|
Ultra 60
The Ultra 60 is a fairly large and heavy computer workstation in a tower enclosure from Sun Microsystems. The Ultra 60 was launched in November 1997 and shipped with Solaris 7. It was available in several specifications. * Sun Ultra 60 workstation # 1 CPU Model 1300 and # 2 CPU Model 2300, with Sun Creator3D graphics – began shipping February 1998. The last order date was August 4, 1999. * Sun Ultra 60 workstation # 1 CPU Model 1300 and # 2 CPU Model 2300, with Sun Elite3D graphics – began shipping March 1998. * Sun Ultra 60 workstation # 1 CPU Models 1360 and # 2 CPU 2360, with Sun Creator and Sun Elite3D graphics – began shipping April 1998. * Sun Ultra 60 workstation # 1 CPU Models 1450 and # 2 CPU 2450 – began shipping in May 1999. * Sun Ultra 60 workstation models began shipping with 18-GB SCSI SCA, 10000-rpm internal drives in November 1999. The Ultra 60 is similar to the higher-cost Sun Ultra 80, but is somewhat smaller and supports fewer CPUs and less memory. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term ''workstation'' has been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a PC connected to a network, but the most common form refers to the class of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, Apollo Computer, DEC, HP, NeXT, and IBM which powered the 3D computer graphics revolution of the late 1990s. Workstations offer higher performance than mainstream personal computers, especially in CPU, graphics, memory, and multitasking. Workstations are optimized for the visualization and manipulation of different types of complex data such as 3D mechanical design, engineering simulations like computational fluid dynamics, animation, medical imaging, image rende ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OpenSolaris
OpenSolaris () is a discontinued open-source computer operating system based on Solaris and created by Sun Microsystems. It was also, perhaps confusingly, the name of a project initiated by Sun to build a developer and user community around the eponymous operating system software. OpenSolaris is a descendant of the UNIX System V Release 4 (SVR4) code base developed by Sun and AT&T in the late 1980s and is the only version of the System V variant of UNIX available as open source. OpenSolaris was developed as a combination of several software ''consolidations'' that were open sourced starting with Solaris 10. It includes a variety of free software, including popular desktop and server software. After Oracle’s acquisition of Sun Microsystems in 2010, Oracle discontinued development of OpenSolaris in house, pivoting to focus exclusively on the development of the proprietary Solaris Express (now Oracle Solaris). Prior to Oracle's close-sourcing Solaris, a group of for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
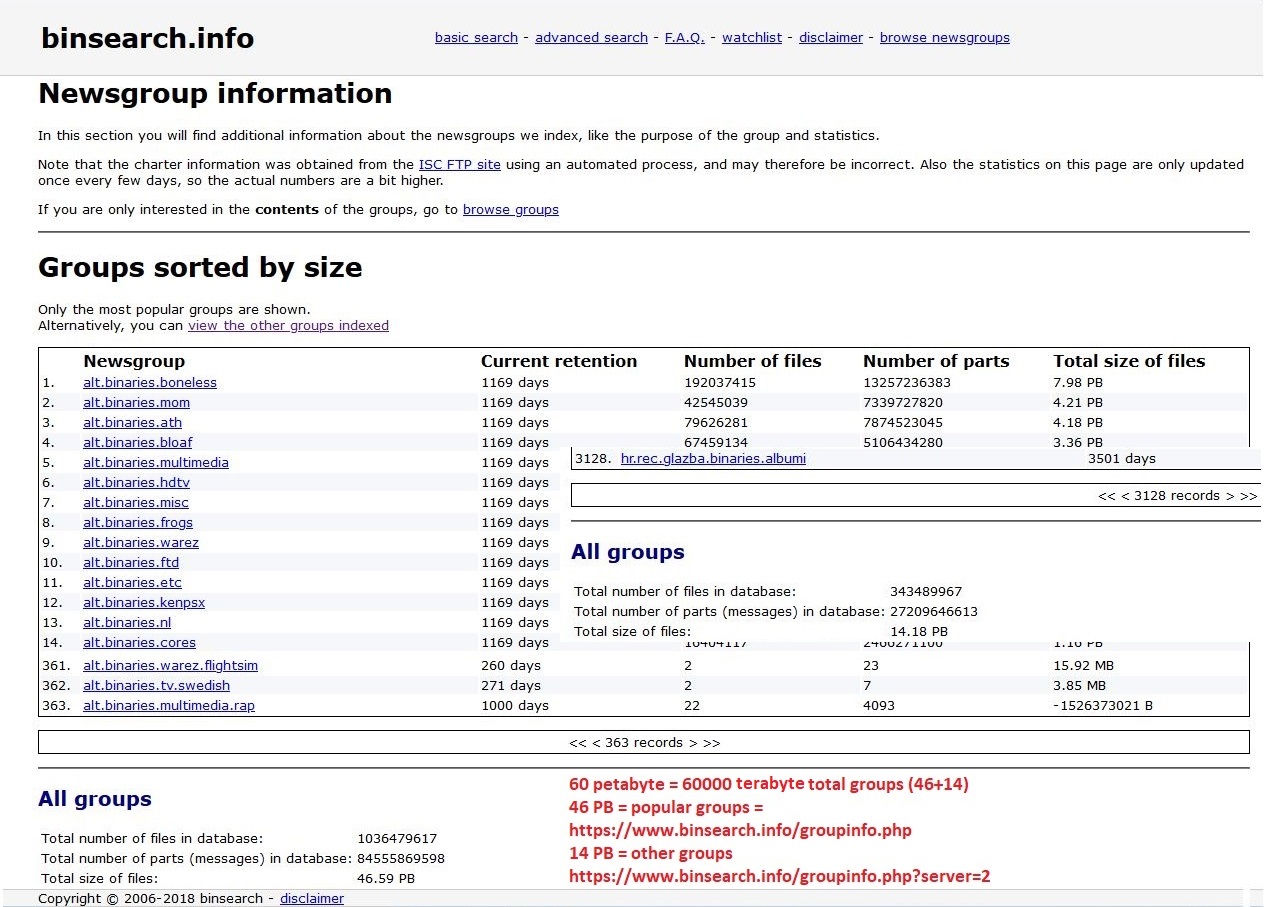
Newsgroup
A Usenet newsgroup is a repository usually within the Usenet system, for messages posted from users in different locations using the Internet. They are discussion groups and are not devoted to publishing news. Newsgroups are technically distinct from, but functionally similar to, discussion forums on the World Wide Web. Newsreader software is used to read the content of newsgroups. Before the adoption of the World Wide Web, Usenet newsgroups were among the most popular Internet services, and have retained their noncommercial nature in contrast to the increasingly ad-laden web. In recent years, this form of open discussion on the Internet has lost considerable ground to individually-operated browser-accessible forums and big media social networks such as Facebook and Twitter. Communication is facilitated by the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP) which allows connection to Usenet servers and data transfer over the internet. Similar to another early (yet still used) prot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SPARCstation 20
The SPARCstation 20 or SS20 (code-named ''Kodiak'') is a discontinued Sun Microsystems workstation introduced in March 1994 based on the SuperSPARC or hyperSPARC CPU. It is one of the last models in the SPARCstation family of Sun "pizza box" computers, which was superseded by the UltraSPARC design in 1995. Specifications Release Price Sun rolled out the SPARCstation 20 for . CPU support The SPARCstation 20 has dual 50 MHz MBus ports that allow it to use faster CPUs than the SPARCstation 10. With two dual-CPU modules and updated firmware, the SPARCstation 20 supports a maximum of four CPUs. The fastest CPU produced for the SPARCstation 20 is the 200 MHz Ross hyperSPARC. The PROM in the SPARCstation 20 determines CPU compatibility. Version 2.25 is the last BootPROM release from Sun, and 2.25R from Ross. Memory The SPARCstation 20 has eight 200-pin DSIMM slots, and supports a maximum of 512 MB of memory with 64 MB modules. Memory modules for the SPARC ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra 10
adopted by British military intelligence in June 1941 for wartime signals intelligence obtained by breaking high-level encrypted enemy radio and teleprinter communications at the Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS) at Bletchley Park. ''Ultra'' eventually became the standard designation among the western Allies for all such intelligence. The name arose because the intelligence obtained was considered more important than that designated by the highest British security classification then used (''Most Secret'') and so was regarded as being ''Ultra Secret''. Several other cryptonyms had been used for such intelligence. The code name ''Boniface'' was used as a cover name for ''Ultra''. In order to ensure that the successful code-breaking did not become apparent to the Germans, British intelligence created a fictional MI6 master spy, Boniface, who controlled a fictional series of agents throughout Germany. Information obtained through code-breaking was often attributed to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Workstation
A workstation is a special computer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by a single user, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems. The term ''workstation'' has been used loosely to refer to everything from a mainframe computer terminal to a PC connected to a network, but the most common form refers to the class of hardware offered by several current and defunct companies such as Sun Microsystems, Silicon Graphics, Apollo Computer, DEC, HP, NeXT, and IBM which powered the 3D computer graphics revolution of the late 1990s. Workstations offer higher performance than mainstream personal computers, especially in CPU, graphics, memory, and multitasking. Workstations are optimized for the visualization and manipulation of different types of complex data such as 3D mechanical design, engineering simulations like computational fluid dynamics, animation, medical imaging, image renderin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra Port Architecture
The Ultra Port Architecture (UPA) bus was developed by Sun Microsystems as a high-speed graphics card to CPU interconnect, beginning with the Ultra 1 workstation in 1995. See also *List of device bandwidths This is a list of interface bit rates, is a measure of information transfer rates, or digital bandwidth capacity, at which digital interfaces in a computer or network can communicate over various kinds of buses and channels. The distinction ca ... External links UPA Bus Whitepaper Computer buses Sun Microsystems hardware {{Compu-hardware-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DIMM
A DIMM () (Dual In-line Memory Module), commonly called a RAM stick, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuits. These memory modules are mounted on a printed circuit board and designed for use in personal computers, workstations, printers, and servers. They are the predominant method for adding memory into a computer system. The vast majority of DIMMs are standardized through JEDEC standards, although there are proprietary DIMMs. DIMMs come in a variety of speeds and sizes, but generally are one of two lengths - PC which are and laptop (SO-DIMM) which are about half the size at . History DIMMs (Dual In-line Memory Module) were a 1990s upgrade for SIMMs (Single In-line Memory Modules) as Intel P5-based Pentium processors began to gain market share. The Pentium had a 64-bit bus width, which would require SIMMs installed in matched pairs in order to populate the data bus. The processor would then access the two SIMMs in parallel. DIMMs w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SunPCi
SunPCi is a series of single-board computers with a connector that effectively allows a PC motherboard to be fitted in Sun Microsystems SPARC-based workstations based on the PCI architecture adding the capability for the workstation to act as a 'IBM PC compatible' computer. The Sun PCi cards included an x86 processor, RAM, expansion ports, and an onboard graphics controller, allowing a complete Wintel operating environment on a Solaris system. The SunPCi software running on Solaris emulates the disk drives that contain the PC filesystem. The PC software running on the embedded hardware is displayed in an X window on the host desktop; there is also a connector on the edge of the board that can optionally be used to connect a PC monitor. History The product arose from the issue of people who were working on a Unix workstation that was typically not Intel-based being sent a file from a Microsoft Windows based PC and being unable to handle the file. Sun termed this problem ''interopera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |