|
USS Hamul
USS ''Hamul'' (AD-20) was the lead ship of a class of two destroyer tenders; she was most likely named after ''Hamal'', the brightest star in the constellation Aries. Laid down on 6 March 1940 as SS ''Sea Panther'', a Maritime Commission type (C3 Cargo) hull under Maritime Commission contract (MC hull 40) by the Federal Shipbuilding & Drydock Company of Kearney, New Jersey. Launched in April 1940 she was delivered to the Lykes Brothers Steamship Company of New Orleans and renamed ''Doctor Lykes''. After two trips to the Orient she was acquired by the United States Navy and commissioned as a cargo ship, USS ''Hamul'' (AK-30), on 14 June 1941 at Charleston, South Carolina. Service history Cargo ship, 1941–1942 In July 1941, ''Hamul'' rendered logistical support for the occupation of Iceland, prior to America's involvement in World War II. After working with General Electric in experiments on night camouflage, ''Hamul'' departed Boston in January, 1942 to head a convoy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Federal Shipbuilding And Drydock Company
The Federal Shipbuilding and Drydock Company was a United States shipyard, active from 1917 to 1948. It was founded during World War I to build ships for the United States Shipping Board. During World War II, it built ships as part of the U.S. Government's Emergency Shipbuilding program. Operated by a subsidiary of the United States Steel Corporation, the shipyard was located at Kearny Point where the mouth of the Hackensack River meets Newark Bay in the Port of New York and New Jersey. The shipyard site is now part of River Terminal, a massive distribution facility that is partially a foreign trade zone. Federal built numerous destroyers, destroyer escorts and a handful of light cruisers as well as merchant ships during and between the wars. Around 570 vessels were contracted for construction by Federal SB&DD Company with about 100 not delivered fully completed due to the end of the World War II. Federal also had a yard at Port Newark during World War II that built destroyer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans . ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nueva Orleans) is a consolidated city-parish located along the in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of Louisiana. With a population of 383,997 according to the 2020 U.S. census, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mobile, Alabama
Mobile ( , ) is a city and the county seat of Mobile County, Alabama, United States. The population within the city limits was 187,041 at the 2020 census, down from 195,111 at the 2010 census. It is the fourth-most-populous city in Alabama, after Huntsville, Birmingham, and Montgomery. Alabama's only saltwater port, Mobile is located on the Mobile River at the head of Mobile Bay on the north-central Gulf Coast. The Port of Mobile has always played a key role in the economic health of the city, beginning with the settlement as an important trading center between the French colonists and Native Americans, down to its current role as the 12th-largest port in the United States.Drechsel, Emanuel. ''Mobilian Jargon: Linguistic and Sociohistorical Aspects of a Native American Pidgin''. New York: Oxford University Press, 1997. Mobile is the principal municipality of the Mobile metropolitan area. This region of 430,197 residents is composed Mobile and Washington counties; it is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrate
Nitrate is a polyatomic ion with the chemical formula . Salts containing this ion are called nitrates. Nitrates are common components of fertilizers and explosives. Almost all inorganic nitrates are soluble in water. An example of an insoluble nitrate is bismuth oxynitrate. Structure The ion is the conjugate base of nitric acid, consisting of one central nitrogen atom surrounded by three identically bonded oxygen atoms in a trigonal planar arrangement. The nitrate ion carries a formal charge of −1. This charge results from a combination formal charge in which each of the three oxygens carries a − charge, whereas the nitrogen carries a +1 charge, all these adding up to formal charge of the polyatomic nitrate ion. This arrangement is commonly used as an example of resonance. Like the isoelectronic carbonate ion, the nitrate ion can be represented by resonance structures: Dietary nitrate A rich source of inorganic nitrate in the human diets come from leafy green foods, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Chile covers an area of , with a population of 17.5 million as of 2017. It shares land borders with Peru to the north, Bolivia to the north-east, Argentina to the east, and the Drake Passage in the far south. Chile also controls the Pacific islands of Juan Fernández, Isla Salas y Gómez, Desventuradas, and Easter Island in Oceania. It also claims about of Antarctica under the Chilean Antarctic Territory. The country's capital and largest city is Santiago, and its national language is Spanish. Spain conquered and colonized the region in the mid-16th century, replacing Inca rule, but failing to conquer the independent Mapuche who inhabited what is now south-central Chile. In 1818, after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Society Islands
The Society Islands (french: Îles de la Société, officially ''Archipel de la Société;'' ty, Tōtaiete mā) are an archipelago located in the South Pacific Ocean. Politically, they are part of French Polynesia, an overseas country of the French Republic. Geographically, they form part of Polynesia. The archipelago is believed to have been named by Captain James Cook during his first voyage in 1769, supposedly in honour of the Royal Society, the sponsor of the first British scientific survey of the islands; however, Cook wrote in his journal that he called the islands ''Society'' "as they lay contiguous to one another." History Dating colonization The first Polynesians are understood to have arrived on these islands around 1000AD. Oral history origin The islanders explain their origins in term of a orally transmitted story. The feathered god Ta'aroa lay in his shell. He called out but no-one answered, so he went back into his shell, where he stayed for aeons. When he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bora Bora
Bora Bora (French: ''Bora-Bora''; Tahitian: ''Pora Pora'') is an island group in the Leeward Islands. The Leeward Islands comprise the western part of the Society Islands of French Polynesia, which is an overseas collectivity of the French Republic in the Pacific Ocean. Bora Bora has a total land area of . The main island, located about northwest of Papeete, is surrounded by a lagoon and a barrier reef. In the center of the island are the remnants of an extinct volcano, rising to two peaks, Mount Pahia and Mount Otemanu; the highest point is at . Bora Bora is part of the Commune of Bora-Bora, which also includes the atoll of Tūpai. The languages spoken in Bora Bora are Tahitian and French. However, due to the high tourism population, many natives of Bora Bora have learned to speak English. Bora Bora is a major international tourist destination, famous for its seaside (and even offshore) luxury resorts. The major settlement, Vaitape, is on the western side of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th-List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the country. The city boundaries encompass an area of about and a population of 675,647 2020 U.S. Census, as of 2020. It is the seat of Suffolk County, Massachusetts, Suffolk County (although the county government was disbanded on July 1, 1999). The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest MSA in the country. A broader combined statistical area (CSA), generally corresponding to the commuting area and includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camouflage
Camouflage is the use of any combination of materials, coloration, or illumination for concealment, either by making animals or objects hard to see, or by disguising them as something else. Examples include the leopard's spotted coat, the battledress of a modern soldier, and the leaf-mimic katydid's wings. A third approach, motion dazzle, confuses the observer with a conspicuous pattern, making the object visible but momentarily harder to locate, as well as making general aiming easier. The majority of camouflage methods aim for crypsis, often through a general resemblance to the background, high contrast disruptive coloration, eliminating shadow, and countershading. In the open ocean, where there is no background, the principal methods of camouflage are transparency, silvering, and countershading, while the bioluminescence, ability to produce light is among other things used for counter-illumination on the undersides of cephalopods such as squid. Some animals, such as chamel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energy, digital industry, additive manufacturing and venture capital and finance, but has since divested from several areas, now primarily consisting of the first four segments. In 2020, GE ranked among the Fortune 500 as the 33rd largest firm in the United States by gross revenue. In 2011, GE ranked among the Fortune 20 as the 14th most profitable company, but later very severely underperformed the market (by about 75%) as its profitability collapsed. Two employees of GE – Irving Langmuir (1932) and Ivar Giaever (1973) – have been awarded the Nobel Prize. On November 9, 2021, the company announced it would divide itself into three investment-grade public companies. On July 18, 2022, GE unveiled the brand names of the companies it wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
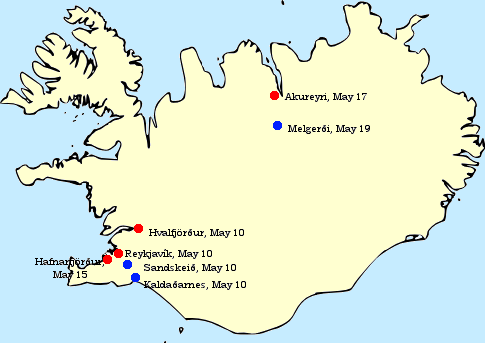
Iceland During World War II
At the beginning of World War II, Iceland was a sovereign kingdom in personal union with Denmark, with King Christian X as head of state. Iceland officially remained neutral throughout World War II. However, the British invaded Iceland on 10 May 1940. On 7 July 1941, the defence of Iceland was transferred from Britain to the United States, which was still a neutral country until five months later. On 17 June 1944, Iceland dissolved its union with Denmark and the Danish monarchy and declared itself a republic, which remains to this day. Background The British government was alarmed by Germany's growing interest in Iceland over the course of the 1930s. The Third Reich's overtures began with friendly competition between German and Icelandic football teams. When war began, Denmark and Iceland declared neutrality and limited visits to the island by military vessels and aircraft of the belligerents. Neutrality During the German occupation of Denmark, contact between the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charleston, South Carolina
Charleston is the largest city in the U.S. state of South Carolina, the county seat of Charleston County, South Carolina, Charleston County, and the principal city in the Charleston metropolitan area, South Carolina, Charleston–North Charleston metropolitan area. The city lies just south of the geographical midpoint of South Carolina's coastline on Charleston Harbor, an inlet of the Atlantic Ocean formed by the confluence of the Ashley River (South Carolina), Ashley, Cooper River (South Carolina), Cooper, and Wando River, Wando rivers. Charleston had a population of 150,277 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The 2020 population of the Charleston metropolitan area, comprising Berkeley County, South Carolina, Berkeley, Charleston County, South Carolina, Charleston, and Dorchester County, South Carolina, Dorchester counties, was 799,636 residents, the third-largest in the state and the 74th-largest metropolitan statistical area in the United States. Charleston was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_1945.jpg)