|
Uchchhishta
''Uchchhishta'' (, , ), known by various regional terms, is an Indian and a Hindu concept related to the contamination of food by saliva. Though the term has various meanings and has no exact parallel in English,Roy p. 107 it is generally translated in English as "leftovers"Olivelle pp. 354-5 or "leavings", but with a denigratory aspect. ''Uchchhishta'' frequently denotes the food scraps remaining after a person has eaten. In a broader sense, it refers to the contamination of a food or hand that has come in contact with saliva or the inside of the mouth. A person or plate is said to be ''uchchhishta'' after coming into contact with ''uchchhishta'' food. ''Uchchhishta'' food, people and utensils are considered to be ritually impure. A person can become purified by washing their hand (Hindus traditionally eat with their fingers) and mouth. It is highly disrespectful to offer ''uchchhishta'' food to someone, however exceptions exist for food from socially superior individuals, and ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Matangi
Matangi (, ) is a Hindu goddess. She is one of the Mahavidyas, ten Tantric goddesses and an aspect of the Hindu Divine Mother. She is considered to be the Tantric form of Sarasvati, the goddess of music and learning. Matangi governs speech, music, knowledge and the arts. Her worship is prescribed to acquire supernatural powers, especially gaining control over enemies, attracting people to oneself, acquiring mastery over the arts and gaining supreme knowledge. Matangi is often associated with pollution, inauspiciousness and the periphery of Hindu society, which is embodied in her most popular form, known as Uchchhishta-Chandalini or Uchchhishta-Matangini. She is described as an outcaste ( Chandalini) and offered left-over or partially eaten food (''Uchchhishta'') with unwashed hands or food after eating, both of which are considered to be impure in classical Hinduism. Matangi is represented as emerald green in colour. While Uchchhishta-Matangini carries a noose, sword, goa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
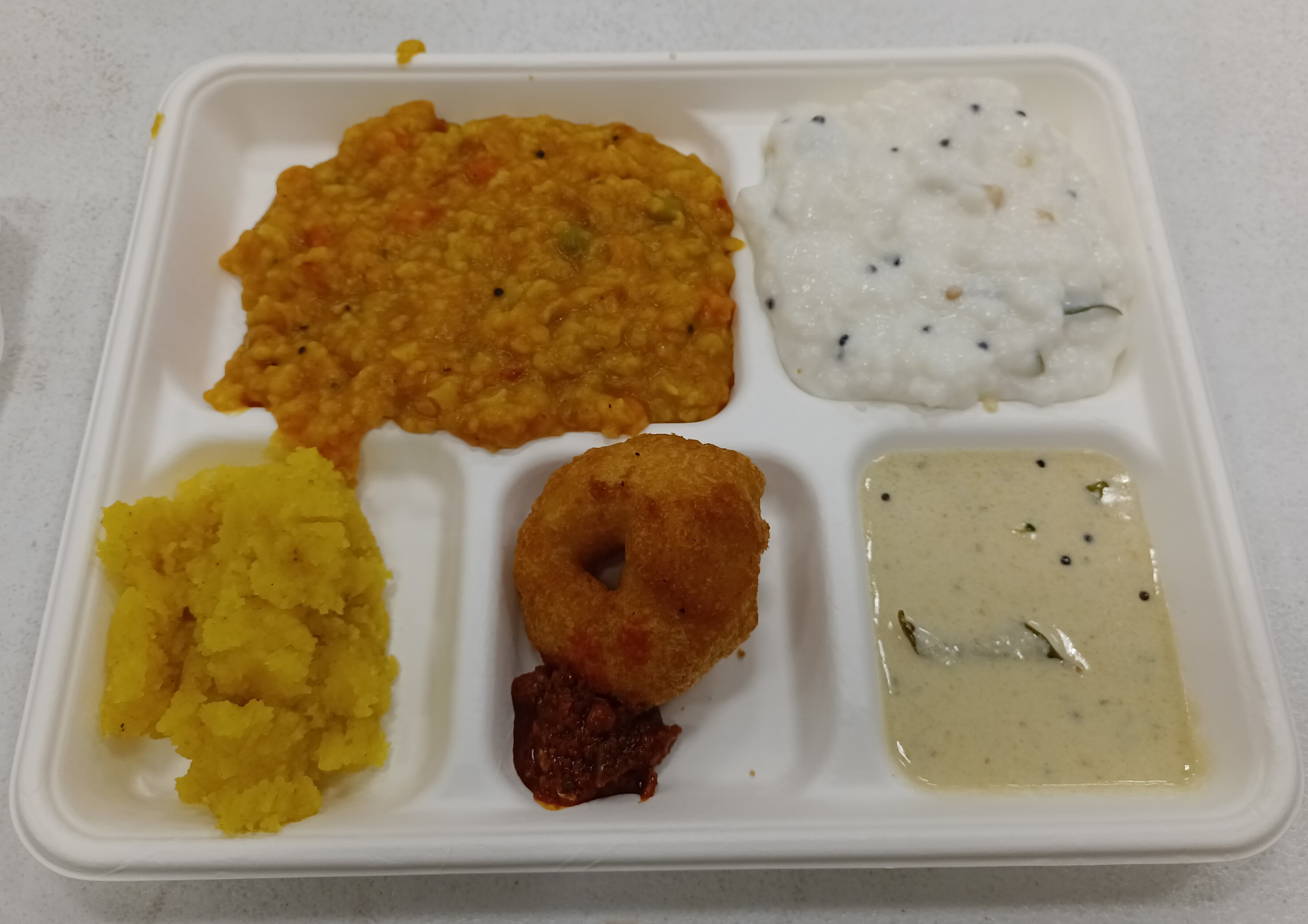
Typical North India Food Prepared For Rongmei Naga
Typical may refer to: * ''Typical'' (album), Peter Hammill * "Typical" (song), song by MuteMath *"Typical", song by Frazier Chorus from ''Sue'', 1987 *''Typical'', story collection by Padgett Powell Padgett Powell (born April 25, 1952 in Gainesville, Florida) is an American novelist in the Southern literary tradition. His debut novel, ''Edisto'' (1984), was nominated for thNational Book Awardand was excerpted in ''The New Yorker''. Powell ..., 1991 * Typical, song by Raven-Symoné from '' This Is My Time'', 2004 See also *'' Typical Rick'', an American Comedy Central television series {{dab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tulu Language
The Tulu language (, Tigalari script: , Kannada script: , Malayalam script: ; ) is a Dravidian language whose speakers are concentrated in Dakshina Kannada and in the southern part of Udupi of Karnataka in south-western India and also in the northern parts of the Kasaragod district of Kerala. The native speakers of Tulu are referred to as Tuluva or Tulu people and the geographical area is unofficially called Tulu Nadu. The Indian census report of 2011 reported a total of 1,846,427 native Tulu speakers in India. The 2001 census had reported a total of 1,722,768 native speakers. There is some difficulty in counting Tulu speakers who have migrated from their native region as they are often counted as Kannada speakers in Indian census reports. Separated early from Proto-South Dravidian, Tulu has several features not found in Tamil–Kannada. For example, it has the pluperfect and the future perfect, like French or Spanish, but formed without an auxiliary ve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kalighat Matangi
Kalighat is a locality of Kolkata (Calcutta), in Kolkata district, West Bengal, India. One of the oldest neighbourhoods in South Kolkata, Kalighat is also densely populated — with a history of cultural intermingling with the various foreign incursions into the area over time. Kalika Temple Kalighat temple has references in 15th century texts. The original temple was a small hut. The present temple was built by the Sabarna Roy Choudhury family of Barisha in 1809. They offered 595 bighas of land to the Temple deity so that worship and service could be continued smoothly. It is believed by some scholars that the name Calcutta was derived from Kalighat. Historically, traders halted at Kalighat to pay patronage to the goddess. The temple was initially on the banks of Hooghly. The river over a period of time has moved away from the temple. The temple is now on the banks of a small canal called Adi Ganga, connecting to Hooghly. The present Dakshina Kali idol of touchstone was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prasad
200px, ''Naivedya'' offered to Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir in Mayapur, India">Mayapur.html" ;"title="Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir, Mayapur">Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir in Mayapur">Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir, Mayapur">Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir in Mayapur, India Prasāda (, Sanskrit: प्रसाद), prasad or prasadam is a religious offering in Hinduism. Most often ''Prasada'' is vegetarian food especially cooked for devotees after praise and thanksgiving to a god. ''Mahaprasada'' (also called ''bhandarā''),Pashaura Singh, Louis E. Fenech, 2014The Oxford Handbook of Sikh Studies/ref> is the consecrated food offered to the deity in a Hindu temple which is then distributed and partaken by all the devotees regardless of any orientation.Chitrita Banerji, 2010Eating India: Exploring the Food and Culture of the Land of SpicesSubhakanta Behera, 2002Construction of an identity discourse: Oriya literature and the Jagannath lovers (1866–1936) pp. 140–177.Susan Pattinson, 2011Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trimurti
The Trimurti ( /t̪ɾimʊɾt̪iː/) is the triple deity of supreme divinity in Hinduism, in which the cosmic functions of creation, preservation, and destruction are personified as a triad of deities. Typically, the designations are that of Brahma the creator, Vishnu the preserver, and Shiva the destroyer. The Om symbol of Hinduism is considered to have an allusion to Trimurti, where the A, U, and M phonemes of the word are considered to indicate creation, preservation and destruction, adding up to represent Brahman. The Tridevi is the trinity of goddess consorts for the Trimurti. Evolution The Puranic period from the 4th to the 12th century CE saw the rise of post-Vedic religion and the evolution of what R. C. Majumdar calls "synthetic Hinduism." Following is a well-known verse from the Vishnu Purana (1.2.66) that mentions Brahma, Vishnu, and Shiva together in a single verse, highlighting their roles within the cosmic functions of creation, preservation, and destr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasishtha
Vasishtha (, ) is one of the oldest and revered Vedic rishis or sages, and one of the Saptarishis (seven great Rishis). Vasishtha is credited as the chief author of Mandala 7 of the ''Rigveda''. Vasishtha and his family are mentioned in Rigvedic verse 10.167.4, other Rigvedic mandalas and in many Vedic texts. His ideas have been influential and he was called the first sage of the Vedanta school of Hindu philosophy by Adi Shankara. The '' Yoga Vasishtha'', ''Vasishtha Samhita'', as well as some versions of the '' Agni Purana'' and ''Vishnu Purana'' are attributed to him. He is the subject of many stories, such as him being in possession of the divine cow Kamadhenu and Nandini her child, who could grant anything to their owners. He is famous in Hindu stories for his legendary conflicts with sage Vishvamitra. In the Ramayana, he was the family priest of the Raghu dynasty and teacher of Rama and his brothers. Etymology Vasishtha is also spelled as ' and is Sanskrit for "most ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shudra
Shudra or ''Shoodra'' (Sanskrit: ') is one of the four varnas of the Hindu class and social system in ancient India. Some sources translate it into English as a caste, or as a social class. Theoretically, Shudras constituted a class like workers. According to Richard Gombrich's study of Buddhist texts, particularly relating to castes in Sri Lankan Buddhist and Tamil Hindu society, The word ''Shudra'' appears in the ''Rigveda'' and it is found in other Hindu texts such as the ''Manusmriti'', ''Arthashastra'', dharmaśāstras and jyotiḥśāstras. In some cases, Shudras participated in the coronation of kings, or were amatya "ministers" and rajas "kings" according to early Indian texts. History Vedas The term ''śūdra'' appears only once in the ''Rigveda''. This mention is found in the mythical story of creation embodied in the '' Puruṣasuktam''. It describes the formation of the four varnas from the body of a primeval man. It states that the brahmin emerged from hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
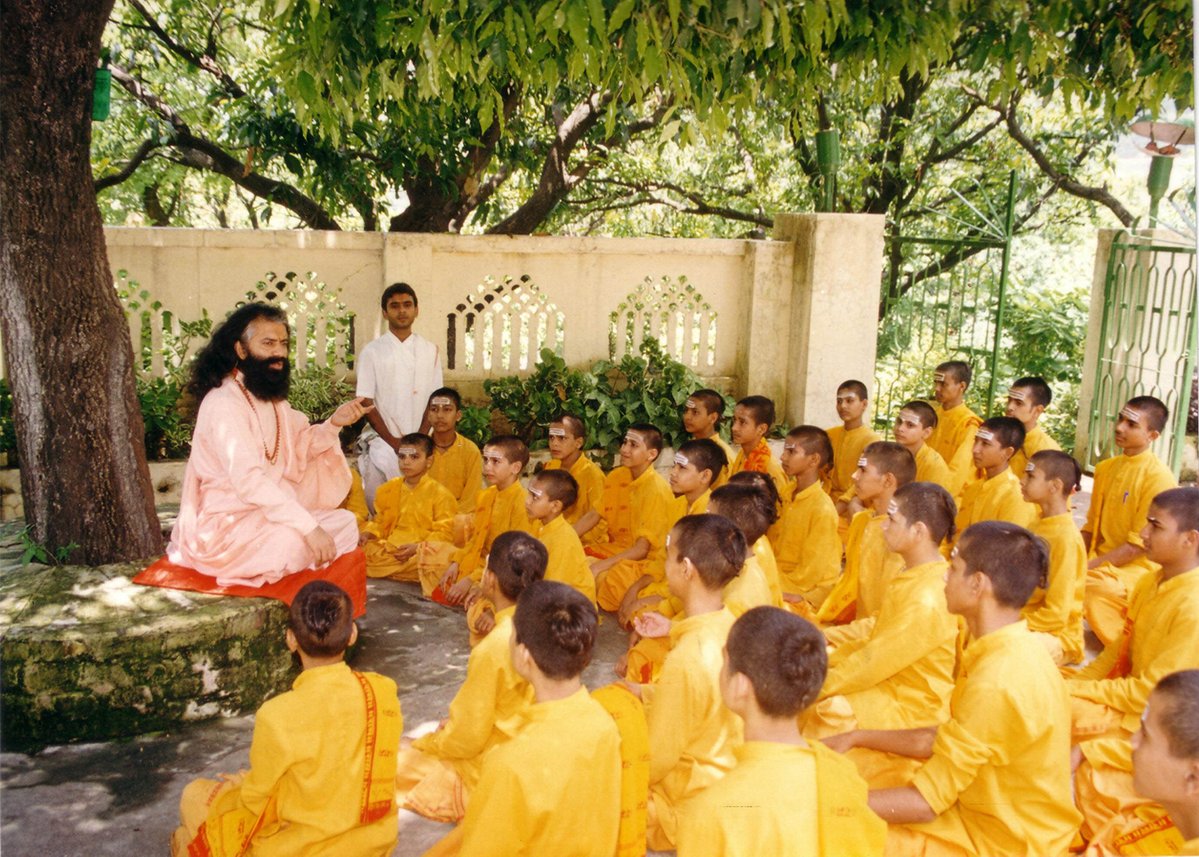
Gurukula
A () is a traditional system of religious education in India with ('students' or 'disciples') living near or with the guru in the same house for a period of time where they learn and get educated by their guruji. Etymology The word is a combination of the Sanskrit words ('teacher' or 'master') and ('family' or 'home'). The term is also used today to refer to residential monasteries or schools operated by modern gurus. History Ancient times The system of education has been in existence since ancient times. The Upanishads (1000-800 BCE) mention multiple , including that of guru Drona at Gurgaon. The (a discourse on the Brahman) is said to have taken place in Guru Varuni's . The vedic school of thought prescribes the (sacred rite of passage) to all individuals before the age of 8 at least by 12. From initiation until the age of 25 all individuals are prescribed to be students and to remain unmarried, a celibates. were supported by public donations. This was fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guru
Guru ( ; International Alphabet of Sanskrit Transliteration, IAST: ''guru'') is a Sanskrit term for a "mentor, guide, expert, or master" of certain knowledge or field. In pan-Indian religions, Indian traditions, a guru is more than a teacher: traditionally, the guru is a reverential figure to the disciple (or ''wikt:शिष्य, shisya'' in Sanskrit, literally ''seeker [of knowledge or truth'']) or student, with the guru serving as a "counsellor, who helps mould values, shares experiential knowledge as much as Knowledge#Hinduism, literal knowledge, an Role model, exemplar in life, an inspirational source and who helps in the spiritual evolution of a student". Whatever language it is written in, Judith Simmer-Brown says that a tantra, tantric spiritual text is often codified in an obscure twilight language so that it cannot be understood by anyone without the verbal explanation of a qualified teacher, the guru. A guru is also one's spiritual guide, who helps one to discover the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apastamba Dharmasutra
''Āpastamba Dharmasūtra'' (Sanskrit: आपस्तम्ब धर्मसूत्र) is a Sanskrit text and one of the oldest Dharma-post vedic smriti related texts of Hinduism that have survived into the modern age from the 1st millennium BCE. It is one of three extant Dharmasutras texts from the Taittiriya school which is relatively newer in comparison to Maitrayaniya shakha of Krishna Yajurveda, the other two being ''Baudhayana Dharmasutra'' and ''Hiranyakesin Dharmasutra''. The ''Apastamba Dharmasutra'' is part of ''Apastamba Kalpasutra'' collection, along with ''Apastamba Shrautasutra'' and ''Apastamba Grihyasutra''. One of the best preserved ancient texts on Dharma, it is also notable for mentioning and citing views of ten ancient experts on Dharma, which has led scholars to conclude that there existed a rich genre of Dharmasutras text in ancient India before this text was composed. Authorship, location and dates The Dharmasutra is attributed to Apastamba, the fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prasad
200px, ''Naivedya'' offered to Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir in Mayapur, India">Mayapur.html" ;"title="Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir, Mayapur">Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir in Mayapur">Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir, Mayapur">Sri Maya Chandrodaya Mandir in Mayapur, India Prasāda (, Sanskrit: प्रसाद), prasad or prasadam is a religious offering in Hinduism. Most often ''Prasada'' is vegetarian food especially cooked for devotees after praise and thanksgiving to a god. ''Mahaprasada'' (also called ''bhandarā''),Pashaura Singh, Louis E. Fenech, 2014The Oxford Handbook of Sikh Studies/ref> is the consecrated food offered to the deity in a Hindu temple which is then distributed and partaken by all the devotees regardless of any orientation.Chitrita Banerji, 2010Eating India: Exploring the Food and Culture of the Land of SpicesSubhakanta Behera, 2002Construction of an identity discourse: Oriya literature and the Jagannath lovers (1866–1936) pp. 140–177.Susan Pattinson, 2011Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |