|
UH 25
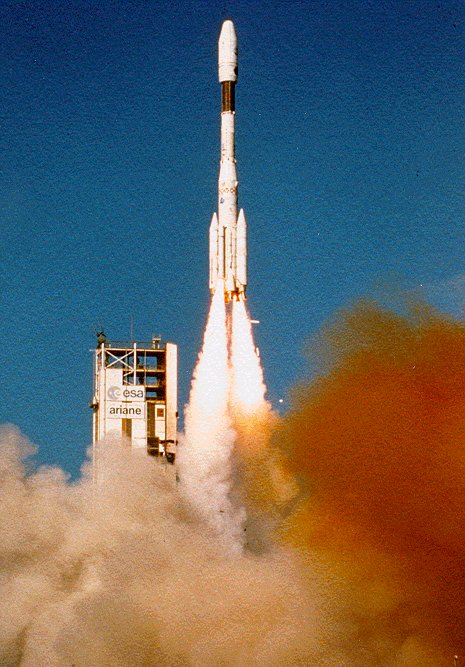
UH 25 is a fuel mixture for rockets. It was developed for the European Ariane 2–4 launch vehicles. UH 25 was developed after a disaster during flight 2 of the Ariane 1 rocket. During launch, one of the four Viking engines on the first stage developed a combustion instability which led to an engine fire, subsequent explosion and destruction of the vehicle. Following this event and starting with Ariane 2, the fuel was changed from pure UDMH to the mixture UH 25. UH 25 was used in Ariane rocket versions 2 through 4, and in the Indian GSLV Mk III UH 25 is a mixture of 75% UDMH and 25% hydrazine hydrate.Tim Furniss: ''Ingenieure bei der Arbeit, Raumschiffe und Raketen'', Tessloff Verlag, Nürnberg (1989), Seite: 31 (German) It is hypergolic with dinitrogen tetroxide as oxidizer, and both can be stored as liquids at room temperature. Danger Like its components, UH 25 is flammable, toxic (carcinogenic) and corrosive. Safety labels See also * Aerozine 50 - a 50:50 mix of hydra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ariane (rocket)
Ariane is a series of European civilian expendable launch vehicles for space launch use. The name comes from the French spelling of the mythological character Ariadne. France first proposed the Ariane project and it was officially agreed upon at the end of 1973 after discussions between France, Germany and the UK. The project was Western Europe's second attempt to develop its own launcher following the unsuccessful Europa project. The Ariane project was code-named L3S (the French abbreviation for third-generation substitution launcher). The European Space Agency (ESA) charged Airbus Defence and Space with the development of all Ariane launchers and of the testing facilities, while Arianespace, a 32.5% CNES (French government space agency) commercial subsidiary created in 1980, handles production, operations and marketing. Arianespace launches Ariane rockets from the Guiana Space Centre at Kourou in French Guiana. Ariane versions Ariane 1 was a three-stage launcher, deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viking (rocket Engine)
The Viking rocket engines were members of a series of bipropellant engines for the first and second stages of the Ariane 1 through Ariane 4 commercial launch vehicles, using storable, hypergolic propellants: dinitrogen tetroxide and UH 25, a mixture of 75% UDMH and 25% hydrazine Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine ... (originally UDMH). The earliest versions, developed in 1965, had a sea-level thrust of about 190 kN. By 1971, the thrust had improved to 540 kN, with resulting engine named Viking 1 and adopted for the Ariane program. The engine first flown on the Ariane 1 rocket in 1979 was Viking 2, with thrust further improved to 611 kN. The version used on the Ariane 4 first stage, which used a cluster of four, had 667 kN thrust each. The sec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mk III
The Launch Vehicle Mark-3 (LVM 3), previously referred to as the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk3), is a three-stage medium-lift launch vehicle developed by the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO). Primarily designed to launch communication satellites into geostationary orbit, it is also due to launch crewed missions under the Indian Human Spaceflight Programme. GSLV Mk III has a higher payload capacity than it's predecessor, GSLV Mk II. After several delays and a sub-orbital test flight on 18 December 2014, ISRO successfully conducted the first orbital test launch of GSLV Mk III on 5 June 2017 from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre. Total development cost of project was . In June 2018, the Union Cabinet approved to build 10 GSLV Mk III rockets over a five-year period. The GSLV Mk III has launched CARE, India's space capsule recovery experiment module, Chandrayaan-2, India's second lunar mission, and will be used to carry Gaganyaan, the first cr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UDMH
Unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH; 1,1-dimethylhydrazine, НДМГ or codenamed Geptil) is a chemical compound with the formula H2NN(CH3)2 that is used as a rocket propellant. It is a colorless liquid, with a sharp, fishy, ammonia-like smell typical for organic amines. Samples turn yellowish on exposure to air and absorb oxygen and carbon dioxide. It is miscible with water, ethanol, and kerosene. In concentration between 2.5% and 95% in air, its vapors are flammable. It is not sensitive to shock. Symmetrical dimethylhydrazine, 1,2-dimethylhydrazine is also known but is not as useful. Production UDMH is produced industrially by two routes. Based on the Olin Raschig process, one method involves reaction of monochloramine with dimethylamine giving 1,1-dimethylhydrazinium chloride: :(CH3)2NH + NH2Cl → (CH3)2NNH2 ⋅ HCl In the presence of suitable catalysts, acetylhydrazine can be N-dimethylated using formaldehyde and hydrogen to give the N,N-dimethyl-N'-acetylhydrazin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrazine Hydrate
Hydrazine is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a simple pnictogen hydride, and is a colourless flammable liquid with an ammonia-like odour. Hydrazine is highly toxic unless handled in solution as, for example, hydrazine hydrate (). Hydrazine is mainly used as a foaming agent in preparing polymer foams, but applications also include its uses as a precursor to polymerization catalysts, pharmaceuticals, and agrochemicals, as well as a long-term storable propellant for in-space spacecraft propulsion. Additionally, hydrazine is used in various rocket fuels and to prepare the gas precursors used in air bags. Hydrazine is used within both nuclear and conventional electrical power plant steam cycles as an oxygen scavenger to control concentrations of dissolved oxygen in an effort to reduce corrosion. the world hydrazine hydrate market amounted to $350 million. About two million tons of hydrazine hydrate were used in foam blowing agents in 2015. Hydra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypergolic
A hypergolic propellant is a rocket propellant combination used in a rocket engine, whose components spontaneously ignite when they come into contact with each other. The two propellant components usually consist of a fuel and an oxidizer. The main advantages of hypergolic propellants are that they can be stored as liquids at room temperature and that engines which are powered by them are easy to ignite reliably and repeatedly. Common hypergolic propellants are difficult to handle due to their extreme toxicity and/or corrosiveness. In contemporary usage, the terms "hypergol" and "hypergolic propellant" usually mean the most common such propellant combination: dinitrogen tetroxide plus hydrazine and/or its relatives monomethylhydrazine (MMH) and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH). History In 1935, Hellmuth Walter discovered that hydrazine hydrate was hypergolic with high-test peroxide of 80-83%. He was probably the first to discover this phenomenon, and set to work develop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dinitrogen Tetroxide
Dinitrogen tetroxide, commonly referred to as nitrogen tetroxide (NTO), and occasionally (usually among ex-USSR/Russia rocket engineers) as amyl, is the chemical compound N2O4. It is a useful reagent in chemical synthesis. It forms an Chemical equilibrium, equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. Its molar mass is 92.011 g/mol. Dinitrogen tetroxide is a powerful oxidizer that is hypergolic (spontaneously reacts) upon contact with various forms of hydrazine, which has made the pair a common bipropellant for rockets. Structure and properties Dinitrogen tetroxide could be regarded as two nitro groups (-NO2) bonded together. It forms an Chemical equilibrium, equilibrium mixture with nitrogen dioxide. The molecule is planar with an N-N bond distance of 1.78Å and N-O distances of 1.19Å. The N-N distance corresponds to a weak bond, since it is significantly longer than the average N-N single bond length of 1.45Å. This exceptionally weak σ bond (amounting to overlapping of the ''sp' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hazard T
A hazard is a potential source of harm. Substances, events, or circumstances can constitute hazards when their nature would allow them, even just theoretically, to cause damage to health, life, property, or any other interest of value. The probability of that harm being realized in a specific ''incident'', combined with the magnitude of potential harm, make up its risk, a term often used synonymously in colloquial speech. Hazards can be classified in several ways; they can be classified as natural, anthropogenic, technological, or any combination, such as in the case of the natural phenomenon of wildfire becoming more common due to human-made climate change or more harmful due to changes in building practices. A common theme across many forms of hazards in the presence of stored energy that, when released, can cause damage. The stored energy can occur in many forms: chemical, mechanical, thermal hazards and by the populations that may be affected and the severity of the associate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aerozine 50
__NOTOC__ Aerozine 50 is a 50:50 mix by weight of hydrazine and unsymmetrical dimethylhydrazine (UDMH), originally developed in the late 1950s by Aerojet General Corporation as a storable, high-energy, hypergolic fuel for the Titan II ICBM rocket engines. Aerozine continues in wide use as a rocket fuel, typically with dinitrogen tetroxide as the oxidizer, with which it is hypergolic. Aerozine 50 is more stable than hydrazine alone, and has a higher density and boiling point than UDMH alone. Pure hydrazine has a higher performance than Aerozine 50, but an unacceptable freezing point. By mixing pure hydrazine with UDMH, hydrazine's inconveniently high freezing point of 2 °C is lowered through freezing-point depression. In addition, UDMH is a more stable molecule; this reduces the chances of straight hydrazine decomposing unexpectedly, increasing safety and allowing the blend to be used as a coolant in regeneratively cooled engines. This type of fuel is mainly used fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-Stoff
C-Stoff (; "substance C") was a reductant used in bipropellant rocket fuels (as a fuel itself) developed by Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft in Germany during World War II. It was developed for use with T-Stoff (a high-test peroxide) as an oxidizer, which together with C-Stoff as the fuel, forms a hypergolic mixture. The proportions of the components in C-Stoff were developed to catalyse the decomposition of T-Stoff, promote combustion with the oxygen released by the decomposition, and sustain uniform combustion through sufficient quantity of the highly reactive hydrazine. The combination of the C-Stoff, used as a rocket fuel, with the T-Stoff used as the oxidizer, often resulted in spontaneous explosion from their combined nature as a hypergolic fuel combination, necessitating strict hygiene in fueling operations; there were numerous catastrophic explosions of the Messerschmitt Me 163 aircraft that employed this fuel system. Another hazard was toxicity to humans of ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
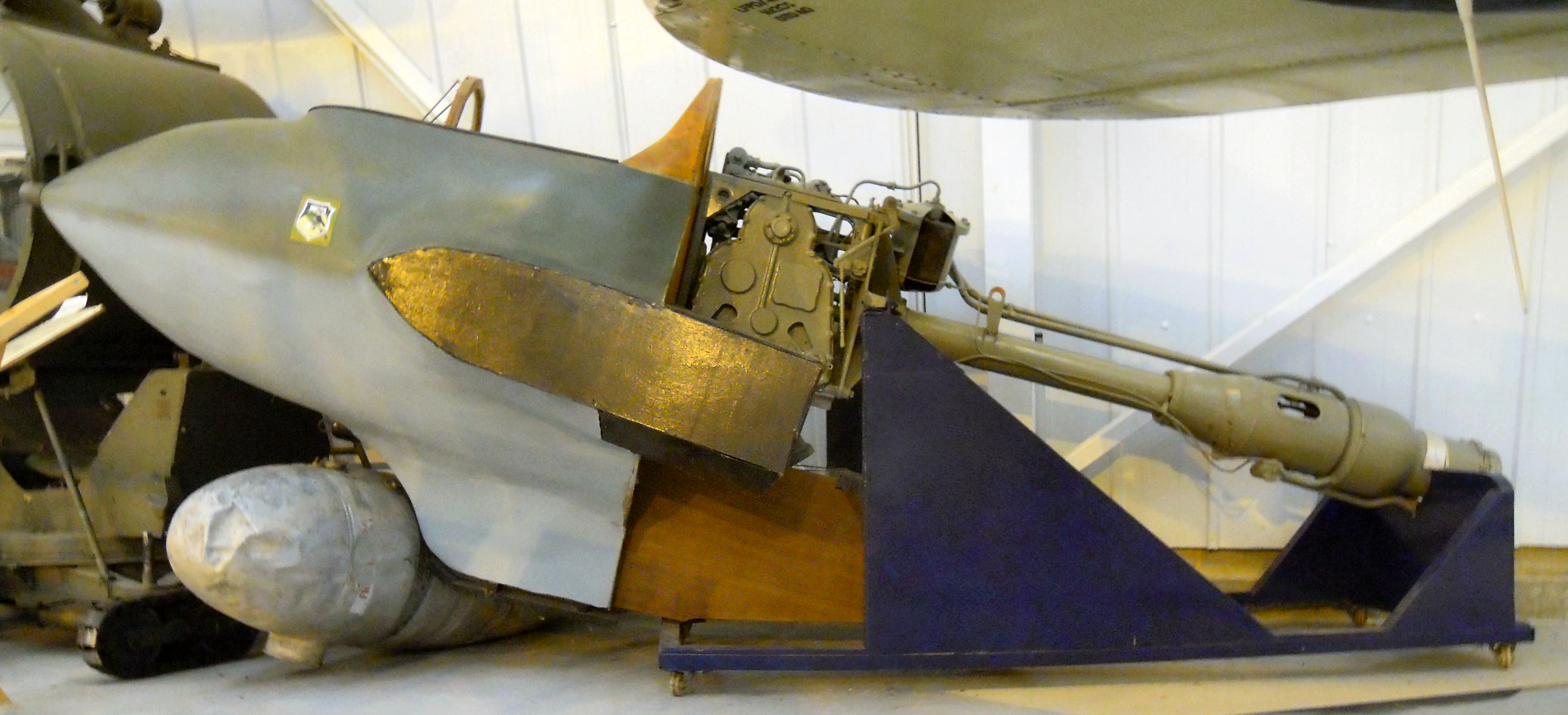
HWK 109-509
The Walter HWK 109-509 was a German liquid-fuel bipropellant rocket engine that powered the Messerschmitt Me 163 Komet and Bachem Ba 349 aircraft. It was produced by Hellmuth Walter Kommanditgesellschaft (HWK) commencing in 1943, with licensed production by the Heinkel firm's facilities in Jenbach, Austria. Design and development Early versions of the Me 163 had been powered by an earlier design running on a "cold engine" fueled with Z-Stoff. This fuel tended to clog the jets in the combustion chamber, causing fluctuations in power and potentially explosions. Worse, however, was the fact that the engine could not be throttled, and when the aircraft leveled off after its climb to altitude it quickly accelerated to speeds that caused serious compressibility issues. The RLM demanded that a version be developed with a throttle. During this period Walter had also been working with a new fuel known as C-Stoff that gave off significant heat and was thus known as the "hot engi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |