|
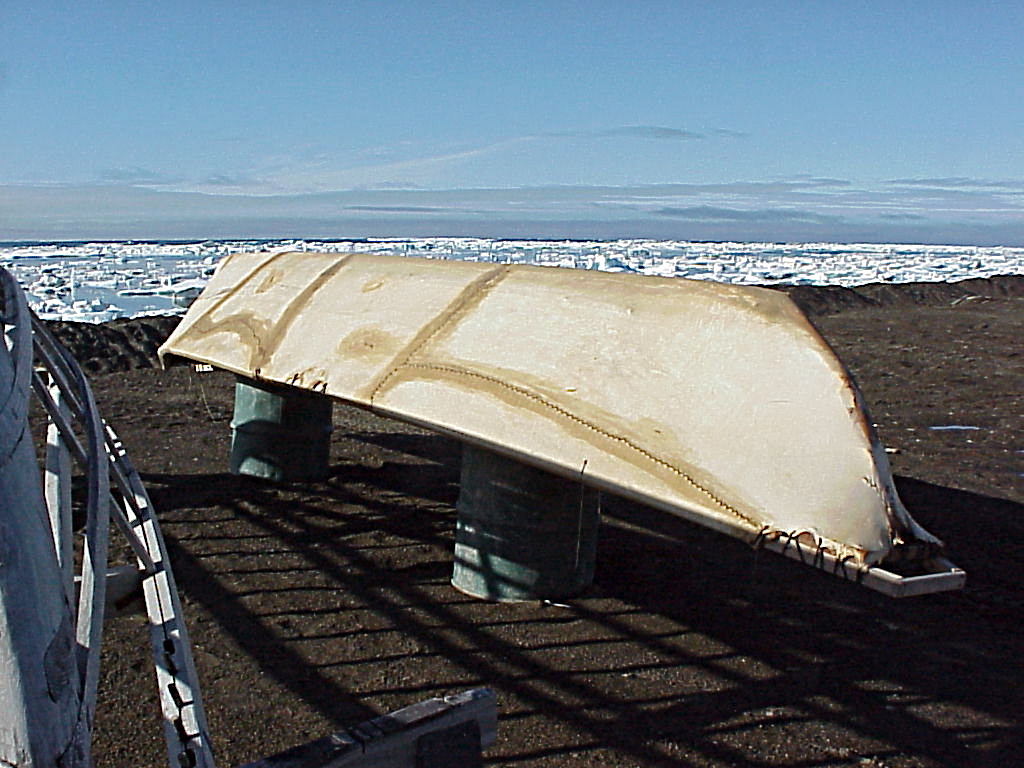
Umiaq
The umiak, umialak, umiaq, umiac, oomiac, oomiak, ongiuk, or anyak is a type of open skin boat, used by the Yupik and Inuit, and was originally found in all coastal areas from Siberia to Greenland. First used in Thule times, it has traditionally been used in summer, for moving people and possessions to seasonal hunting grounds, and for hunting whales and walrus.Umiaks at the Although the umiak was usually propelled by oars (women) or paddles (men), sails—sometimes made from seal s—were also used, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inuit
Inuit (singular: Inuk) are a group of culturally and historically similar Indigenous peoples traditionally inhabiting the Arctic and Subarctic regions of North America and Russia, including Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories, Yukon (traditionally), Alaska, and the Chukotsky District of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Inuit languages are part of the Eskaleut languages, also known as Inuit-Yupik-Unangan, and also as Eskimo–Aleut. Canadian Inuit live throughout most of Northern Canada in the territory of Nunavut, Nunavik in the northern third of Quebec, the Nunatsiavut in Labrador, and in various parts of the Northwest Territories and Yukon (traditionally), particularly around the Arctic Ocean, in the Inuvialuit Settlement Region. These areas are known, by Inuit Tapiriit Kanatami and the Government of Canada, as Inuit Nunangat. In Canada, sections 25 and 35 of the Constitution Act of 1982 classify Inuit as a distinctive group of Abo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hans Egede
Hans Poulsen Egede (31 January 1686 – 5 November 1758) was a Denmark–Norway, Danish-Norwegian Lutheran missionary priest who launched mission efforts to Greenland, which led him to be styled the Apostle of Greenland. He established a successful mission among the Inuit and is credited with revitalizing Danish-Norwegian interest in the island after contact had been broken for about 300 years. He founded Greenland's capital Godthåb, now known as Nuuk. Background Hans Egede was born into the home of a Danish-born civil servant, the priest son Povel Hansen Egede, and the Norwegian-born Kirsten Jensdatter Hind, daughter of a local merchant, in Harstad Municipality, Harstad, Norway, nearly north of the Arctic Circle. His paternal grandfather had been a vicar in Vester Egede on southern Zealand (Denmark), Zealand, Denmark. Hans was schooled by an uncle, a clergyman in a local Lutheran Church. In 1704 he travelled to Copenhagen to enter the University of Copenhagen, where he earned ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five oceanic divisions. It spans an area of approximately and is the coldest of the world's oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, although some oceanographers call it the Arctic Mediterranean Sea. It has also been described as an estuary of the Atlantic Ocean. It is also seen as the northernmost part of the all-encompassing world ocean. The Arctic Ocean includes the North Pole region in the middle of the Northern Hemisphere and extends south to about 60°N. The Arctic Ocean is surrounded by Eurasia and North America, and the borders follow topographic features: the Bering Strait on the Pacific side and the Greenland Scotland Ridge on the Atlantic side. It is mostly covered by sea ice throughout the year and almost completely in winter. The Arctic Ocean's surface temperature and salinity vary seasonally as the ice cover melts and freezes; its salinity is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utqiaġvik, Alaska
Utqiagvik ( ; , ), formerly known as Barrow ( ), is the borough seat and largest city of the North Slope Borough in the U.S. state of Alaska. Located north of the Arctic Circle, it is one of the northernmost cities and towns in the world and the northernmost in the United States, with nearby Point Barrow as the country's northernmost point. Utqiaġvik's population was 4,927 at the 2020 census, an increase from 4,212 in 2010. It is the 12th-most populated city in Alaska. Name The location has been home to the Iñupiat, an indigenous Inuit ethnic group, for more than 1,500 years. The city's Iñupiaq name refers to a place for gathering wild roots. It is derived from the Iñupiat word , also used for '' Claytonia tuberosa'' (" Eskimo potato"). The name was first recorded by European explorers in 1853 as "Ot-ki-a-wing" by Commander Rochfort Maguire, Royal Navy. John Simpson's native map dated 1855 has the name "Otkiawik", which was later misprinted on a British Admiralty char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
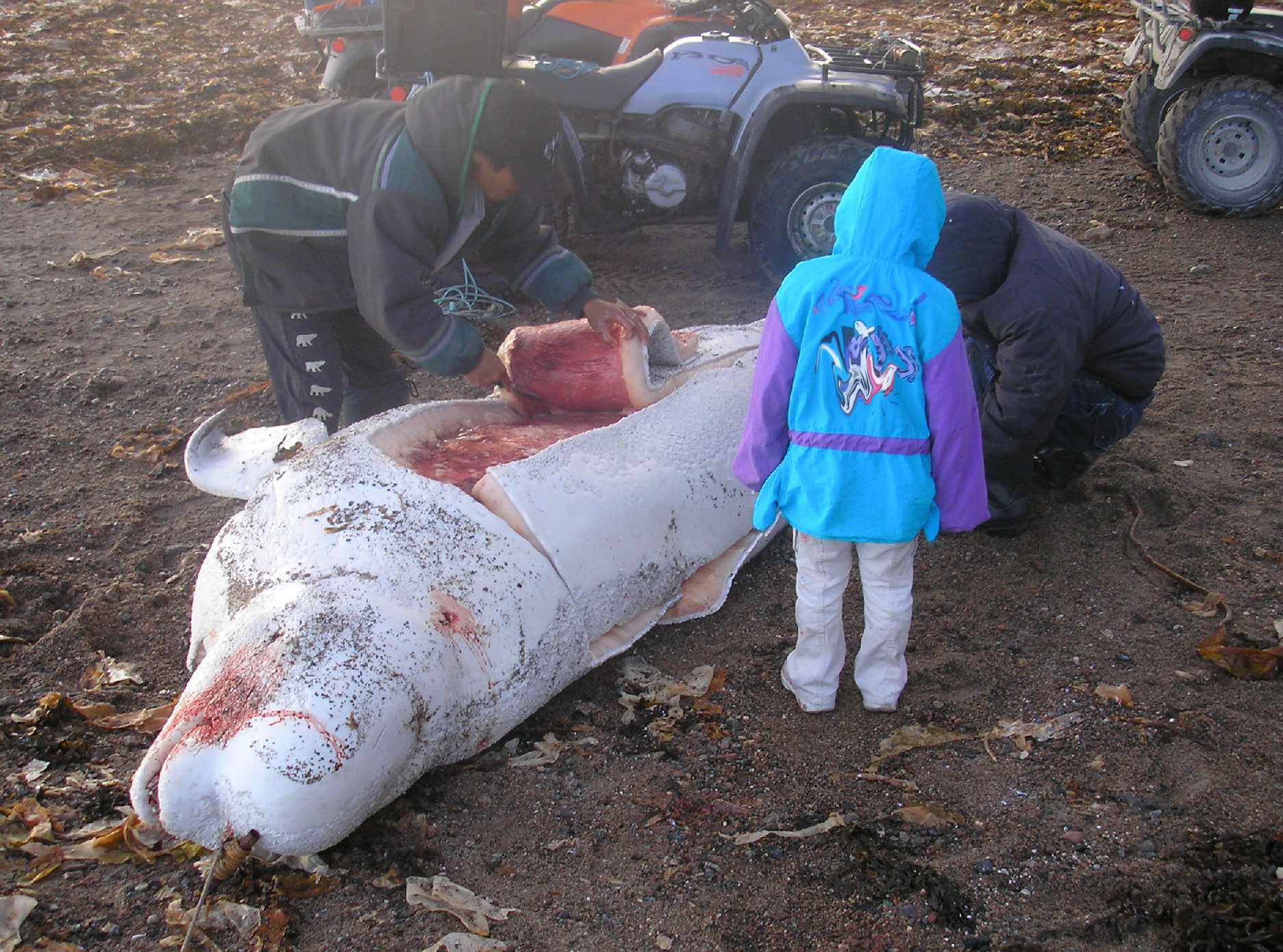
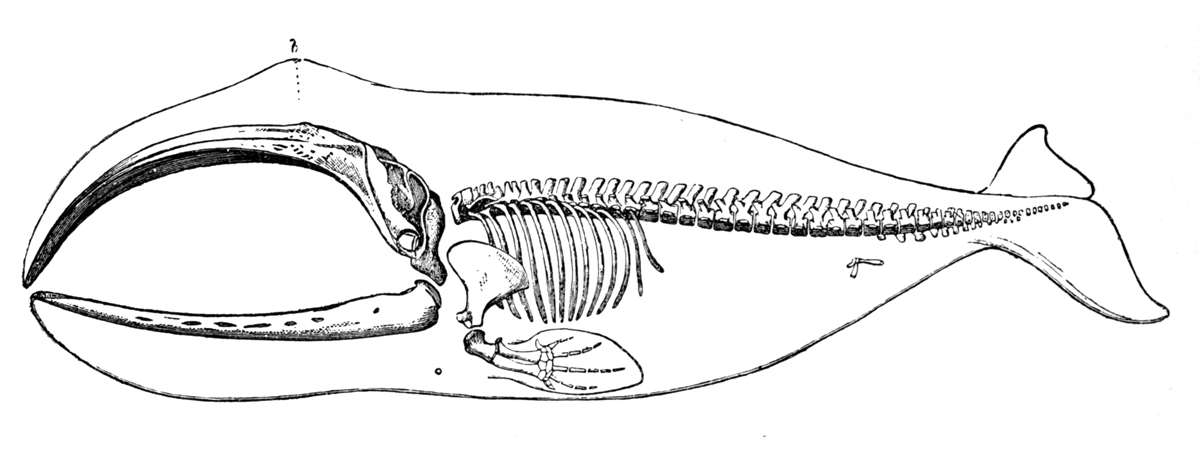
Bowhead Whale
The bowhead whale (''Balaena mysticetus''), sometimes called the Greenland right whale, Arctic whale, and polar whale, is a species of baleen whale belonging to the family Balaenidae and is the only living representative of the genus '' Balaena''. It is the only baleen whale endemic to the Arctic and subarctic waters, and is named after its characteristic massive triangular skull, which it uses to break through Arctic ice. Bowheads have the largest mouth of any animal representing almost one-third of the length of the body, the longest baleen plates with a maximum length of , and may be the longest-lived mammals, with the ability to reach an age of more than 200 years. The bowhead was an early whaling target. Their population was severely reduced before a 1966 moratorium was passed to protect the species. Of the five stocks of bowhead populations, three are listed as "endangered", one as " vulnerable", and one as "lower risk, conservation dependent" according to the IUCN Red ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (or aluminum in North American English) is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol Al and atomic number 13. It has a density lower than that of other common metals, about one-third that of steel. Aluminium has a great affinity towards oxygen, passivation (chemistry), forming a protective layer of aluminium oxide, oxide on the surface when exposed to air. It visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, magnetism, nonmagnetic, and ductility, ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al, which is highly abundant, making aluminium the abundance of the chemical elements, 12th-most abundant element in the universe. The radioactive decay, radioactivity of aluminium-26, 26Al leads to it being used in radiometric dating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arctic Ice Pack
The Arctic ice pack is the sea ice cover of the Arctic Ocean and its vicinity. The Arctic ice pack undergoes a regular seasonal cycle in which ice melts in spring and summer, reaches a minimum around mid-September, then increases during fall and winter. Summer ice cover in the Arctic is about 50% of winter cover. Some of the ice survives from one year to the next. Currently, 28% of Arctic Oceanic basin, basin sea ice is Sea ice#Old sea ice, multi-year ice, thicker than seasonal ice: up to thick over large areas, with ridges up to thick. Besides the regular seasonal cycle there has been an underlying trend of Arctic sea ice decline, declining sea ice in the Arctic in recent decades as well. Climatic importance Energy balance effects Sea ice has an important effect on the heat balance of the Polar regions of Earth, polar oceans, since it insulates the (relatively) warm ocean from the much colder air above, thus reducing heat loss from the oceans. Sea ice is highly albedo, r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snowmobile
A snowmobile, also known as a snowmachine (chiefly Alaskan), motor sled (chiefly Canadian), motor sledge, skimobile, snow scooter, or simply a sled is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow. Their engines normally drive a continuous track at the rear, while skis at the front provide directional control. The earliest snowmobiles were powered by readily available industrial four-stroke, air-cooled engines. These would quickly be replaced by lighter and more powerful two-stroke gasoline internal combustion engines and since the mid-2000s four-stroke engines had re-entered the market. The challenges of cross-country transportation in the winter led to the invention of an all-terrain vehicle specifically designed for travel across deep snow where other vehicles foundered. , the snowmobile market has been shared between the four large North American makers (Bombardier Recreational Products (BRP), Arctic Cat, Yamaha, and Polaris) and some specialized m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aboriginal Whaling
Aboriginal whaling or indigenous whaling is the hunting of whales by indigenous peoples recognised by either IWC (International Whaling Commission) or the hunting is considered as part of indigenous activity by the country. It is permitted under international regulation, but in some countries remains a contentious issue. (The hunting of smaller cetaceans is covered at Dolphin drive hunting.) It is usually considered part of the subsistence economy. In some places, whaling has been superseded by whale watching instead. This article deals with communities that continue to hunt; details about communities that have ended the practice may be found in History of whaling. International regulation Under the terms of the 1986 moratorium, the International Whaling Commission allows the activity to be carried out by aboriginal groups if it occurs on a subsistence basis, similar to subsistence fishing. This Aboriginal Subsistence Whaling is restricted to native peoples and others working ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |