|
UIQ
UIQ (formerly known as User Interface Quartz) was a software platform based upon Symbian OS, created by UIQ Technology AB. It is a graphical user interface layer that provides additional components to the core operating system, to enable the development of feature-rich mobile phones that are open to expanded capabilities through third-party applications. History UIQ was the result of 'Quartz', a user interface for pen PDAs that was one of the three provisional interfaces that were designed by Symbian Ltd. The first three Quartz phones never made it to market, including Psion's "Odin" in a joint venture with Motorola, which was cancelled in January 2001, causing Psion's shares to deteriorate. Engineers thereafter created a lighter version of the software which was presented in 2002, and first shipped that year with Sony Ericsson P800. Sony Ericsson was the main OEM using the UIQ platform in its products. Motorola also developed some products using UIQ, but abandoned the platform ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UIQ Technology
UIQ Technology AB was a Swedish company that developed and licensed the UIQ software based on Symbian OS which was used in smartphone offerings from Sony Ericsson, Motorola, BenQ and Arima. They were based in the Soft Center Science & Research Park in Ronneby, Sweden, and at the time of its closure in 2009 was jointly owned by Motorola and Sony Ericsson. History UIQ Technology was established in April 1999 as Symbian AB, a wholly owned subsidiary of Symbian Ltd., following their acquisition of Ericsson Mobile Applications Lab from Ericsson Mobile Communications. Using technology gained from the acquisition they created the UIQ platform which launched in 2002 and as the company changed its name to UIQ Technology. In 2002 Sony Ericsson and Motorola (both members of Symbian Ltd.) came close to a joint venture, but this was abandoned when Motorola chose to use a Linux-based platform in 2003. As a result, Sony Ericsson was the main licensee for UIQ. On 7 November 2006, Sony Erics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbian
Symbian is a discontinued mobile operating system (OS) and computing platform designed for smartphones. It was originally developed as a proprietary software OS for personal digital assistants in 1998 by the Symbian Ltd. consortium. Symbian OS is a descendant of Psion's EPOC, and was released exclusively on ARM processors, although an unreleased x86 port existed. Symbian was used by many major mobile phone brands, like Samsung, Motorola, Sony Ericsson, and above all by Nokia. It was also prevalent in Japan by brands including Fujitsu, Sharp and Mitsubishi. As a pioneer that established the smartphone industry, it was the most popular smartphone OS on a worldwide average until the end of 2010, at a time when smartphones were in limited use, when it was overtaken by iOS and Android. It was notably less popular in North America. The Symbian OS platform is formed of two components: one being the microkernel-based operating system with its associated libraries, and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
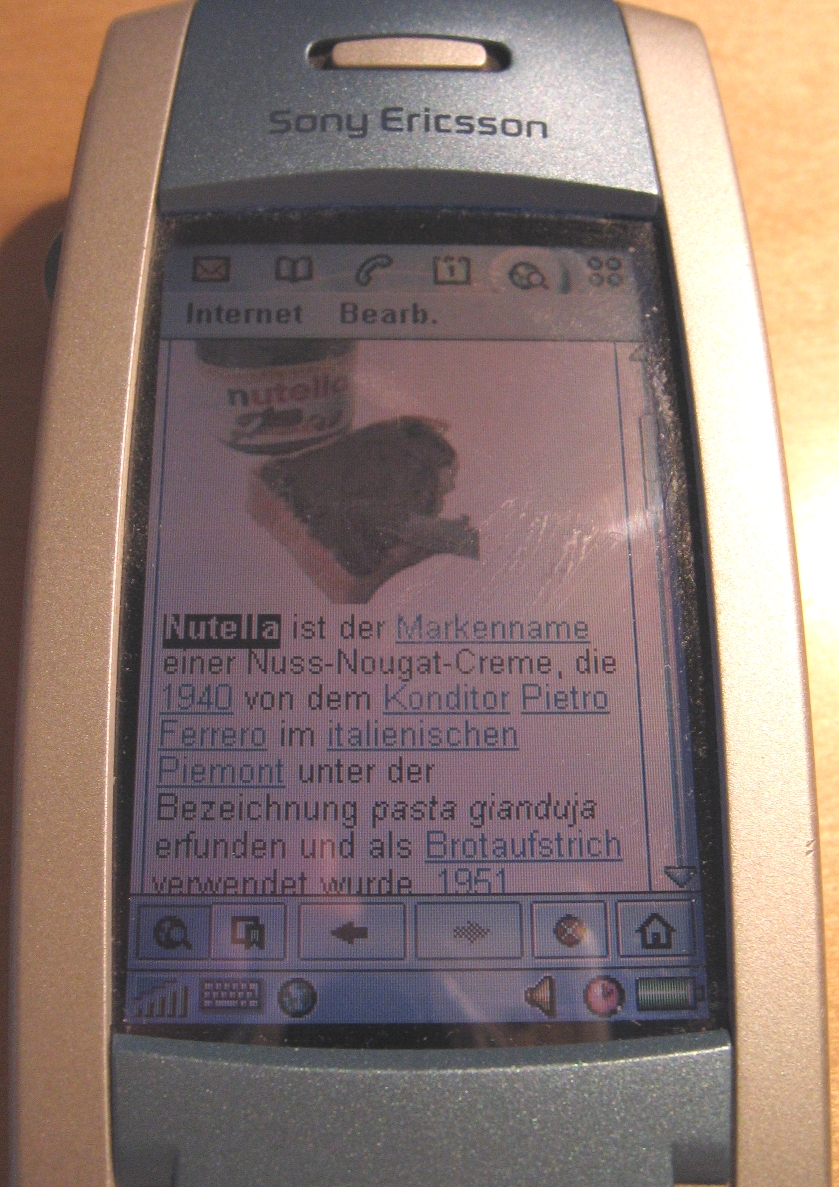
Sony Ericsson P800
The Sony Ericsson P800 is a smartphone introduced in 2002 based upon UIQ version 2.0 (which itself is based upon Symbian OS v7.0) from Sony Ericsson. The P800 is considered the successor of the Ericsson R380, and initial design work was done within Ericsson, but it was produced after Sony & Ericsson merged their mobile phone businesses. The P800 uses the UIQ (version 2.0) user interface and has a touch screen much like a PDA. It is powered by an ARM9 processor running at 156MHz, which was also used for the successive models Sony Ericsson P900, Sony Ericsson P910. It came with a 16MB Memory Stick Duo but supports up to 128MB. The touchscreen displays 4,096 colours (12-bit colour depth). It was succeeded in 2003 by the Sony Ericsson P900. A long awaited updated version of the "P" series phones, the Sony Ericsson P990 was launched at the Symbian Smartphone Show in September 2005. It is based upon the UIQ3 platform (utilizing Symbian OS v9.1). The latest successor is the Sony ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola RIZR Z8
Motorola Rizr (, styled RIZR) is a series of slide mobile phones from Motorola, and is one of the series in the 4LTR line. The first model was released in late 2006. It is a sliding phone (in the style of competing Samsung and LG phones), where the numeric keys are hidden beneath the screen of the phone when closed. Z3 The Motorola Rizr Z3 was released in July 2006. Design and appearance The Rizr Z3 uses a technical form factor, where the user can push on a plastic ''push bar'' located under the screen in order to open the phone. When opened, the top portion slides upwards, revealing the standard keys (including numeric, star, and pound keys). These keys are covered when the phone is closed, but the remaining keys, including the side keys, can be used normally once the keypad is unlocked; such keys can be set to automatically lock shortly after the device is closed to prevent accidental activation when in a purse or pocket. It also has 2 mini lights, located at either side o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Symbian Ltd
Symbian Ltd. was a software development and licensing consortium company, known for the Symbian operating system (OS), for smartphones and some related devices. Its headquarters were in Southwark, London, England, with other offices opened in Cambridge, Sweden, Silicon Valley, Japan, India, China, South Korea, and Australia. It was established on 24 June 1998 as a partnership between Psion, Nokia, Ericsson, Motorola, and Sony, to exploit the convergence between personal digital assistants (PDAs) and mobile phones, and a joint-effort to prevent Microsoft from extending its desktop computer monopoly into the mobile devices market. Ten years to the day after it was established, on 24 June 2008, Nokia announced that they intended to acquire the shares that they did not own already, at a cost of €264 million. On the same day the Symbian Foundation was announced, with the aim to "provide royalty-free software and accelerate innovation", and the pledged contribution of the Symbi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Series 60
The S60 Platform (formerly Series 60 User Interface) was a software platform for smartphones that runs on top of the Symbian operating system. It was created by Nokia based on the 'Pearl' user interface from Symbian Ltd. It was introduced at COMDEX in November 2001 and first shipped with the Nokia 7650 smartphone. The platform has since seen 5 updated editions. Series 60 was renamed to ''S60'' in November 2005. In 2008, the Symbian Foundation was formed to consolidate all the assets of different Symbian platforms (S60, UIQ, MOAP), making it open source. In 2009, based on the code base of S60, the first iteration of the platform since the creation of Symbian Foundation was launched as S60 5th Edition, or Symbian^1, on top of Symbian OS 9.4 as its base. Subsequent iterations were named Symbian^2 (Japanese market only) and Symbian^3. The S60 software was a multivendor standard for smartphones that supports application development in Java MIDP, C++, Python and Adobe Flas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motorola Razr3
The Motorola Razr3 (often stylized as RAZR3) is a cancelled series of clamshell/flip mobile phones from Motorola, as the successor to the popular RAZR (and RAZR2) series. The Razr3 consisted of one prototype model, the VE1. Due to the bankruptcy of UIQ Technology and Motorola's subsequent move to Android in 2009, the Razr3's worldwide release was cancelled. However, the phone was released in South Korea by SK Telecom in late 2009 as model V13, featuring CDMA instead of GSM/HSDPA. The Razr3 featured the Symbian smartphone operating system with the UIQ UIQ (formerly known as User Interface Quartz) was a software platform based upon Symbian OS, created by UIQ Technology AB. It is a graphical user interface layer that provides additional components to the core operating system, to enable the deve ... interface, an external touchscreen, and a 5.0 megapixel camera with an LED flash. V13 The RAZR3 V13 was released by carrier SK Telecom on November 6, 2009 exclusively to South Kore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Android OS
Android is a mobile operating system based on a modified version of the Linux kernel and other open-source software, designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablets. Android is developed by a consortium of developers known as the Open Handset Alliance and commercially sponsored by Google. It was unveiled in November 2007, with the first commercial Android device, the HTC Dream, being launched in September 2008. Most versions of Android are proprietary. The core components are taken from the Android Open Source Project (AOSP), which is free and open-source software (FOSS) primarily licensed under the Apache License. When Android is installed on devices, the ability to modify the otherwise free and open-source software is usually restricted, either by not providing the corresponding source code or by preventing reinstallation through technical measures, thus rendering the installed version proprietary. Most Android devices ship with additional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Software Development Kit
A software development kit (SDK) is a collection of software development tools in one installable package. They facilitate the creation of applications by having a compiler, debugger and sometimes a software framework. They are normally specific to a hardware platform and operating system combination. To create applications with advanced functionalities such as advertisements, push notifications, etc; most application software developers use specific software development kits. Some SDKs are required for developing a platform-specific app. For example, the development of an Android app on the Java platform requires a Java Development Kit. For iOS applications (apps) the iOS SDK is required. For Universal Windows Platform the .NET Framework SDK might be used. There are also SDKs that add additional features and can be installed in apps to provide analytics, data about application activity, and monetization options. Some prominent creators of these types of SDKs include Google, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Mode
In computing, native software or data-formats are those that were designed to run on a particular operating system. In a more technical sense, native code is code written specifically for a certain processor. In contrast, cross-platform software can be run on multiple operating systems and/or computer architectures. For example, a Game Boy receives its software through a cartridge, which contains code that runs natively on the Game Boy. The only way to run this code on another processor is to use an emulator, which simulates an actual Game Boy. This usually comes at the cost of speed. Applications Something running on a computer natively means that it is running without any external layer requiring fewer software layers. For example, in Microsoft Windows the Native API is an application programming interface specific for Windows NT kernel, which can be used to give access to some kernel functions, which cannot be directly accessed through a more universal Windows API. Ope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Color Depth
Color depth or colour depth (see spelling differences), also known as bit depth, is either the number of bits used to indicate the color of a single pixel, or the number of bits used for each color component of a single pixel. When referring to a pixel, the concept can be defined as bits per pixel (bpp). When referring to a color component, the concept can be defined as bits per component, bits per channel, bits per color (all three abbreviated bpc), and also bits per pixel component, bits per color channel or bits per sample (bps). Modern standards tend to use bits per component, but historical lower-depth systems used bits per pixel more often. Color depth is only one aspect of color representation, expressing the precision with which the amount of each primary can be expressed; the other aspect is how broad a range of colors can be expressed (the gamut). The definition of both color precision and gamut is accomplished with a color encoding specification which assigns a di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |