|
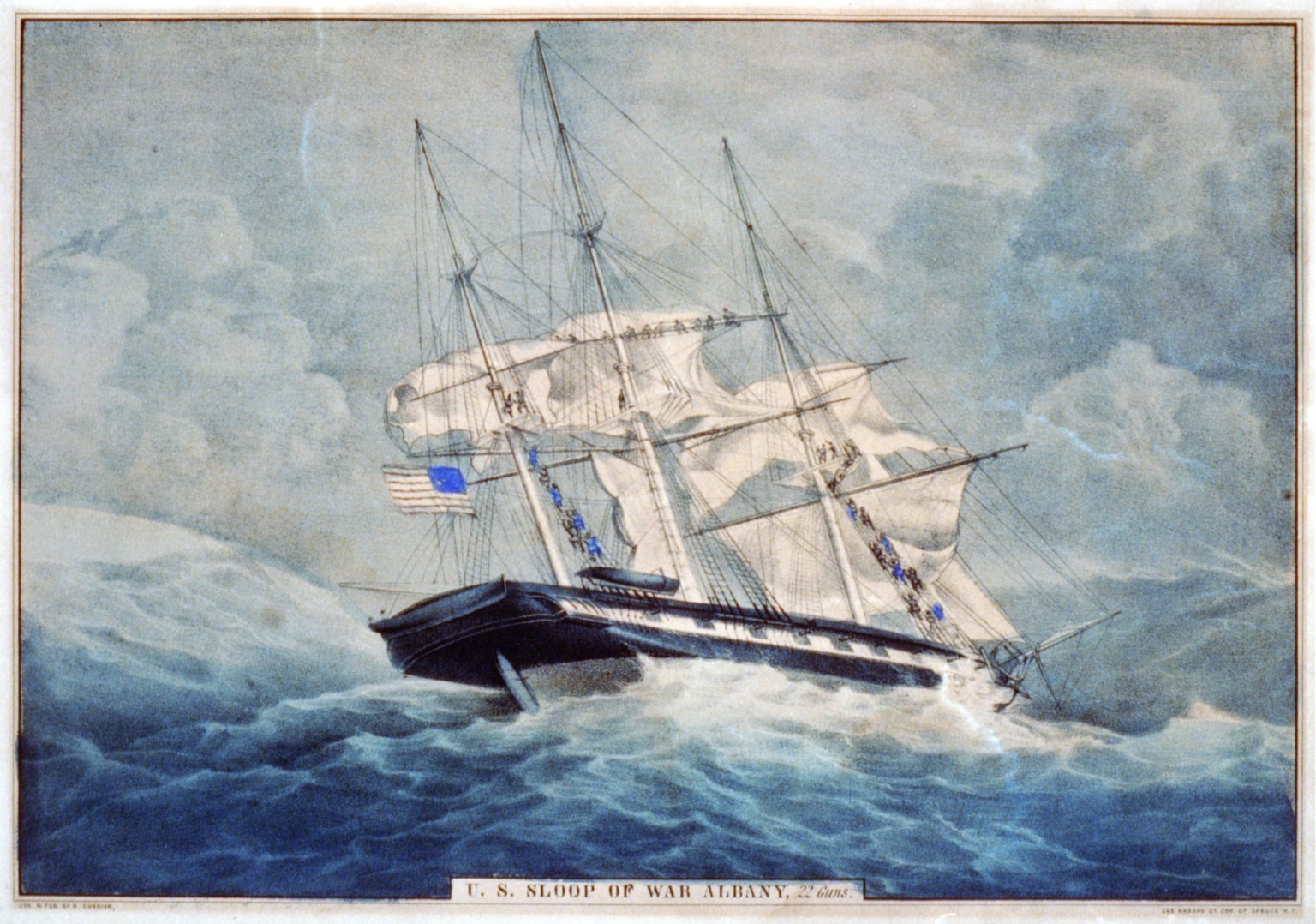
USS Boston (1825)
The fourth USS ''Boston'' was an 18-gun sloop of war, launched on 15 October 1825 by the Boston Navy Yard and commissioned the following year, Master Commandant Beekman V. Hoffman in command. ''Boston'' served on the Brazil Station 1826-1829 and the Mediterranean Station 1830–1832. She was then laid up at Boston Navy Yard until joining the West Indies Squadron in 1836. Except for two short periods in ordinary at New York Navy Yard she served continuously for the next 10 years. ''Boston'' cruised on the West Indies (1836–39), East Indies (1841-43), and Brazil (1843–46) Stations, returning to the United States in 1846. She was then ordered to join Commodore Conner's Home Squadron blockading the Mexican east coast. While ''en route'' to her new station, ''Boston'' was wrecked on Eleuthera Island, Bahamas, during a squall on 15 November 1846. Although the sloop was a total loss, all hands were saved. See also *List of sloops of war of the United States Navy This i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Conner (naval Officer)
Commodore David Conner (1792 – 20 March 1856) was an officer of the United States Navy. He served in the War of 1812 and led the Home Squadron during the Mexican–American War. He led the successful naval assault during the siege of Veracruz which included the landing of 10,000 U.S. troops, the largest U.S. military amphibious assault at the time. He served on the Board of Navy Commissioners; as the first Chief of the Bureau of Construction, Equipment, and Repair; as a Special Diplomatic Agent to Mexico and commanded the Philadelphia Naval Yard. Early life Conner was born in Harrisburg, Pennsylvania. He was the son of David Conner, an Irishman and Abigail Rhodes, who was of English descent. He worked in Philadelphia and then joined the U.S. Navy on 16 January 1809. He served his first few years as a midshipman on the frigate . Military career During the War of 1812 Conner served in during her chase of HMS ''Belvidera'' and her actions with in February 1813 and the Marc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shipwrecks In The Atlantic Ocean
A shipwreck is the wreckage of a ship that is located either beached on land or sunken to the bottom of a body of water. Shipwrecking may be intentional or unintentional. Angela Croome reported in January 1999 that there were approximately three million shipwrecks worldwide (an estimate rapidly endorsed by UNESCO and other organizations). When a ship's crew has died or abandoned the ship, and the ship has remained adrift but unsunk, they are instead referred to as ghost ships. Types Historic wrecks are attractive to maritime archaeologists because they preserve historical information: for example, studying the wreck of revealed information about seafaring, warfare, and life in the 16th century. Military wrecks, caused by a skirmish at sea, are studied to find details about the historic event; they reveal much about the battle that occurred. Discoveries of treasure ships, often from the period of European colonisation, which sank in remote locations leaving few livi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Built In Boston
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, warfare, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion dead weight tons. Of these 28% were oil tankers, 43% were bulk carriers, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sloops Of The United States Navy
A sloop is a sailboat with a single mast typically having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail aft of (behind) the mast. Such an arrangement is called a fore-and-aft rig, and can be rigged as a Bermuda rig with triangular sails fore and aft, or as a gaff-rig with triangular foresail(s) and a gaff rigged mainsail. Sailboats can be classified according to type of rig, and so a sailboat may be a sloop, catboat, cutter, ketch, yawl, or schooner. A sloop usually has only one headsail, although an exception is the Friendship sloop, which is usually gaff-rigged with a bowsprit and multiple headsails. If the vessel has two or more headsails, the term cutter may be used, especially if the mast is stepped further towards the back of the boat. When going before the wind, a sloop may carry a square-rigged topsail which will be hung from a topsail yard and be supported from below by a crossjack. This sail often has a large hollow foot, and this foot is sometim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliography Of Early American Naval History
Historical accounts for early U.S. naval history now occur across the spectrum of two and more centuries. This Bibliography lends itself primarily to reliable sources covering early U.S. naval history beginning around the American Revolution period on through the 18th and 19th centuries and includes sources which cover notable naval commanders, Presidents, important ships, major naval engagements and corresponding wars. The bibliography also includes sources that are not committed to the subject of U.S. naval history per se but whose content covers this subject extensively. Among the contemporary and earlier historical accounts are primary sources, historical accounts, often derived from letters, dispatches, government and military records, captain's logs and diaries, etc., written by authors who were involved in or closely associated to the historical episode in question. Primary source material is often collected, compiled and published by other editors also, sometimes many yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sloops Of War Of The United States Navy
This is a list of sloops of war of the United States Navy. Sailing sloops of war *, scuttled 3 September 1814 to prevent capture *, lost after 28–29 September 1854 with approx. 197 aboard *, captured 14 December 1814 * *, wrecked 15 November 1846, no fatalities *, wrecked 27 May 1863 *, wrecked 2 November 1842, 3 killed * * * * * *, lost in July or August 1815 with 134 aboard * * * * *, burned to prevent capture November 1777 *, captured 20 April 1814 *, wrecked 27 May 1863 * *, scuttled 20 April 1861 * * *, foundered 8 August 1813, 42 killed *, captured 27 April 1777 * *, foundered with the loss of all hands 10 September 1829 *, wrecked 24 April 1778 * * *, lost with all hands after 18 September 1860 * * * * * * USS Ohio (1812), captured 12 August 1814 * * *, wrecked 17–19 July 1841, no fatalities * * *, burned and exploded 27 April 1863 *, captured 1814 *, destroyed to prevent capture 14 August 1779 * * * *, foundered 8 August 1813, 42 killed * * * *, captured October 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bahamas
The Bahamas (), officially the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is an island country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the North Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 3,000 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola (split between the Dominican Republic and Haiti) and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the U.S. state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing of ocean space. The Bahama Islands were inhabited by the Lucayans, a branch of the Arawakan-speaking Taíno, for many centuries. Christopher Columbus was the first European to see the islands, making his first landfall in the "New World" in 1492 when he landed on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eleuthera Island
Eleuthera () refers both to a single island in the archipelagic state of The Commonwealth of the Bahamas and to its associated group of smaller islands. Eleuthera forms a part of the Great Bahama Bank. The island of Eleuthera incorporates the smaller Harbour Island. "Eleuthera" derives from the feminine form of the Greek adjective ἐλεύθερος (''eleútheros''), meaning "free". Known in the 17th century as Cigateo, it lies 80 km (50 miles) east of Nassau. It is long and thin—180 km (110 miles) long and in places little more than 1.6 km (1.0 mile) wide. Its eastern side faces the Atlantic Ocean, and its western side faces the Great Bahama Bank. The topography of the island varies from wide rolling pink sand beaches to large outcrops of ancient coral reefs, and its population is approximately 11,000. The principal economy of the island is tourism. Geography and wildlife The name Eleuthera refers both to the single Bahamian island and is also used to refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and to the east by the Gulf of Mexico. Mexico covers ,Mexico '' The World Factbook''. . making it the world's 13th-largest country by area; with approximately 12 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Squadron
The Home Squadron was part of the United States Navy in the mid-19th century. Organized as early as 1838, ships were assigned to protect coastal commerce, aid ships in distress, suppress piracy and the Atlantic slave trade, make coastal surveys, and train ships to relieve others on distant stations. It was discontinued in 1861 after the outbreak of the American Civil War, when the Union blockade forced a reassignment of ships to close off Southern ports. History Mexican–American War During the Mexican–American War the ships of the Home Squadron, commanded by Commodore David Conner, USN fought in several engagements against Mexican forces. Many of the Home Squadron vessels were attached to vice commander Commodore Matthew C. Perry's Mosquito Fleet which was involved in the battles of Tuxpan, Tabasco, Villahermosa and Veracruz. No ship-to-ship combat occurred though several merchant vessels were captured, the Home Squadron primarily operated against Mexican coastal fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |