|
Ululating
Ululation (, ), trilling or lele, is a long, wavering, high-pitched vocal sound resembling a Howl (sound), howl with a Trill (music), trilling quality. It is produced by emitting a high pitched loud voice accompanied with a rapid back and forth movement of the tongue and the uvula. Around the world Ululation is practiced either alone or as part of certain styles of singing, on various occasions of communal ritual events (like weddings) used to express strong emotion. Ululation is practised in all parts of Africa, the Middle East, Americas and as far east as Central Asia, Central and South Asia. It is also practiced in a few places in Europe among the diaspora community originating from these areas. Middle East Ululation is commonly used in Middle Eastern weddings. In the Arab world, ''zaghārīt'' (Arabic: زغاريت) is a ululation performed to honor someone. For example, zagharits are widely performed and documented in Egyptian movies featuring traditional Egyptian wedding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexico
''Lexico'' was a dictionary website that provided a collection of English and Spanish dictionaries produced by Oxford University Press (OUP), the publishing house of the University of Oxford. While the dictionary content on ''Lexico'' came from OUP, this website was operated by Dictionary.com, whose eponymous website hosts dictionaries by other publishers such as Random House. The website was closed and redirected to Dictionary.com on 26 August 2022. Before the Lexico site was launched, the ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' and ''New Oxford American Dictionary'' were hosted by OUP's own website ''Oxford Dictionaries Online'' (''ODO''), later known as ''Oxford Living Dictionaries''. The dictionaries' definitions have also appeared in Google Dictionary, Google definition search and the Dictionary (software), Dictionary application on macOS, among others, licensed through the Oxford Dictionaries API. History In the 2000s, OUP allowed access to content of the ''Compact Oxford Englis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simcha
''Simcha'' ( ; , ) is a Hebrew language, Hebrew word that means "gladness", or "joy", and is often used as a given name. Uses The concept of simcha is an important one in Jewish philosophy. A popular teaching by Rabbi Nachman of Breslov, a 19th-century Chassidic Rabbi, is "Mitzvah Gedolah Le'hiyot Besimcha Tamid", "it is a great mitzvah (commandment) to always be in a state of happiness". When a person is happy one is much more capable of serving God and going about one's daily activities than when depressed or upset. Jews often use ''simcha'' in its capacity as a Hebrew and Yiddish noun meaning festive occasion. The term is used for any happy occasion, such as a wedding, bar mitzvah or engagement. Holidays The day of Simchat Torah, "Rejoice in the Law", marks the completion and beginning of the annual cycle of reading the Torah. Other uses Simcha is also the name of a kosher beer from Saxony, Germany. It was also a slang term used in Jewish-American organized crime circles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
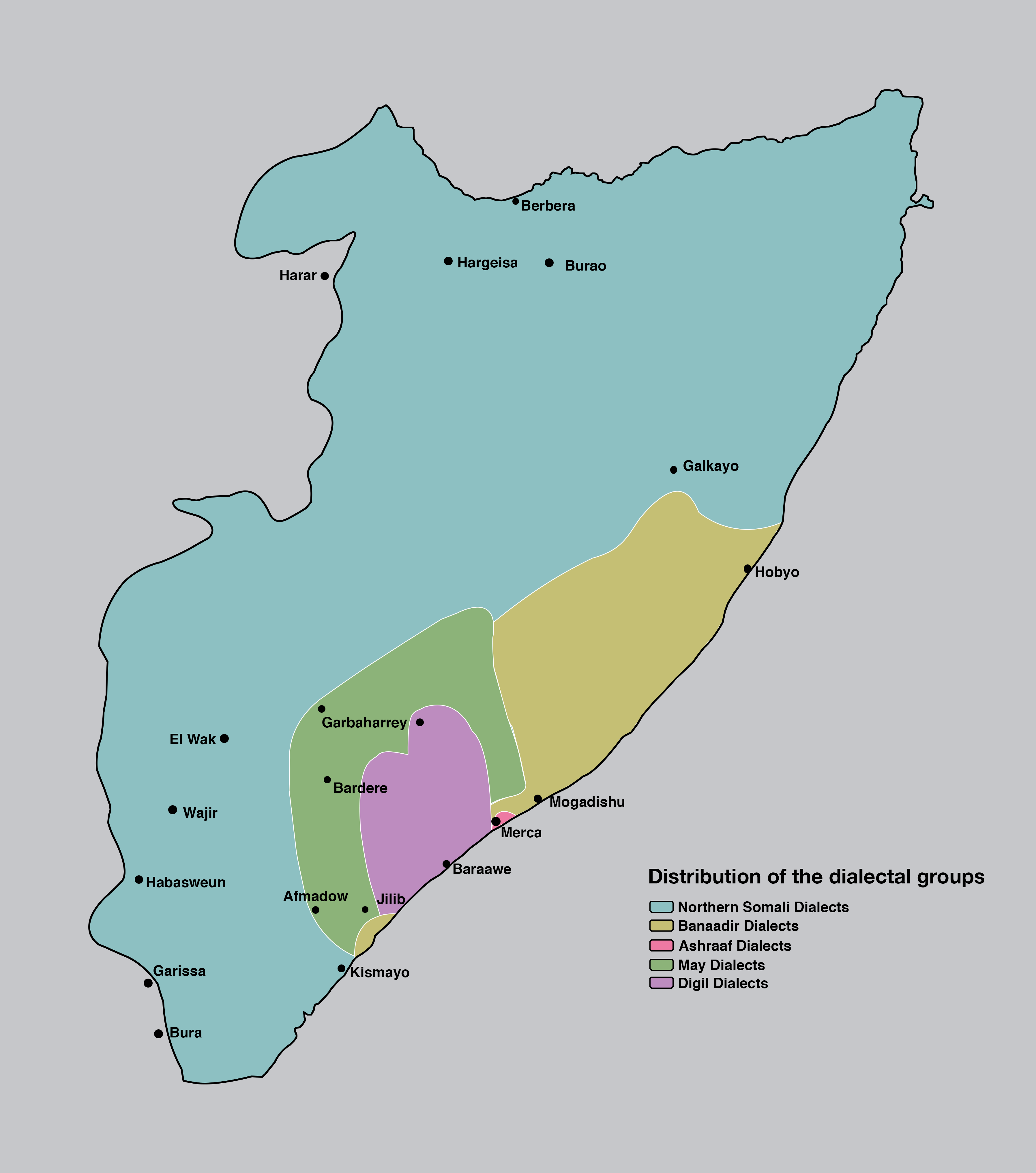
Somali Language
Somali is an Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language belonging to the Cushitic languages, Cushitic branch, primarily spoken by the Somalis, Somali people, native to Greater Somalia. It is an official language in Somalia, Somaliland, and Ethiopia; one of the two national languages in Djibouti; and a recognised minority language in Kenya. Somali is officially written in the Latin script (Somali Latin alphabet), with the Arabic script (Wadaad's writing) and several local scripts (Osmanya script, Osmanya, Kaddare script, Kaddare and Gadabuursi Somali Script, Borama scripts) being informally used.Lewis, I.M. (1958)The Gadabuursi Somali Script ''Bulletin of the School of Oriental and African Studies'', University of London, Vol. 21, pp. 134–156. Classification Somali is classified within the Cushitic branch of the Afroasiatic family, specifically, Lowland East Cushitic languages, Lowland East Cushitic in addition to Afar language, Afar and Saho language, Saho. Somali is the bes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Ethiopia
Ethiopian music is a term that can mean any music of Ethiopian origin, however, often it is applied to a genre, a distinct modal system that is pentatonic, with characteristically long intervals between some notes. The music of the Ethiopian Highlands uses a fundamental modal system called '' qenet'', of which there are four main modes: , , , and . Three additional modes are variations on the above: tezeta minor, bati major, and bati minor. Abatte Barihun, liner notes of the album Ras Deshen, 200. Some songs take the name of their qenet, such as tizita, a song of reminiscence. When played on traditional instruments, these modes are generally not tempered (that is, the pitches may deviate slightly from the Western-tempered tuning system), but when played on Western instruments such as pianos and guitars, they are played using the Western-tempered tuning system. Music in the Ethiopian highlands is generally monophonic or heterophonic. In certain southern areas, some music is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Music Of Eritrea
The music of Eritrea, is a diverse mix of traditional and popular styles originating from ancient to modern times. The nine major ethnic groups of Eritrea—Afar, Bilen, Hedareb, Kunama, Nara, Rashaida, Saho, Tigre and Tigrinya—celebrate autonomous music-making expressed through a rich heritage of vocalists, instrumentalists and activities within the country and throughout the international diaspora. The country's music is informed by a range of ethnolinguistic group dynamics in the region, by its shared pre-colonial history with and revolutionized independence from Ethiopia, and by its exposure to globalized American music in the mid-twentieth century. Notable musicians Notable Eritrean musicians were Edris Wad Amir, Ibrahim Wad Goret, Edris M. Ali, Zainab Bashir, Fatima Ibrahim, Engineer Asgedom Woldemichael, Wad Asheikh, Yemane Baria, Osman Abderrehim, Alamin Abdeletif and Atowe Birhan Segid. Yemane Baria wrote one political song, and he was in jail. Also of note is Berek ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P'ent'ay
P'ent'ay (from Geʽez: ) is an originally Amharic– Tigrinya language term for Pentecostal Christians. Today, the term refers to all Evangelical Protestant denominations and organisations in Ethiopian and Eritrean societies. Alternative terms include Ethiopian–Eritrean Evangelicalism or the Ethiopian–Eritrean Evangelical Church. Sometimes the denominations and organizations are known as Wenigēlawī (from Geʽez: "evangelical"). Evangelical Christianity was originally introduced by American and European Protestant missionary work, which began in the 19th century among various peoples, including Christians schismed from the Orthodox Tewahedo church, other branches of Christianity, or converted from non-Christian religions or traditional faith practices. Since the creation of P'ent'ay churches and organisations, prominent movements among them have been Pentecostalism, the Baptist tradition, Lutheranism, Methodism, Presbyterianism, the Mennonites, and the Eastern-orien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church
The Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church () is one of the Oriental Orthodox Churches with its headquarters in Asmara, Eritrea. It was given autocephaly by Shenouda III of Alexandria, pope of the Coptic Orthodox Church, after Eritrea gained its independence from Ethiopia in 1993. Thus, the Eritrean Church accords a primacy of honor to the Coptic Church. Sources differ on the percentage of Christians in the Eritrean population, with most figures being close to one-half, although some sources report slightly more than 60%. Almost 90% of Eritrean Christians are followers of Oriental Orthodoxy. The rest of the population is almost entirely Muslim. History Origins ''Tewahedo'' ( ''täwaḥədo'') is a Geʽez word meaning "being made one". According to the ''Catholic Encyclopedia'' (1917 edition) article on the Henoticon: around 500 AD bishops within the Patriarchates of Alexandria, Antioch and Jerusalem refused to accept the "two natures" doctrine decreed by the Council of Chalce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church
The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church () is the largest of the Oriental Orthodox Churches. One of the few Christian churches in Africa originating before European colonization of the continent, the Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church dates back to the Christianization of the Kingdom of Aksum in 330, and has between 36 million and 51 million adherents in Ethiopia. It is a founding member of the World Council of Churches. The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church is in communion with the other Oriental Orthodox churches (the Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church, the Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria, the Malankara Orthodox Syrian Church, the Armenian Apostolic Church, and the Syriac Orthodox Church). The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church had been administratively part of the Coptic Orthodox Church, Coptic Orthodox Church of Alexandria from the first half of the 4th century until 1959, when it was granted autocephaly with its own patriarch by Pope Cyril VI of Alexandria, Pope o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mizrahi Music
Mizrahi music ( ' , "Eastern music/Oriental music") refers to a music genre in Israel that combines elements from the Middle East, North Africa, and Europe; and is mostly performed by Israelis of Mizrahi Jewish descent. It is usually sung in Modern Hebrew, or literary Hebrew. Emergence of Mizrahi music Background Mizrahi Jews who immigrated from the Arab countries have, over the last 50 years, created a unique musical style that combines elements of Arabic, Turkish, and Greek music. This is not to be confused with the New Hebrew Style, as the Mizrahi style is more spontaneous. After World War II, many Jewish families made Aliyah to the new state of Israel, founded in 1948. The Muzika Mizrahit movement started in the 1950s with homegrown performers in neighborhoods with a high concentration of Jews from Arab countries who would play at weddings and other events. They performed songs in Hebrew, but in an Arabic style, on traditional Arabic instruments—the oud, kanun, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henna
Henna is a reddish dye prepared from the dried and powdered leaves of the henna tree. It has been used since at least the ancient Egyptian period as a hair and body dye, notably in the temporary body art of mehndi (or "henna tattoo") resulting from the staining of the skin using dyes from the henna plant. After henna stains reach their peak colour, they hold for a few days and then gradually wear off by way of exfoliation, typically within one to three weeks. Henna has been used in ancient Egypt, ancient Near East and the Indian subcontinent to dye skin, hair, and fingernails; as well as fabrics including silk, wool, and leather. Historically, henna was used in West Asia including the Arabian Peninsula and in Carthage, other parts of North Africa, West Africa, Central Africa, the Horn of Africa and the Indian subcontinent. The name ''henna'' is used in other skin and hair dyes, such as ''black henna'' and ''neutral henna'', neither of which is derived from the henna plant. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bar Miswa
A ''bar mitzvah'' () or ''bat mitzvah'' () is a coming of age ritual in Judaism. According to Jewish law, before children reach a certain age, the parents are responsible for their child's actions. Once Jewish children reach that age, they are said to "become" ''b'nai mitzvah'', at which point they begin to be held accountable for their own actions. Traditionally, the father of a ''bar'' or ''bat mitzvah'' offers thanks to God that he is no longer punished for his child's sins. In Orthodox communities, boys become ''bar mitzvah'' at 13 and girls become ''bat mitzvah'' at 12. In most Reform, Reconstructionist, and Conservative communities, the milestone is 13 regardless of gender. After this point, children are also held responsible for knowing Jewish ritual law, tradition, and ethics, and are able to participate in all areas of Jewish community life to the same extent as adults. In some Jewish communities, men's and women's roles differ in certain respects. For example, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |