|
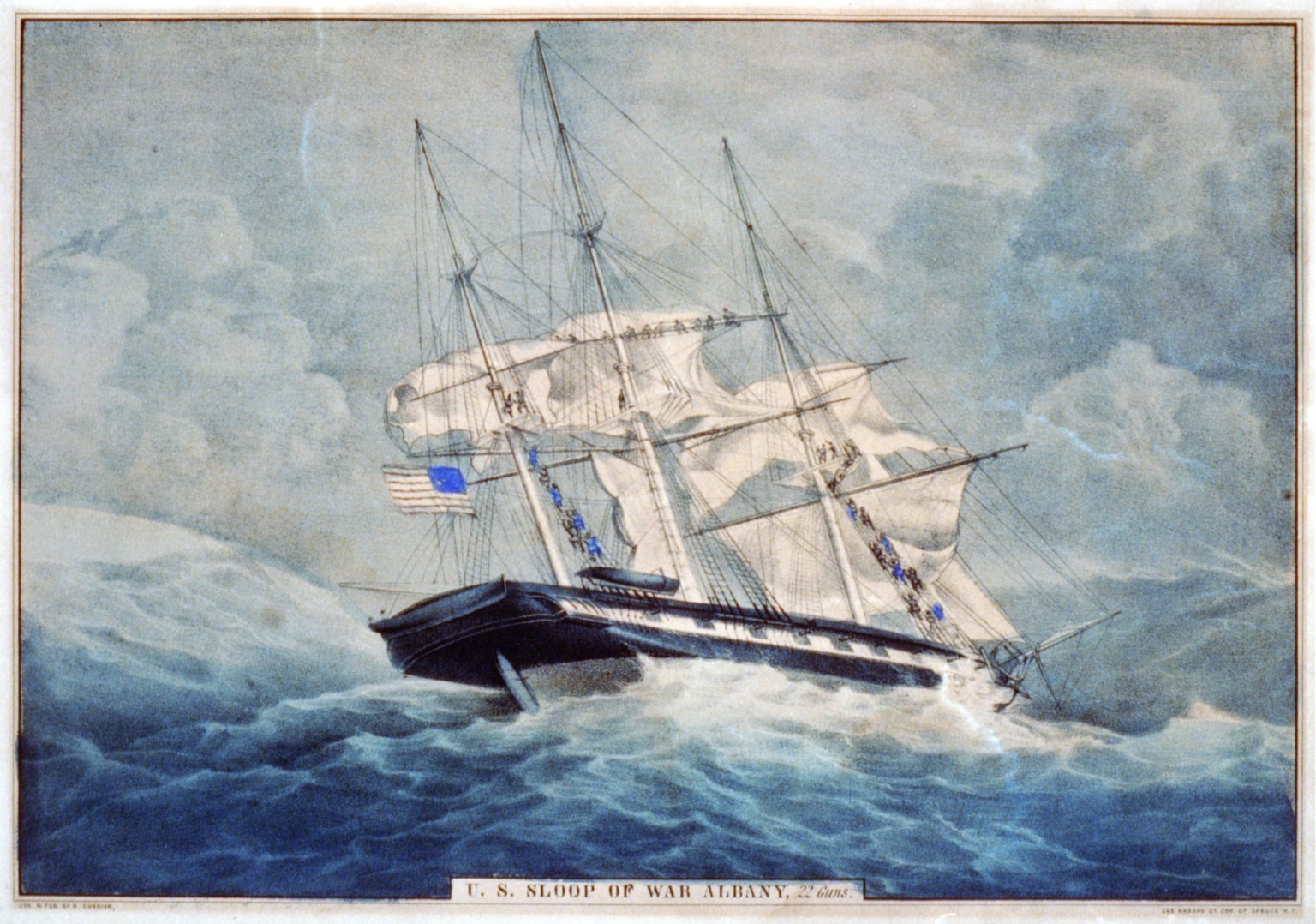
USS Macedonian (1836)
The second USS ''Macedonian'', was a three-masted, wooden-hulled sailing frigate of the US Navy, carrying 36 guns. Rebuilt from the keel of the first at Gosport (later Norfolk) Navy Yard, Portsmouth, Virginia beginning in 1832, the new ''Macedonian'' was launched and placed in service in 1836, with Captain Thomas ap Catesby Jones in command. Service history West Indies Squadron ''Macedonian'' was assigned to the West Indies Squadron to cruise in the West Indies and along the west coast of Africa from 1839 to 1847 as a continuing deterrent to Caribbean pirates. By a joint resolution of Congress on 3 March 1847 ''Macedonian'' and sloop-of-war were placed in civilian hands to carry food to Ireland during the Great Famine of the late 1840s. With a volunteer crew, ''Macedonian'', Captain George C. De Kay in command, departed New York on 15 June with 12,000 barrels of provisions for Ireland donated by private citizens of the United States, returning to Brooklyn Navy Yard some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norfolk Naval Shipyard
The Norfolk Naval Shipyard, often called the Norfolk Navy Yard and abbreviated as NNSY, is a U.S. Navy facility in Portsmouth, Virginia, for building, remodeling and repairing the Navy's ships. It is the oldest and largest industrial facility that belongs to the U.S. Navy as well as the most comprehensive. Located on the Elizabeth River, the yard is just a short distance upriver from its mouth at Hampton Roads. It was established as Gosport Shipyard in 1767. Destroyed during the American Revolutionary War, it was rebuilt and became home to the first operational drydock in the United States in the 1830s. Changing hands during the American Civil War, it served the Confederate States Navy until it was again destroyed in 1862, when it was given its current name. The shipyard was again rebuilt, and has continued operation through the present day. History British control The Gosport Shipyard was founded on November 1, 1767, by Andrew Sprowle on the western shore of the Elizabet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joel Abbot (naval Officer)
Joel Abbot (January 18, 1793 – December 14, 1855) was a U.S. naval officer who served notably in the War of 1812, and commanded a ship during Commodore Matthew Perry's 1853-1854 visit to Japan. Commodore Joel Abbot was Admiral Perry's second in command when they opened Japan in 1853–1854. Military career Abbot was born in Westford, Massachusetts on January 18, 1793, son of Joel and Lydia (Cummings) Abbot. He entered the Navy at the age of 19 as midshipman at the beginning of the War of 1812.''Who Was Who in American History - the Military'', Marquis Who's Who, 1976, page 1. He served first on the frigate and next on Lake Champlain with Commodore Macdonough, who, when he asked Abbot if he were ready to die for his country received the reply "Certainly, sir; that is what I came into the service for." For his success in this dangerous exploit, and for his bravery in the engagement at Cumberland Head on 11 September 1814, the young officer received a sword of honor from Congr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portobelo, Panama
Portobelo (Modern Spanish: "Puerto Bello" ("beautiful port"), historically in Portuguese: Porto Belo) is a historic port and corregimiento in Portobelo District, Colón Province, Panama. Located on the northern part of the Isthmus of Panama, it is northeast of the modern port of Colón now at the Atlantic entrance to the Panama Canal. It has a population of 4,559 , and functions as the seat of Portobelo District. Established in 1597 for its deep natural harbor, it joined Veracruz ( to the northwest) as ports used by the Spanish Empire to ship treasure from the mines of Peru (via Panama City on the Pacific side of the Isthmus and overland to Portobelo) back to Spain. The city was repeatedly captured by British privateers and pirates, culminating in a successful siege by the Royal Navy in 1739, during the War of Jenkins' Ear. Its economy received a major boost in the late-19th century during the construction of the Panama Canal. In 1980, UNESCO designated the Fortifications o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colón, Panama
Colón () is a city and Port#Seaport, seaport in Panama, beside the Caribbean Sea, lying near the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic entrance to the Panama Canal. It is the capital of Panama's Colón Province and has traditionally been known as Panama's second city. Originally it was located entirely on Manzanillo Island, surrounded by Limon Bay, Panama, Limon Bay, Manzanillo Bay, and the Folks River, Panama, Folks River; however, since the disestablishment of the Panama Canal Zone, the city's limits have been redefined to include Fort Gulick, a former United States Army, U.S. Army base, as well as the former Panama Canal Zone towns of Cristóbal, Colón, Cristobal, Margarita, Panama, Margarita, and Coco Solo. History The city was founded in 1850 as the Atlantic terminal of the Panama Canal Railway, Panama Railroad, then underwent construction to meet the demand during the California Gold Rush for a fast route to California. For a number of years early in its history, the sizable United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veracruz (city)
Veracruz (), also known as Heroica Veracruz, is a major port city and municipal seat for the surrounding municipality of Veracruz on the Gulf of Mexico and the most populous city in the Mexican state of Veracruz. The city is located along the coast in the central part of the state, southeast of the state capital Xalapa. It is the most populous city in the state of Veracruz. Part of the city extends into the neighboring municipality of Boca del Río. At the 2020 census, Veracruz Municipality had a population of 607,209 inhabitants. The city of Veracruz had a population of 537,952 inhabitants, 405,952 in Veracruz municipality and 132,011 in Boca del Río municipality.2020 census tables: INEGI Developed during Spanish colonization, Veracruz is Mexico's oldest, largest, and historically most significant port. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
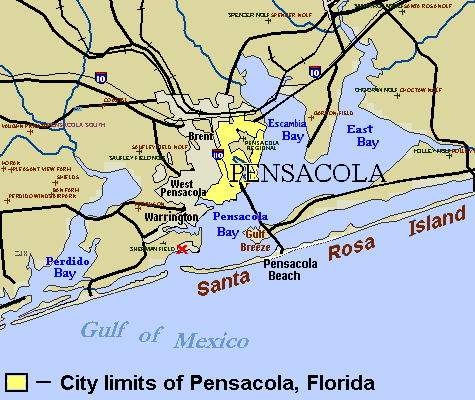
Pensacola, Florida
Pensacola ( ) is a city in the Florida panhandle in the United States. It is the county seat and only incorporated city, city in Escambia County, Florida, Escambia County. The population was 54,312 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. It is the principal city of the Pensacola metropolitan area, which had 509,905 residents in the 2020 census. Pensacola was first settled by the Spanish Empire in 1559, antedating the establishment of St. Augustine, Florida, St. Augustine by six years, but was abandoned due to a significant hurricane and not resettled until 1698. Pensacola is a Port of Pensacola, seaport on Pensacola Bay, which is protected by the barrier island of Santa Rosa Island (Florida), Santa Rosa and connects to the Gulf of Mexico. A large Naval Air Station Pensacola, United States Naval Air Station, the first in the United States, is located in Pensacola. It is the base of the Blue Angels flight-demonstration team and the National Naval Aviation Museum. The Univers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portsmouth, New Hampshire
Portsmouth is a city in Rockingham County, New Hampshire, Rockingham County, New Hampshire, United States. At the 2020 United States census, 2020 census it had a population of 21,956. A historic seaport and popular summer tourist destination on the Piscataqua River bordering the state of Maine, Portsmouth was formerly the home of the Strategic Air Command's Pease Air Force Base, since converted to Portsmouth International Airport at Pease. History Indigenous peoples of the Americas, American Indians of the Abenaki and other Algonquian languages-speaking nations, and their predecessors, inhabited the territory of coastal New Hampshire for thousands of years before European contact. The first known European to explore and write about the area was Martin Pring in 1603. The Piscataqua River is a tidal estuary with a swift current, but forms a good natural harbor. The west bank of the harbor was settled by European colonists in 1630 and named Strawbery Banke, after the many wild Fra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and the Confederate States of America, Confederacy ("the South"), which was formed in 1861 by U.S. state, states that had Secession in the United States, seceded from the Union. The Origins of the American Civil War, central conflict leading to war was a dispute over whether Slavery in the United States, slavery should be permitted to expand into the western territories, leading to more slave states, or be prohibited from doing so, which many believed would place slavery on a course of ultimate extinction. Timeline of events leading to the American Civil War, Decades of controversy over slavery came to a head when Abraham Lincoln, who opposed slavery's expansion, won the 1860 presidential election. Seven Southern slave states responded to Lincoln's victory by seceding f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three U
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious and cultural significance in many societies. Evolution of the Arabic digit The use of three lines to denote the number 3 occurred in many writing systems, including some (like Roman and Chinese numerals) that are still in use. That was also the original representation of 3 in the Brahmic (Indian) numerical notation, its earliest forms aligned vertically. However, during the Gupta Empire the sign was modified by the addition of a curve on each line. The Nāgarī script rotated the lines clockwise, so they appeared horizontally, and ended each line with a short downward stroke on the right. In cursive script, the three strokes were eventually connected to form a glyph resembling a with an additional stroke at the bottom: ३. The Indian digits spread to the Caliphate in the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smyrna
Smyrna ( ; , or ) was an Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek city located at a strategic point on the Aegean Sea, Aegean coast of Anatolia, Turkey. Due to its advantageous port conditions, its ease of defence, and its good inland connections, Smyrna rose to prominence. Since about 1930, the city's name has been İzmir. Two sites of the ancient city are today within İzmir's boundaries. The first, probably founded by indigenous peoples, rose to prominence during the Archaic period in Greece, Archaic Period as one of the principal ancient Greek settlements in western Anatolia. The second, whose foundation is associated with Alexander the Great, reached metropolitan proportions during the period of the Roman Empire. Most of the ancient city's present-day remains date to the Roman era, the majority from after a 2nd-century AD earthquake. In practical terms, a distinction is often made between these. ''Old Smyrna'' was the initial settlement founded around the 11th century BC, first as an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Squadron
The Home Squadron was part of the United States Navy in the mid-19th century. Organized as early as 1838, ships were assigned to protect coastal commerce, aid ships in distress, suppress piracy and the Atlantic slave trade, make coastal surveys, and train ships to relieve others on distant stations. It was discontinued in 1861 after the outbreak of the American Civil War, when the Union blockade forced a reassignment of ships to close off Southern ports. History Mexican–American War During the Mexican–American War the ships of the Home Squadron, commanded by Commodore David Conner, USN fought in several engagements against Mexican forces. Many of the Home Squadron vessels were attached to vice commander Commodore Matthew C. Perry's Mosquito Fleet which was involved in the battles of Tuxpan, Tabasco, Villahermosa and Veracruz. No ship-to-ship combat occurred though several merchant vessels were captured, the Home Squadron primarily operated against Mexican coastal fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |