|
USS Wasp (1775)
USS ''Wasp'' was originally a merchant schooner named ''Scorpion'', built at Baltimore, and purchased under authority from the Second Continental Congress dated 2 December 1775 by Col. Benjamin Harrison sometime between 2 and 18 December 1775, the first US naval ship to be given that name. She was outfitted in Baltimore from December 1775 to early 1776; and commissioned in December 1775 or January 1776, Capt. William Hallock in command. ''Wasp'' set sail from Baltimore on 14 January 1776 in company with and a convoy of ships bound for the Delaware Capes. By virtue of their voyage to meet Commodore Esek Hopkins' squadron at the Delaware Capes, ''Wasp'' and ''Hornet'' appear to be the first ships of the Continental Navy to get to sea. They joined Hopkins' squadron on 13 February; and, four days later, the first American squadron to put to sea began its maiden voyage. Interpreting his orders rather liberally, by ignoring those portions which related to operations in the Chesapeak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Navy
The Continental Navy was the navy of the United States during the American Revolutionary War and was founded October 13, 1775. The fleet cumulatively became relatively substantial through the efforts of the Continental Navy's patron John Adams and vigorous Congressional support in the face of stiff opposition, when considering the limitations imposed upon the Patriot supply pool. The main goal of the navy was to intercept shipments of British matériel and generally disrupt British maritime commercial operations. The initial fleet consisted of converted merchantmen because of the lack of funding, manpower, and resources, with exclusively designed warships being built later in the conflict. The vessels that successfully made it to sea met with success only rarely, and the effort contributed little to the overall outcome of the war. The fleet did serve to highlight a few examples of Continental resolve, notably launching Captain John Barry into the limelight. It provided need ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Continental Marines
The Continental Marines were the amphibious infantry of the American Colonies (and later the United States) during the American Revolutionary War. The Corps was formed by the Continental Congress on November 10, 1775 and was disbanded in 1783. Their mission was multi-purpose, but their most important duty was to serve as onboard security forces, protecting the captain of a ship and his officers. During naval engagements, in addition to manning the cannons along with the crew of the ship, Marine sharpshooters were stationed in the fighting tops of a ship's masts specifically to shoot the opponent's officers, naval gunners, and helmsmen. In all, there were 131 Colonial Marine officers and probably no more than 2,000 enlisted Colonial Marines. Though individual Marines were enlisted for the few U.S. Naval vessels, the organization would not be re-created until 1798. Despite the gap between the disbanding of the Continental Marines and the current organization, the Continental Mar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe
William Howe, 5th Viscount Howe, KB PC (10 August 172912 July 1814) was a British Army officer who rose to become Commander-in-Chief of British land forces in the Colonies during the American War of Independence. Howe was one of three brothers who had distinguished military careers. In historiography of the American war he is usually referred to as Sir William Howe to distinguish him from his brother Richard, who was 4th Viscount Howe at that time. Having joined the army in 1746, Howe saw extensive service in the War of the Austrian Succession and Seven Years' War. He became known for his role in the capture of Quebec in 1759 when he led a British force to capture the cliffs at Anse-au-Foulon, allowing James Wolfe to land his army and engage the French in the Battle of the Plains of Abraham. Howe also participated in the campaigns to take Louisbourg, Belle Île and Havana. He was appointed Lieutenant-Governor of the Isle of Wight, a post he held until 1795. Howe wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Howe, 1st Earl Howe
Admiral of the Fleet Richard Howe, 1st Earl Howe, (8 March 1726 – 5 August 1799) was a British naval officer. After serving throughout the War of the Austrian Succession, he gained a reputation for his role in amphibious operations against the French coast as part of Britain's policy of naval descents during the Seven Years' War. He also took part, as a naval captain, in the decisive British naval victory at the Battle of Quiberon Bay in November 1759. In North America, Howe is best known for his service during the American Revolutionary War, when he acted as a naval commander and a peace commissioner with the American rebels; he also conducted a successful relief during the Great Siege of Gibraltar in the later stages of the War. Howe later commanded the victorious British fleet during the Glorious First of June in June 1794 during the French Revolutionary Wars. Early career Howe was born in Albemarle Street, London, the second son of Emanuel Howe, 2nd Visco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
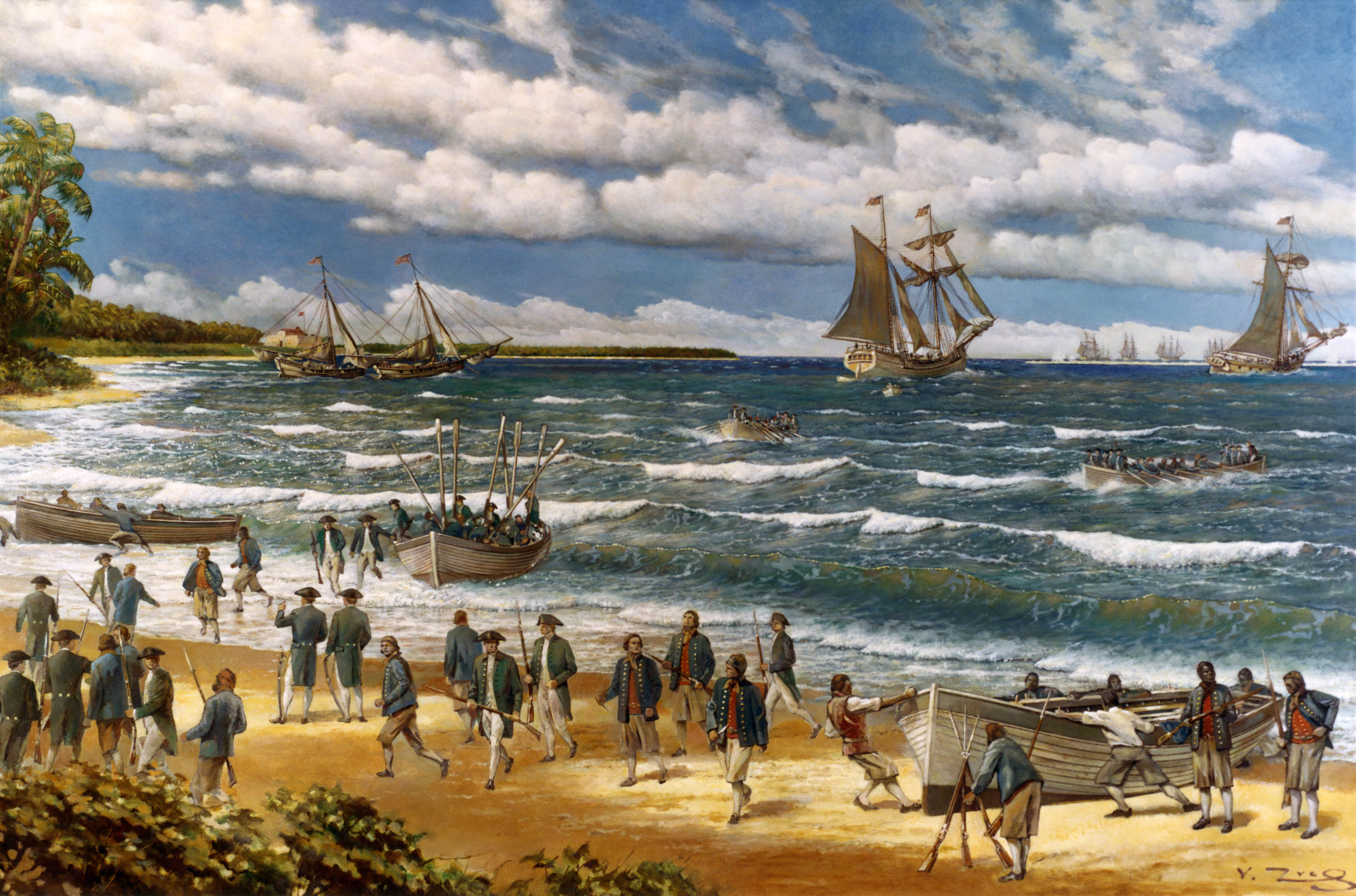
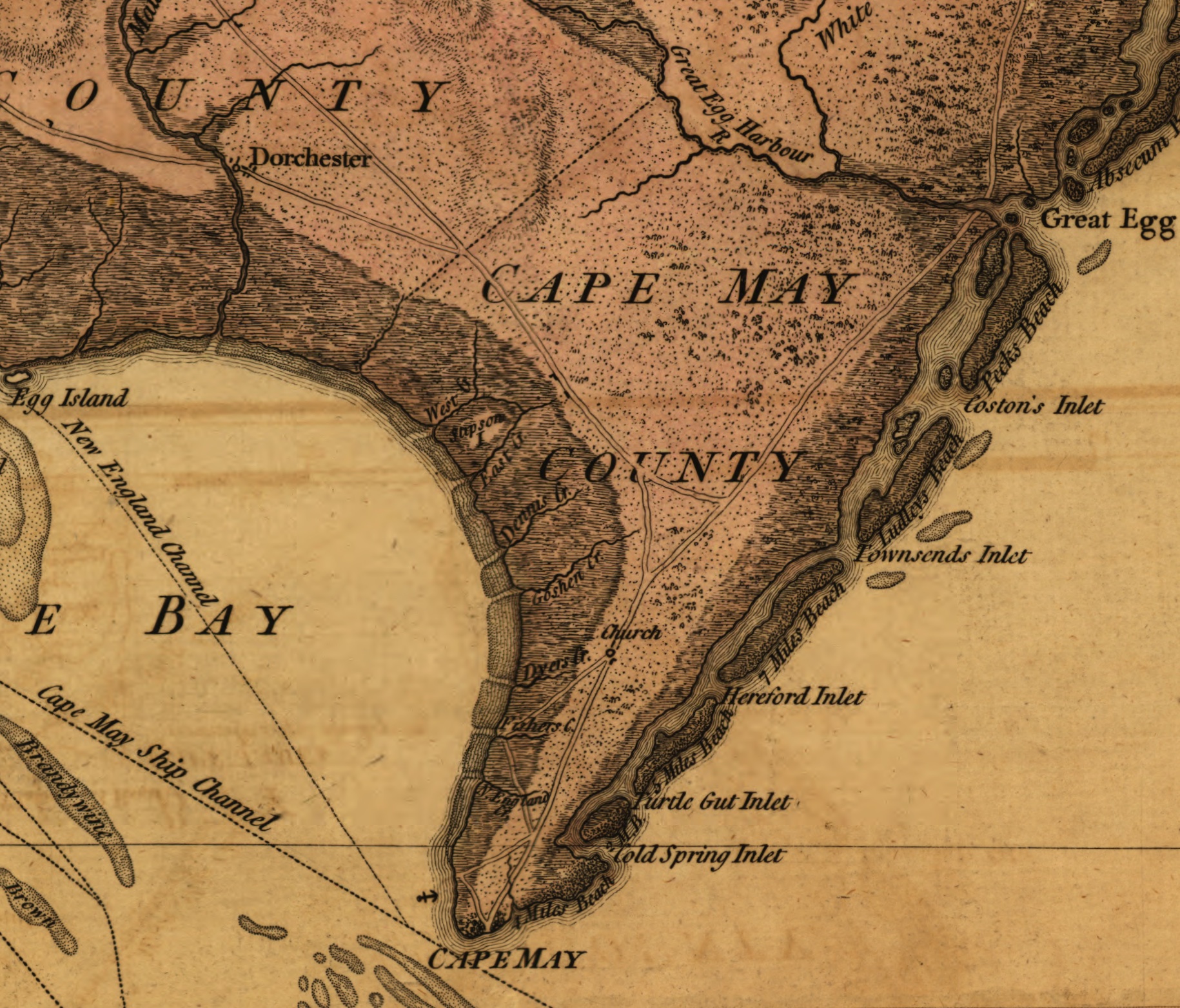
Nancy (1775)
''Nancy'' was an American sailing vessel, noted in sources as either a brig or a brigantine, that was chartered to transport war supplies during the American Revolutionary War. After learning that independence had been declared, her captain, according to his daughter, raised the first American flag in a foreign port. Evading British capture, she was later intentionally destroyed with a huge blast on June 29, 1776, during the Battle of Turtle Gut Inlet near Cape May, New Jersey. History Construction ''Nancy'' was built by Barney Harris in Wilmington, Delaware, and was owned by Joseph Shallcross, Joseph Tatnall, and others. Her captain was Hugh Montgomery, also from Wilmington. Another part owner was Vincent Gilpin, who named the brig after his daughter Ann. Nancy is a diminutive form of Ann Military charter On March 1, 1776, Robert Morris of the Pennsylvania Committee of Safety chartered ''Nancy'' to transport gunpowder and arms for the revolution. Later in March, sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delaware Bay
Delaware Bay is the estuary outlet of the Delaware River on the northeast seaboard of the United States. It is approximately in area, the bay's freshwater mixes for many miles with the saltwater of the Atlantic Ocean. The bay is bordered inland by the states of Delaware and New Jersey, and the Delaware Capes, Cape Henlopen and Cape May, on the Atlantic. Delaware Bay is bordered by six counties: Sussex, Kent, and New Castle in Delaware, along with Cape May, Cumberland, and Salem in New Jersey. The Cape May–Lewes Ferry crosses Delaware Bay from Cape May, New Jersey, to Lewes, Delaware. The bay's ports are managed by the Delaware River and Bay Authority. The shores of the bay are largely composed of salt marshes and mudflats, with only small communities inhabiting the shore of the lower bay. Several of the rivers hold protected status for their salt marsh wetlands bordering the bay, which serves as a breeding ground for many aquatic species, including horseshoe crabs. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christiana Creek
Christiana may refer to: * Christiana incident (or riot), 1851, an armed intervention by citizens in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania to save a fugitive slave Geography * Christiana, Delaware, US * Christiana, Pennsylvania, US * Christiana, Tennessee, US * Christiana, Dane County, Wisconsin, town, US * Christiana, Vernon County, Wisconsin, town, US * Freetown Christiania, autonomous neighborhood in Copenhagen, Denmark * Christiana Island, Cyclades, Greece * Christiana, Jamaica * Christiana, North West, a town in the North West Province of South Africa * Christiana Hundred, an unincorporated subdivision of New Castle County, Delaware, US * Christiana, Norway, a former name (1624-1924) for the present-day Norwegian capital Oslo People * Christiana Figueres (born 1956), Costa Rican diplomat * Christianna Brand (1907–1988), British crime writer and children's author * Christiana Cavendish * Christiana Mariana von Ziegler (1695–1760), German poet and writer * Christiana of Schles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Man-of-war
The man-of-war (also man-o'-war, or simply man) was a Royal Navy expression for a powerful warship or frigate from the 16th to the 19th century. Although the term never acquired a specific meaning, it was usually reserved for a ship armed with cannon and propelled primarily by sails, as opposed to a galley which is propelled primarily by oars. Description The man-of-war was developed in Portugal in the early 15th century from earlier roundships with the addition of a second mast to form the carrack. The 16th century saw the carrack evolve into the galleon and then the ship of the line. The evolution of the term has been given thus: The man-of-war design developed by Sir John Hawkins had three masts, each with three to four sails. The ship could be up to 60 metres long and could have up to 124 guns: four at the bow, eight at the stern, and 56 in each broadside. All these cannons required three gun decks to hold them, one more than any earlier ship. It had a maximum sai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of New York (state), New York, Pennsylvania, New Jersey, and Delaware, before emptying into Delaware Bay. It is the longest free-flowing river in the Eastern United States. The river has been recognized by the National Wildlife Federation as one of the country's Great Waters. The river's drainage basin, watershed drains an area of and provides drinking water for 17 million people. The river has two branches that rise in the Catskill Mountains of New York: the West Branch Delaware River, West Branch at Mount Jefferson (New York), Mount Jefferson in Jefferson, New York, Jefferson, Schoharie County, New York, Schoharie County, and the East Branch Delaware River, East Branch at Grand Gorge, New York, Grand Gorge, Delaware County, New York, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia, Pennsylvania
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania#Municipalities, largest city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the List of United States cities by population, sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Act of Consolidation, 1854, Since 1854, the city has been coextensive with Philadelphia County, Pennsylvania, Philadelphia County, the List of counties in Pennsylvania, most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the Delaware Valley, the Metropolitan statistical area, nation's seventh-largest and one of List of largest cities, world's largest metropolitan regions, with 6.245 million residents . The city's population at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census was 1,603,797, and over 56 million people live within of Philadelphia. Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces of New Brunswick to the northeast and Quebec to the north. The Atlantic Ocean is to the east and southeast, and Long Island Sound is to the southwest. Boston is New England's largest city, as well as the capital of Massachusetts. Greater Boston is the largest metropolitan area, with nearly a third of New England's population; this area includes Worcester, Massachusetts (the second-largest city in New England), Manchester, New Hampshire (the largest city in New Hampshire), and Providence, Rhode Island (the capital of and largest city in Rhode Island). In 1620, the Pilgrims, Puritan Separatists from England, established Plymouth Colony, the second successful English settlement in America, following the Jamestown Settlement in Virg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)

