|
Ugly Duckling Theorem
The ugly duckling theorem is an argument showing that classification is not really possible without some sort of bias. More particularly, it assumes finitely many properties combinable by logical connectives, and finitely many objects; it asserts that any two different objects share the same number of ( extensional) properties. The theorem is named after Hans Christian Andersen's 1843 story " The Ugly Duckling", because it shows that a duckling is just as similar to a swan as two swans are to each other. It was derived by Satosi Watanabe in 1969. Mathematical formula Suppose there are n things in the universe, and one wants to put them into classes or categories. One has no preconceived ideas or biases about what sorts of categories are "natural" or "normal" and what are not. So one has to consider all the possible classes that could be, all the possible ways of making a set out of the n objects. There are 2^n such ways, the size of the power set of n objects. One can use that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argument
An argument is a series of sentences, statements, or propositions some of which are called premises and one is the conclusion. The purpose of an argument is to give reasons for one's conclusion via justification, explanation, and/or persuasion. Arguments are intended to determine or show the degree of truth or acceptability of another statement called a conclusion. The process of crafting or delivering arguments, argumentation, can be studied from three main perspectives: the logical, the dialectical and the rhetorical perspective. In logic, an argument is usually expressed not in natural language but in a symbolic formal language, and it can be defined as any group of propositions of which one is claimed to follow from the others through deductively valid inferences that preserve truth from the premises to the conclusion. This logical perspective on argument is relevant for scientific fields such as mathematics and computer science. Logic is the study of the form ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propositional Function
In propositional calculus, a propositional function or a predicate is a sentence expressed in a way that would assume the value of true or false, except that within the sentence there is a variable (''x'') that is not defined or specified (thus being a free variable), which leaves the statement undetermined. The sentence may contain several such variables (e.g. ''n'' variables, in which case the function takes ''n'' arguments). Overview As a mathematical function, ''A''(''x'') or ''A''(''x'', ''x'', ..., ''x''), the propositional function is abstracted from predicates or propositional forms. As an example, consider the predicate scheme, "x is hot". The substitution of any entity for ''x'' will produce a specific proposition that can be described as either true or false, even though "''x'' is hot" on its own has no value as either a true or false statement. However, when a value is assigned to ''x'', such as lava, the function then has the value ''true''; while one assigns to '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaphors Referring To Birds
A metaphor is a figure of speech that, for rhetorical effect, directly refers to one thing by mentioning another. It may provide, or obscure, clarity or identify hidden similarities between two different ideas. Metaphors are usually meant to create a likeness or an analogy. Analysts group metaphors with other types of figurative language, such as antithesis, hyperbole, metonymy, and simile. According to Grammarly, "Figurative language examples include similes, metaphors, personification, hyperbole, allusions, and idioms." One of the most commonly cited examples of a metaphor in English literature comes from the " All the world's a stage" monologue from '' As You Like It'': All the world's a stage, And all the men and women merely players; They have their exits and their entrances And one man in his time plays many parts, His Acts being seven ages. At first, the infant... :—William Shakespeare, '' As You Like It'', 2/7 This quotation expresses a metaphor because the worl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontology
Ontology is the philosophical study of existence, being. It is traditionally understood as the subdiscipline of metaphysics focused on the most general features of reality. As one of the most fundamental concepts, being encompasses all of reality and every entity within it. To articulate the basic structure of being, ontology examines the commonalities among all things and investigates their classification into basic types, such as the Theory of categories, categories of particulars and Universal (metaphysics), universals. Particulars are unique, non-repeatable entities, such as the person Socrates, whereas universals are general, repeatable entities, like the color ''green''. Another distinction exists between Abstract and concrete, concrete objects existing in space and time, such as a tree, and abstract objects existing outside space and time, like the number 7. Systems of categories aim to provide a comprehensive inventory of reality by employing categories such as Substance t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Machine Learning
Machine learning (ML) is a field of study in artificial intelligence concerned with the development and study of Computational statistics, statistical algorithms that can learn from data and generalise to unseen data, and thus perform Task (computing), tasks without explicit Machine code, instructions. Within a subdiscipline in machine learning, advances in the field of deep learning have allowed Neural network (machine learning), neural networks, a class of statistical algorithms, to surpass many previous machine learning approaches in performance. ML finds application in many fields, including natural language processing, computer vision, speech recognition, email filtering, agriculture, and medicine. The application of ML to business problems is known as predictive analytics. Statistics and mathematical optimisation (mathematical programming) methods comprise the foundations of machine learning. Data mining is a related field of study, focusing on exploratory data analysi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arguments
An argument is a series of sentences, statements, or propositions some of which are called premises and one is the conclusion. The purpose of an argument is to give reasons for one's conclusion via justification, explanation, and/or persuasion. Arguments are intended to determine or show the degree of truth or acceptability of another statement called a conclusion. The process of crafting or delivering arguments, argumentation, can be studied from three main perspectives: the logical, the dialectical and the rhetorical perspective. In logic, an argument is usually expressed not in natural language but in a symbolic formal language, and it can be defined as any group of propositions of which one is claimed to follow from the others through deductively valid inferences that preserve truth from the premises to the conclusion. This logical perspective on argument is relevant for scientific fields such as mathematics and computer science. Logic is the study of the forms of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theorems
In mathematics and formal logic, a theorem is a statement (logic), statement that has been Mathematical proof, proven, or can be proven. The ''proof'' of a theorem is a logical argument that uses the inference rules of a deductive system to establish that the theorem is a logical consequence of the axioms and previously proved theorems. In mainstream mathematics, the axioms and the inference rules are commonly left implicit, and, in this case, they are almost always those of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory with the axiom of choice (ZFC), or of a less powerful theory, such as Peano arithmetic. Generally, an assertion that is explicitly called a theorem is a proved result that is not an immediate consequence of other known theorems. Moreover, many authors qualify as ''theorems'' only the most important results, and use the terms ''lemma'', ''proposition'' and ''corollary'' for less important theorems. In mathematical logic, the concepts of theorems and proofs have been formal system ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Riddle Of Induction
The new riddle of induction was presented by Nelson Goodman in '' Fact, Fiction, and Forecast'' as a successor to Hume's original problem. It presents the logical predicates grue and bleen which are unusual due to their time-dependence. Many have tried to solve the new riddle on those terms, but Hilary Putnam and others have argued such time-dependency depends on the language adopted, and in some languages it is equally true for natural-sounding predicates such as "green". For Goodman they illustrate the problem of projectible predicates and ultimately, which empirical generalizations are law-like and which are not. Goodman's construction and use of ''grue'' and ''bleen'' illustrates how philosophers use simple examples in conceptual analysis. Grue and bleen Goodman defined "grue" relative to an arbitrary but fixed time ''t'': an object is grue if and only if it is observed before ''t'' and is green, or else is not so observed and is blue. An object is "bleen" if and only if i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
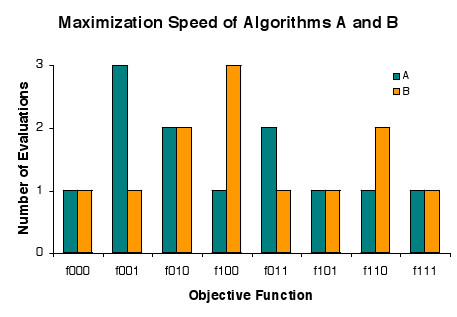
No Free Lunch Theorem
In mathematical folklore, the "no free lunch" (NFL) theorem (sometimes pluralized) of David Wolpert and William Macready, alludes to the saying "no such thing as a free lunch", that is, there are no easy shortcuts to success. It appeared in the 1997 "No Free Lunch Theorems for Optimization". Wolpert had previously derived no free lunch theorems for machine learning (statistical inference).Wolpert, David (1996),The Lack of ''A Priori'' Distinctions between Learning Algorithms, ''Neural Computation'', pp. 1341–1390. In 2005, Wolpert and Macready themselves indicated that the first theorem in their paper "state that any two optimization algorithms are equivalent when their performance is averaged across all possible problems". The "no free lunch" (NFL) theorem is an easily stated and easily understood consequence of theorems Wolpert and Macready actually prove. It is objectively weaker than the proven theorems, and thus does not encapsulate them. Various investigators have exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
No Free Lunch In Search And Optimization
In computational complexity and optimization the no free lunch theorem is a result that states that for certain types of mathematical problems, the computational cost of finding a solution, averaged over all problems in the class, is the same for any solution method. The name alludes to the saying " no such thing as a free lunch", that is, no method offers a "short cut". This is under the assumption that the search space is a probability density function. It does not apply to the case where the search space has underlying structure (e.g., is a differentiable function) that can be exploited more efficiently (e.g., Newton's method in optimization) than random search or even has closed-form solutions (e.g., the extrema of a quadratic polynomial) that can be determined without search at all. For such probabilistic assumptions, the outputs of all procedures solving a particular type of problem are statistically identical. A colourful way of describing such a circumstance, introduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nelson Goodman
Henry Nelson Goodman (7 August 1906 – 25 November 1998) was an American philosopher, known for his work on counterfactuals, mereology, the problem of induction, irrealism, and aesthetics. Life and career Goodman was born in Somerville, Massachusetts, the son of Sarah Elizabeth (née Woodbury) and Henry Lewis Goodman. He was of Jewish origins. He graduated from Harvard University, AB, '' magna cum laude'' (1928). During the 1930s, he ran an art gallery in Boston, Massachusetts, while studying for a Harvard PhD in philosophy, which he completed in 1941. His experience as an art dealer helps explain his later turn towards aesthetics, where he became better known than in logic and analytic philosophy. During World War II, he served as a psychologist in the US Army. He taught at the University of Pennsylvania, 1946–1964, where his students included Noam Chomsky, Sidney Morgenbesser, Stephen Stich, and Hilary Putnam. He was a research fellow at the Harvard Center for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boolean Function
In mathematics, a Boolean function is a function whose arguments and result assume values from a two-element set (usually , or ). Alternative names are switching function, used especially in older computer science literature, and truth function (or logical function), used in logic. Boolean functions are the subject of Boolean algebra and switching theory. A Boolean function takes the form f:\^k \to \, where \ is known as the Boolean domain and k is a non-negative integer called the arity of the function. In the case where k=0, the function is a constant element of \. A Boolean function with multiple outputs, f:\^k \to \^m with m>1 is a vectorial or ''vector-valued'' Boolean function (an S-box in symmetric cryptography). There are 2^ different Boolean functions with k arguments; equal to the number of different truth tables with 2^k entries. Every k-ary Boolean function can be expressed as a propositional formula in k variables x_1,...,x_k, and two propositional formulas a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |