|
Umatilla (tribe)
The Umatilla are a Sahaptin-speaking Native American tribe who traditionally inhabited the Columbia Plateau region of the northwestern United States, along the Umatilla and Columbia rivers."Umatilla," in Barbara A. Leitch, ''A Concise Dictionary of Indian Tribes of North America.'' Algonac, MI: Reference Publications, Inc., 1979; pp. 490-491. The Umatilla people are called Imatalamłáma, a Umatilla person is called Imatalamłá (with orthographic ł representing IPA /ɬ/). Some sources say that ''Umatilla'' is derived from ''imatilám-hlama'': ''hlama'' means 'those living at' or 'people of' and there is an ongoing debate about the meaning of ''imatilám'', but it is said to be an island in the Columbia River. B. Rigsby and N. Rude mention the village of ''ímatalam'' that was situated at the mouth of the Umatilla River and where the language was spoken. The Nez Perce refer to the Umatilla people as ''hiyówatalampoo'' (Aoki (1994:171)). History Early development The Umatilla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Umatilla Language
Umatilla (Tamalúut or Imatalamłaamí Sɨ́nwit) is a variety of Southern Sahaptin, part of the Sahaptian subfamily of the Plateau Penutian group. It was spoken during late aboriginal times along the Columbia River and is therefore also called Columbia River Sahaptin. It is currently spoken as a first language by a few dozen elders and some adults in the Umatilla Reservation in Oregon. Some sources say that ''Umatilla'' is derived from ''imatilám-hlama'': ''hlama'' means 'those living at' or 'people of' and there is an ongoing debate about the meaning of ''imatilám'', but it is said to be an island in the Columbia River. B. Rigsby and N. Rude mention the village of ''ímatalam'' that was situated at the mouth of the Umatilla River and where the language was spoken. The Umatillas pronounce the word ''ímatalam''. A Umatilla person is called ''imatalamłá'' (with orthographic ł representing IPA /ɬ/) and the Umatilla people are called ''imatalamłáma''. The Nez Perce ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penutian Language
Penutian is a proposed grouping of language families that includes many Native American languages of western North America, predominantly spoken at one time in British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and California. The existence of a Penutian stock or phylum has been the subject of debate among specialists. Even the unity of some of its component families has been disputed. Some of the problems in the comparative study of languages within the phylum are the result of their early extinction and limited documentation. Some of the more recently proposed subgroupings of Penutian have been convincingly demonstrated. The Miwokan and the Costanoan languages have been grouped into a Utian language family by Catherine Callaghan. Callaghan has more recently provided evidence supporting a grouping of Utian and Yokutsan into a Yok-Utian family. There also seems to be convincing evidence for the Plateau Penutian grouping (originally named ''Shahapwailutan'' by J. N. B. Hewitt and John W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
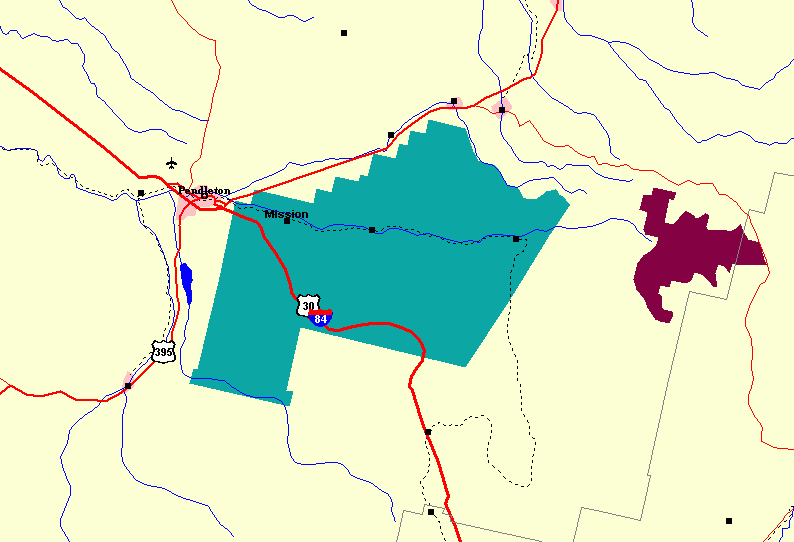
Umatilla Indian Reservation
The Umatilla Indian Reservation is an Indian reservation in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. It was created by The Treaty of 9 June 1855 between the United States and members of the Walla, Cayuse, and Umatilla tribes. It lies in northeastern Oregon, east of Pendleton. The reservation is mostly in Umatilla County, with a very small part extending south into Union County. It is managed by the three Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation. Located on the north side of the Blue Mountains, the reservation was established for two Sahaptin-speaking Native American tribes: the Umatilla and Walla Walla, and for the Cayuse, whose language, now extinct, was an isolate. All the tribes historically inhabited the Columbia Plateau region. The tribes share land and a governmental structure as part of their confederation. Geography, demographics and headquarters The reservation has a land area of and a tribal population of 2,927 as of the 2000 census. In ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Confederated Tribes Of The Umatilla Indian Reservation
The Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation are the federally recognized confederations of three Sahaptin-speaking Native Americans of the United States, Native American tribes who traditionally inhabited the Columbia River Plateau region: the Cayuse people, Cayuse, Umatilla people, Umatilla, and Walla Walla people, Walla Walla. When the leaders of the Walla Walla, Cayuse, and Umatilla peoples signed the Treaty of Walla Walla with the United States in 1855, they ceded of their homeland that is now northeastern Oregon and southeastern Washington (state), Washington. This was done in exchange for a Indian reservation, reservation of and the promise of annuities in the form of goods and supplies. The tribes share the Umatilla Indian Reservation, Reservation, which consists of in Umatilla County, in northeast Oregon state. The tribes have created a joint political structure as part of their confederation. The tribal offices are just east of Pendleton, Oregon. Almo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Reservation
An American Indian reservation is an area of land land tenure, held and governed by a List of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States#Description, U.S. federal government-recognized Native American tribal nation, whose government is Tribal sovereignty in the United States, autonomous, subject to regulations passed by the United States Congress and administered by the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs, and not to the state governments of the United States, U.S. state government in which it is located. Some of the country's 574 List of Native American Tribal Entities, federally recognized tribes govern more than one of the 326 List of Indian reservations in the United States, Indian reservations in the United States, while some share reservations, and others have no reservation at all. Historical piecemeal land allocations under the Dawes Act facilitated sales to non–Native Americans, resulting in some reservations becoming severely fragmented, with pie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walla Walla Council (1855)
The Walla Walla Council (1855) was a meeting in the Pacific Northwest between the United States and sovereign tribal nations of the Cayuse, Nez Perce, Umatilla, Walla Walla, and Yakama. The council occurred on May 29 – June 11; the treaties signed at this council on June 9 were ratified by the U.S. Senate four years later in 1859. These treaties codified the constitutional relationship between the people living on the Nez Perce, Umatilla, and Yakama reservations; it was one of the earliest treaties obtained in the Pacific Northwest. Washington Territory's first governor Isaac I. Stevens secured this treaty, allowing larger portions of the land to be given to the two largest and most powerful tribes: Yakama and Nez Perce; these reservations encompassed most of their traditional hunting grounds. The smaller tribes moved to the smaller of the three reservations. Stevens was able to acquire of land. The United States government later violated these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infectious
infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune systems. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Treatment for infections depends on the type of pathogen involved. Common medications include: * Antibiotics for bacterial infections. * Antivirals for viral infections. * Antifungals for fungal infections. * Antiprotozoals for protozoan infections. * Antihelminthics for infections caused by parasitic worms. Infectious diseases remain a significant global health concern, causing approximately 9.2 million deaths in 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smallpox
Smallpox was an infectious disease caused by Variola virus (often called Smallpox virus), which belongs to the genus '' Orthopoxvirus''. The last naturally occurring case was diagnosed in October 1977, and the World Health Organization (WHO) certified the global eradication of the disease in 1980, making smallpox the only human disease to have been eradicated to date. The initial symptoms of the disease included fever and vomiting. This was followed by formation of ulcers in the mouth and a skin rash. Over a number of days, the skin rash turned into the characteristic fluid-filled blisters with a dent in the center. The bumps then scabbed over and fell off, leaving scars. The disease was transmitted from one person to another primarily through prolonged face-to-face contact with an infected person or rarely via contaminated objects. Prevention was achieved mainly through the smallpox vaccine. Once the disease had developed, certain antiviral medications could poten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yakima People
The Yakama are a Native American tribe with nearly 10,851 members, based primarily in eastern Washington state. Yakama people today are enrolled in the federally recognized tribe, the Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation. Their Yakama Indian Reservation, along the Yakima River, covers an area of approximately 1.2 million acres (5,260 km2). Today the nation is governed by the Yakama Tribal Council, which consists of representatives of 14 tribes. Many Yakama people engage in ceremonial, subsistence, and commercial fishing for salmon, steelhead, and sturgeon in the Columbia River and its tributaries, including within land ceded by the tribe to the United States. Their right to fish in their former territory is protected by treaties and was re-affirmed in late 20th-century court cases such as ''United States v. Washington'' (known as the Boldt Decision, 1974) and ''United States v. Oregon'' ('' Sohappy v. Smith'', 1969), though more than a century of U.S. indust ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palouse People
The Palouse are a Sahaptin tribe recognized in the Treaty of 1855 with the United States along with the Yakama. It was negotiated at the Walla Walla Council (1855), 1855 Walla Walla Council. A variant spelling is Palus. Today they are enrolled in the Federally recognized tribe, federally recognized Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation and some are also represented by the Colville Confederated Tribes, the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation and Nez Perce, Nez Perce Tribe. Ethnography The people are one of the Sahaptin language, Sahaptin-speaking groups of Native Americans of the United States, Native Americans living on the Columbia Plateau in eastern Washington (state), Washington, northeastern Oregon, and North Central Idaho: these included the Nez Perce people, Nez Percé, Cayuse people, Cayuse, Walla Walla (tribe), Walla Walla, Umatilla people, Umatilla and the Yakima people, Yakama. The Palouse (Palus) territory extends from the confluence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Walla Walla (tribe)
Walla Walla (), Walawalałáma ("People of Wallula, Washington, Walula region along Walla Walla River"), sometimes Walúulapam, are a Sahaptin people, Sahaptin Indigenous people of the Northwest Plateau. The duplication in their name expresses the diminutive form. The name ''Walla Walla'' is translated several ways but most often as "many waters". Many of the Walla Walla live on the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation. They share land and a governmental structure with the Cayuse people, Cayuse and the Umatilla tribes as part of the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla. The Indian reservation, reservation is located in the area of Pendleton, Oregon, United States, near the Blue Mountains (Oregon), Blue Mountains. Some Walla Walla are also enrolled in the Federally recognized tribe, federally recognized Confederated Tribes and Bands of the Yakama Nation. History The people are a Sahaptin language, Sahaptin-speaking tribe that traditionally inhabited the interior C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cayuse People
The Cayuse are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American tribe in what is now the state of Oregon in the United States. The Cayuse tribe shares a Umatilla Indian Reservation, reservation and government in northeastern Oregon with the Umatilla people, Umatilla and the Walla Walla people, Walla Walla tribes as part of the Confederated Tribes of the Umatilla Indian Reservation. The reservation is located near Pendleton, Oregon, at the base of the Blue Mountains (Pacific Northwest), Blue Mountains. The Cayuse called themselves the Liksiyu in the Cayuse language. Originally located in present-day northeastern Oregon and southeastern Washington (state), Washington, they lived adjacent to territory occupied by the Nez Perce people, Nez Perce and had close associations with them. Like other Indigenous peoples of the Northwest Plateau, the Cayuse placed a high premium on warfare and were skilled horsemen. They developed the Cayuse horse, Cayuse pony. The Cayuse ceded most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |