is higher than that of air. History Cyclopropane was discovered in 1881 by August Freund, who also proposed the correct structure for the substance in his first paper. Freund treated 1,3-Dibromopropane, 1,3-dibromopropane with sodium, causing an intramolecular Wurtz reaction leading directly to cyclopropane. The yield of the reaction was improved by Gustavson ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epoxide Opening
In organic chemistry, an epoxide is a cyclic ether, where the ether forms a three-atom ring: two atoms of carbon and one atom of oxygen. This triangular structure has substantial ring strain, making epoxides highly reactive, more so than other ethers. They are produced on a large scale for many applications. In general, low molecular weight epoxides are colourless and nonpolar, and often volatile. Nomenclature A compound containing the epoxide functional group can be called an epoxy, epoxide, oxirane, and ethoxyline. Simple epoxides are often referred to as oxides. Thus, the epoxide of ethylene (C2H4) is ethylene oxide (C2H4O). Many compounds have trivial names; for instance, ethylene oxide is called "oxirane". Some names emphasize the presence of the epoxide functional group, as in the compound ''1,2-epoxyheptane'', which can also be called ''1,2-heptene oxide''. A polymer formed from epoxide precursors is called an ''epoxy''. However, few if any of the epoxy groups in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |