|
USS Reid (DD-369)
The third USS ''Reid'' (DD-369) was a in the United States Navy before and during World War II. She was named for Samuel Chester Reid, a U.S. Navy officer in the War of 1812 who helped design the 1818 version of the flag of the United States. History ''Reid'' was laid down 25 June 1934 by Federal Shipbuilding and Drydock Company, Kearny, New Jersey; launched 11 January 1936; sponsored by Mrs. Beatrice Reid Power; and commissioned 2 November 1936, Captain Robert B. Carney in command. From 1937 into 1941, ''Reid'' participated in training and fleet maneuvers in the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Pacific Ocean, Pacific. During the attack on Pearl Harbor, ''Reid''s gunners fired at the Japanese planes and downed one of them. After the attack, ''Reid'' patrolled off the Hawaiian Islands, Palmyra Atoll, and Johnston Island during December. In January 1942, she escorted a convoy to San Francisco, California. Returning to Hawaii for more patrol duty, she later steamed to Midw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Chester Reid
Samuel Chester Reid (24 August 1783 – 28 January 1861) was an officer in the United States Navy who commanded a privateer during the War of 1812. He is also noted for having helped design the 1818 version of the flag of the United States, which first established the rule of keeping thirteen stripes and adding one star for each U.S. state. Early life and family Reid was born in Norwich, Connecticut, to John and Rebecca (Chester) Reid. John Reid, a lieutenant in the British Navy, was captured during the American Revolutionary War before resigning and joining the American side. Rebecca Chester's father, John Chester (Connecticut soldier), John Chester, was among the soldiers at Battle of Bunker Hill, Bunker Hill, and afterward a member of the Connecticut convention that ratified the United States constitution. Naval career Reid joined the United States Navy in 1794. He served in USS Constellation (1797), ''Constellation'' with Commodore (rank), Commodore Thomas Truxtun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
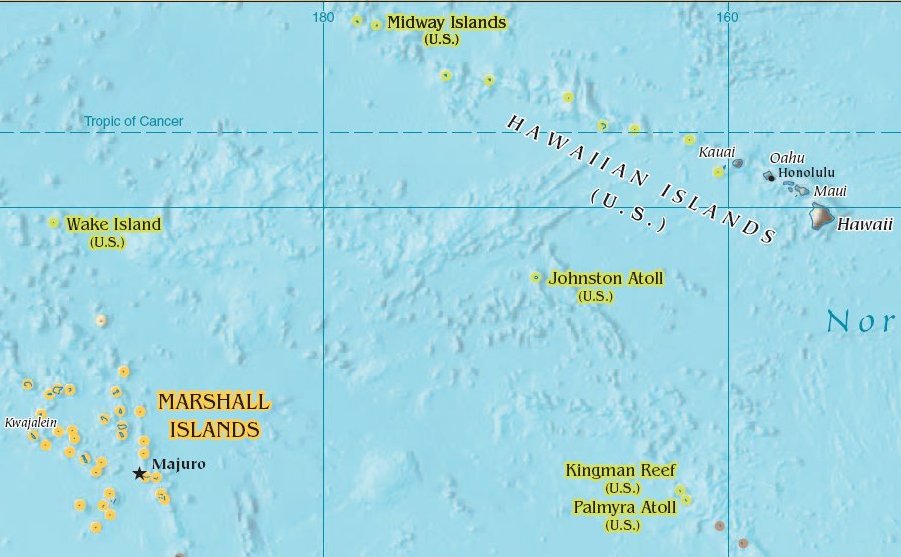
Johnston Island
Johnston Atoll is an unincorporated territory of the United States, under the jurisdiction of the United States Air Force (USAF). The island is closed to public entry, and limited access for management needs is only granted by a letter of authorization from the USAF. A special use permit is also required from the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (USFWS) to access the island by boat or enter the waters surrounding the island, which are designated as a National Wildlife Refuge and part of the Pacific Islands Heritage Marine National Monument. The Johnston Atoll National Wildlife Refuge extends from the shore out to 12 nautical miles, continuing as part of the National Wildlife Refuge System out to 200 nautical miles. The Pacific Remote Islands Marine National Monument extends from the shore out to 200 nautical miles. The isolated atoll has been under the control of the U.S. military since 1934. During that time, it was variously used as a naval refueling depot, an airbase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Guinea
New Guinea (; Hiri Motu: ''Niu Gini''; , fossilized , also known as Papua or historically ) is the List of islands by area, world's second-largest island, with an area of . Located in Melanesia in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, the island is separated from Mainland Australia, Australia by the wide Torres Strait, though both landmasses lie on the same continental shelf, and were united during episodes of low sea level in the Pleistocene glaciations as the combined landmass of Sahul. Numerous smaller islands are located to the west and east. The island's name was given by Spanish explorer Yñigo Ortiz de Retez during his maritime expedition of 1545 due to the perceived resemblance of the indigenous peoples of the island to those in the Guinea (region), African region of Guinea. The eastern half of the island is the major land mass of the nation of Papua New Guinea. The western half, known as Western New Guinea, forms a part of Indonesia and is organized as the provinces of Pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon Islands
Solomon Islands, also known simply as the Solomons,John Prados, ''Islands of Destiny'', Dutton Caliber, 2012, p,20 and passim is an island country consisting of six major islands and over 1000 smaller islands in Melanesia, part of Oceania, to the northeast of Australia. It is directly adjacent to Autonomous Region of Bougainville, Bougainville, a part of Papua New Guinea to the west, Australia to the southwest, New Caledonia and Vanuatu to the southeast, Fiji, Wallis and Futuna, and Tuvalu to the east, and Nauru and the Federated States of Micronesia to the north. It has a total area of 28,896 square kilometres (11,157 sq mi), and a population of 734,887 according to the official estimates for mid-2023. Its capital and largest city, Honiara, is located on the largest island, Guadalcanal. The country takes its name from the wider area of the Solomon Islands (archipelago), Solomon Islands archipelago, which is a collection of Melanesian islands that also includes the Autonomous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Hebrides
New Hebrides, officially the New Hebrides Condominium () and named after the Hebrides in Scotland, was the colonial name for the island group in the South Pacific Ocean that is now Vanuatu. Native people had inhabited the islands for three thousand years before the first Europeans arrived in 1606 from a Spanish expedition led by Portuguese navigator Pedro Fernandes de Queirós. The islands were named by Captain James Cook in 1774 and subsequently colonised by both the British and the French. The two countries eventually signed an agreement making the islands an Anglo-French condominium that provided for joint sovereignty over the archipelago with two parallel administrations, one British, one French. In some respects, that divide continued even after independence, with schools teaching in either one language or the other. The condominium lasted from 1906 until 1980, when New Hebrides gained its independence as the Republic of Vanuatu. Politics and economy The New Hebrides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Espiritu Santo
Espiritu Santo (, ; ) is the largest island in the nation of Vanuatu, with an area of and a population of around 40,000 according to the 2009 census. Geography The island belongs to the archipelago of the New Hebrides in the Pacific region of Melanesia. It is in the Sanma Province of Vanuatu. The town of Luganville, on Espiritu Santo's southeast coast, is Vanuatu's second-largest settlement and the provincial capital. Roads run north and west from Luganville, but most of the island is far from the limited road network. Around Espiritu Santo lie a number of small islands and islets; among them are: Dany Island, Araki Island, Araki, Elephant Island (Vanuatu), Elephant Island, Sakao Island (Sanma, Vanuatu), Sakao, Lataroa, Lataro, Thion (Vanuatu), Thion, Malohu, Malwepe, Malvapevu, Malparavu, Maltinerava, Oyster Island, Tangoa Island, Tangoa, and Bokissa. Vanuatu's highest peak is the Mount Tabwemasana in west-central Espiritu Santo. History A Spanish East Indies, Spanish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guadalcanal
Guadalcanal (; indigenous name: ''Isatabu'') is the principal island in Guadalcanal Province of Solomon Islands, located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, northeast of Australia. It is the largest island in the Solomons by area and the second-largest by population (after Malaita). The island is mainly covered in dense tropical rainforest and has a mountainous hinterland. Guadalcanal was first charted by Europeans during the Spanish expedition of Álvaro de Mendaña de Neira, Álvaro de Mendaña in 1568. The name comes from the village of Guadalcanal, Seville, Guadalcanal, in the province of Sevilla (province), Seville, in Andalusia, Spain, birthplace of Pedro de Ortega Valencia, a member of Mendaña's expedition. During 1942 and 1943, it was the scene of the Guadalcanal campaign and saw bitter fighting between Japanese and U.S. troops. The Americans were ultimately victorious. At the end of World War II, Honiara, on the north coast of Guadalcanal, became the new capital of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suva Harbor
Suva (, ) is the capital and the most populous city of Fiji. It is the home of the country's largest metropolitan area and serves as its major port. The city is located on the southeast coast of the island of Viti Levu, in Rewa Province, Central Division. In 1877, the capital of Fiji was moved to Suva from Levuka, the main European colonial settlement at the time, due to the restrictive geography and environs of the latter. The administration of the colony was transferred from Levuka to Suva in 1882. As of the 2017 census, the city of Suva had a population of 93,970, and Suva's metropolitan area, which includes its independent suburbs, had a population of 185,913. The combined urban population of Suva and the towns of Lami, Nasinu, and Nausori that border it was around 330,000: over a third of the nation's population (This urban complex, excluding Lami, is also known as the Suva-Nausori corridor). Suva is the political, economic, and cultural centre of Fiji. It is also t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Harbor, Alaska
Dutch Harbor is a harbor on Amaknak Island in Unalaska, Alaska. It was the location of the Battle of Dutch Harbor in June, 1942 when the Imperial Japanese Navy attacked it just seven months after the attack on Pearl Harbor in Hawaii. To this day, it remains one of the few sites in the United States to be subjected to an aerial bombardment by a foreign power. Dutch Harbor is now the home of an important fishing industry. History Russian to American Druzhinin, the commander of the Russian ship ''Zakharii I Elisaveta'', is credited for discovering the deep-water harbor now known as Dutch Harbor. Dutch Harbor is located within the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, more precisely on Amaknak Island in the Fox Islands. A mile-long spit extending from the northeast end of Amaknak Island makes Dutch Harbor a natural port, protecting ships from the waves and currents of the Bering Sea, although winds off the Bering Sea have tossed shipments from decks of ships. Dutch Harbor is close to some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adak, Alaska
Adak (; , ), formerly Adak Station, is a city located on Adak Island, in the Aleutians West Census Area, Alaska, United States. At the 2020 census, the population was 171, down from 326 in 2010. It is the westernmost municipality in the United States and the southernmost city in Alaska. Attu Station, Alaska, is further west in the Aleutian Islands, but is not incorporated and, as it lies west of the 180th meridian, may be considered the second easternmost place instead. (See Extreme points of the United States.) The city is the former location of the Naval Air Facility Adak, NAVFAC Adak. History 19th century The Aleutian Islands were historically occupied by the Unanga, more commonly known now as the Aleuts. The once heavily populated island was eventually abandoned in the early 19th century as the Aleutian Island hunters followed the Russian fur trade eastward, and famine set in on the Andreanof Island group. However, they continued to hunt and fish actively around the is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the northernmost, westernmost, and easternmost (the Aleutian Islands cross the 180th meridian into the eastern hemisphere) state in the United States. It borders the Canadian territory of Yukon and the province of British Columbia to the east. It shares a western maritime border, in the Bering Strait, with Russia's Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. The Chukchi and Beaufort Seas of the Arctic Ocean lie to the north, and the Pacific Ocean lies to the south. Technically, it is a semi-exclave of the U.S., and is the largest exclave in the world. Alaska is the largest U.S. state by area, comprising more total area than the following three largest states of Texas, California, and Montana combined, and is the seventh-largest subnational division i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kiska Island
Kiska (, ) is one of the Rat Islands, a group of the Aleutian Islands of Alaska. It is about long and varies in width from . It is part of Aleutian Islands Wilderness and as such, special permission is required to visit it. The island has no permanent population. History European discovery (1741) In 1741 while returning from his second voyage at sea during the Great Northern Expedition, Danish-born Russian explorer Vitus Bering made the first European discovery of most of the Aleutian Islands, including Kiska. Georg Wilhelm Steller, a naturalist-physician aboard Bering's ship, wrote: On 25 October 1741 we had very clear weather and sunshine, but even so it hailed at various times in the afternoon. We were surprised in the morning to discover a large tall island at 51° to the north of us. Prior to European contact, Kiska Island had been densely populated by native peoples for thousands of years. After discovery (1741–1939) Kiska, and the other Rat Islands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |