|
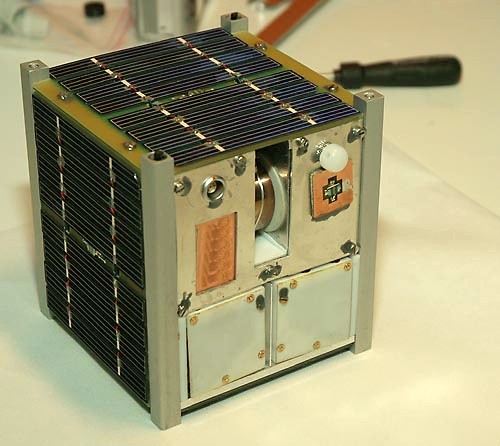
UPSat
UPSat was the first satellite manufactured in Greece to be successfully launched into orbit, by the University of Patras and Libre Space Foundation (an earlier Greek-made communications satellite, HELMARS-SAT, although entirely constructed by 1999, was not launched due to budget limitations). It was part of the QB50 mission with ID GR-02. The UPSat mission was the first satellite launched into orbit made entirely of open-source software and open-source hardware. Open-source The UPSat mission developed an open-source hardware and software 2U cubesat, minimizing the use of commercial off the shelf components, and providing hardware and software designs under the provisions of the CERN-OHLv2 and GNU-GPLv3 licenses respectfully. The vast majority of its components were designed from scratch in an open-source software and hardware way. Mission UPSat, as part of the QB50 cubesat constellation, was launched to the International Space Station at April 18, 2017 11:11 EDT at Cape Can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libre Space Foundation
Libre Space Foundation (LSF) is a Greece, Greek Nonprofit organization, non-profit organization dedicated to developing open-source technologies for space exploration. It was founded in 2015 by the creators of SatNOGS, a global network of satellite Ground station, ground stations, now operated by the foundation. In 2017 it launched its first satellite, UPSat, which was the first satellite manufactured in Greece and the first satellite made entirely with open-source software and open-source hardware. Since then it has gotten two more satellites to orbit while working on other projects as well, such as designing and manufacturing a Hybrid-propellant rocket, hybrid-fueled sounding rocket. Background In 2014 the founders of the Libre Space Foundation participated in NASA's SpaceApps Challenge at the Hackerspace.gr, Athens Hackerspace with their SatNOGS project, an open source network of Ground station, ground stations. They didn't win but competed in another competition the same year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Patras
The University of Patras (UPatras; , ''Panepistímio Patrón'', ΠΠ) is a public university in Patras, Greece. It is the third-largest university in Greece with respect to the size of the student body, the staff, and the number of departments."''The EEC recommends that the Institution should develop and implement a pragmatic strategic planning process to set priorities for the university as a whole and for each School with an explicitly defined set of targets and timelines. The EEC evaluated and scored according to our estimate of where UPatras stands in relation to our understanding of an international norm of excellence. Although we are conscious of the severe constraints imposed by the Greek State, we have not used them as an excuse for not identifying areas of improvement. Please note that an EEC member gave a worthy of merit vote by taking into account with a heavier weight the negative influence of the external environment on UPatras's ability to plan, strategise and ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SatNOGS
SatNOGS (Satellite Networked Open Ground Station) project is a free software and open source hardware platform aimed to create a satellite ground station network. The scope of the project is to create a full stack of open technologies based on open standards, and the construction of a full ground station as a showcase of the stack. History The SatNOGS project was initiated during NASA SpaceApps Challenge in 2014 at Athens Hackerspace. The project then took part in and won the first place of the Hackaday Prize 2014 competition. SatNOGS is currently a project of the Libre Space Foundation. Overview SatNOGS aims to provide a stack of technologies needed for a distributed network of low Earth orbit satellite ground stations. In order to implement such a stack the four following different sub-projects are developed Network SatNOGS Network is a web application for scheduling observations across the network of ground stations. Database SatNOGS Database is a crowd-source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
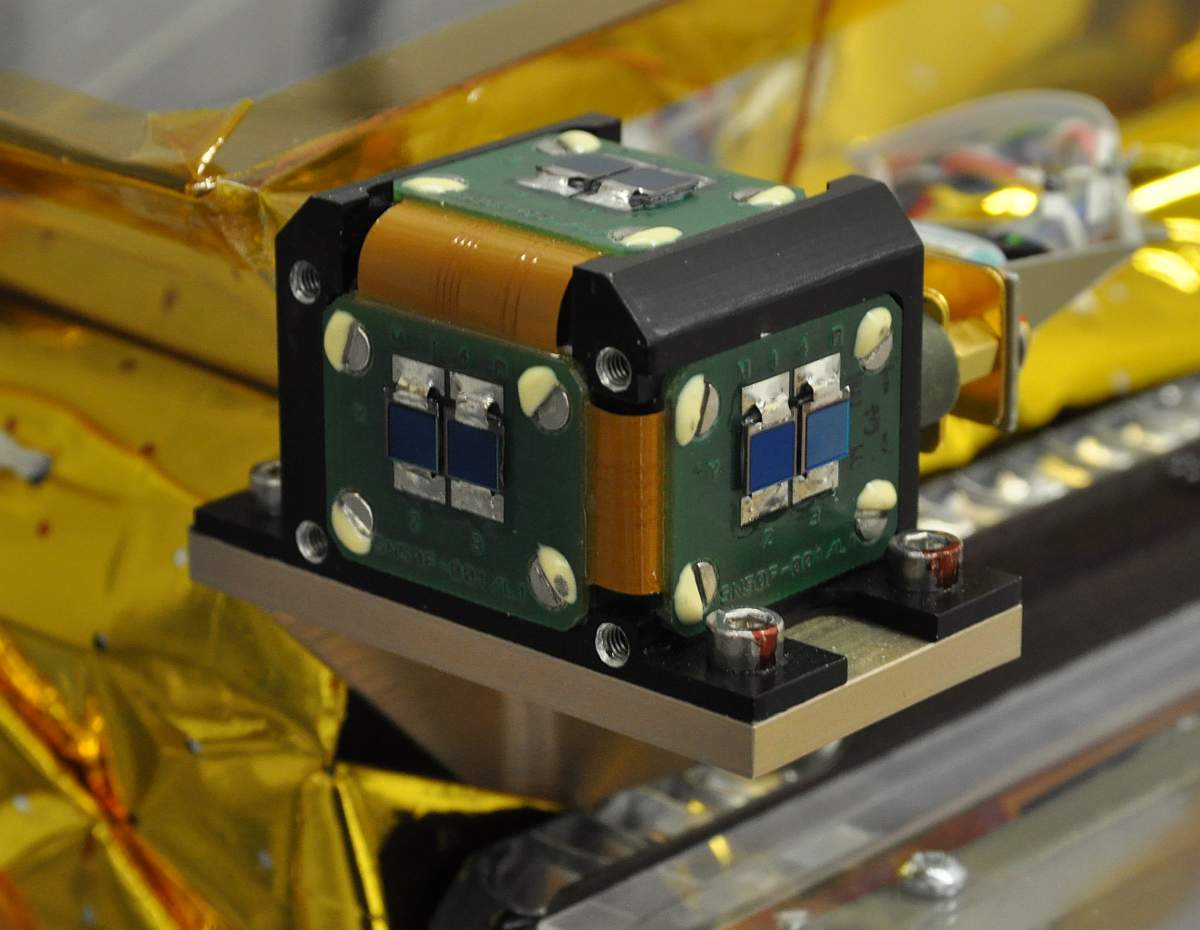
Sun Sensor
A Sun sensor is a navigational instrument used by spacecraft to detect the position of the Sun. Sun sensors are used for Spacecraft attitude control, attitude control, solar array pointing, gyroscope, gyro updating, and safe mode (spacecraft), fail-safe recovery. In addition to spacecraft, Sun sensors find use in ground-based weather stations and Sun-tracking systems, and aerial vehicles including Balloon (aeronautics), balloons and Unmanned aerial vehicle, UAVs. Mechanism There are various types of Sun sensors, which differ in their technology and performance characteristics. Sun presence sensors provide a binary number, binary output, indicating when the Sun is within the sensor's field of view. Analog electronics, Analog and digital electronics, digital Sun sensors, in contrast, indicate the angle of the Sun by continuous and discrete signal outputs, respectively. In typical Sun sensors, a thin slit at the top of a rectangular chamber allows a line of light to fall on an array ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MPPT
Maximum power point tracking (MPPT), or sometimes just power point tracking (PPT), is a technique used with variable power sources to maximize energy extraction as conditions vary. The technique is most commonly used with photovoltaic (PV) solar systems but can also be used with wind turbines, optical power transmission and thermophotovoltaics. PV solar systems have varying relationships to inverter systems, external grids, battery banks, and other electrical loads. The central problem addressed by MPPT is that the efficiency of power transfer from the solar cell depends on the amount of available sunlight, shading, solar panel temperature and the load's electrical characteristics. As these conditions vary, the load characteristic ( impedance) that gives the highest power transfer changes. The system is optimized when the load characteristic changes to keep power transfer at highest efficiency. This optimal load characteristic is called the ''maximum power point'' (MPP). MPPT is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FreeRTOS
FreeRTOS is a real-time operating system Kernel (operating system), kernel for embedded devices that has been ported to 40 microcontroller platforms. It is distributed under the MIT License. History The FreeRTOS kernel was originally developed by Richard Barry around 2003, and was later developed and maintained by Barry's company, Real Time Engineers Ltd. In 2017, the firm passed stewardship of the FreeRTOS project to Amazon Web Services (AWS). Barry continues to work on FreeRTOS as part of an AWS team. With the transition to Amazon control, subsequent releases of the project also switched licensing from GPL version 2 (with special exceptions for static linking to proprietary code outside the FreeRTOS kernel itself) to MIT. Implementation FreeRTOS is designed to be small and simple. It is mostly written in the C (programming language), C programming language to make it easy to port and maintain. It also comprises a few assembly language functions where needed, mostly in archite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetometer
A magnetometer is a device that measures magnetic field or magnetic dipole moment. Different types of magnetometers measure the direction, strength, or relative change of a magnetic field at a particular location. A compass is one such device, one that measures the direction of an ambient magnetic field, in this case, the Earth's magnetic field. Other magnetometers measure the magnetic dipole moment of a magnetic material such as a ferromagnet, for example by recording the effect of this magnetic dipole on the induced current in a coil. The invention of the magnetometer is usually credited to Carl Friedrich Gauss in 1832. Earlier, more primitive instruments were developed by Christopher Hansteen in 1819, and by William Scoresby by 1823. Magnetometers are widely used for measuring the Earth's magnetic field, in geophysical surveys, to detect magnetic anomalies of various types, and to determine the dipole moment of magnetic materials. In an aircraft's attitude and heading ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QB50
A CubeSat is a class of small satellite with a form factor of cubes. CubeSats have a mass of no more than per unit,, url=https://static1.squarespace.com/static/5418c831e4b0fa4ecac1bacd/t/5f24997b6deea10cc52bb016/1596234122437/CDS+REV14+2020-07-31+DRAFT.pdf , title=Cubesat Design Specification , publisher= Cal Poly SLO , year=2020 , location=San Luis Obispo , pages=12 and often use commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) components for their electronics and structure. CubeSats are deployed into orbit from the International Space Station, or launched as secondary payloads on a launch vehicle. , more than 2,300 CubeSats have been launched. In 1999, California Polytechnic State University (Cal Poly) professor Jordi Puig-Suari and Bob Twiggs, a professor at Stanford University Space Systems Development Laboratory, developed the CubeSat specifications to promote and develop the skills necessary for the design, manufacture, and testing of small satellites intended for low Earth orbit (LEO) that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Geomagnetic Reference Field
The International Geomagnetic Reference Field (IGRF) is a standard mathematical description of the large-scale structure of the Earth's main magnetic field and its secular variation. It was created by fitting parameters of a mathematical model of the magnetic field to measured magnetic field data from surveys, observatories and satellites across the globe. The IGRF has been produced and updated under the direction of the International Association of Geomagnetism and Aeronomy (IAGA) since 1965. The IGRF model covers a significant time span, and so is useful for interpreting historical data. (This is unlike the World Magnetic Model, which is intended for navigation in the next few years.) It is updated at 5-year intervals, reflecting the most accurate measurements available at that time. The current 13th edition of the IGRF model (IGRF-13) was released in December 2019 and is valid from 1900 until 2025. For the interval from 1945 to 2015, it is "definitive" (a "DGRF"), meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |