|
UF6
Uranium hexafluoride, sometimes called hex, is the inorganic compound with the formula . Uranium hexafluoride is a volatile, white solid that is used in enriching uranium for nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. Preparation Uranium dioxide is converted with hydrofluoric acid (HF) to uranium tetrafluoride: : The resulting is subsequently oxidized with fluorine to give the hexafluoride: : In samples contaminated with uranium trioxide, uranyl fluoride, an oxyfluoride compound is produced in the HF step: : which can be fluorinated to produce the same product, uranium hexafluoride. : The fluorination step in both reactions above are highly exothermic. Properties Physical properties At atmospheric pressure, sublimes at 56.5 °C. The solid-state structure was determined by neutron diffraction at 77 K and 293 K.J. C. Taylor, P. W. Wilson, J. W. Kelly: „The structures of fluorides. I. Deviations from ideal symmetry in the structure of crystalline UF6: a neutron diffraction a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranyl Fluoride
Uranyl fluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It is most notable as a contaminant in the production of uranium tetrafluoride. As shown by X-ray crystallography, the uranyl centers are surrounded by six fluoride ligands . This salt is very soluble in water as well as hygroscopic. It changes in color from brilliant orange to yellow after reacting with water. Uranyl fluoride is stable in air up to 300 °C, above which slow decomposition to occurs. When heated to decomposition, emits toxic hydrofluoric acid fumes. It is formed in the hydrolysis of uranium hexafluoride (): : It can also be formed in the hydrofluorination of uranium trioxide (): : References [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Hexachloride
Uranium hexachloride is the inorganic compound with the formula . It features uranium in the +6 oxidation state. hydrolyzes readily but is stable under inert atmosphere. It is soluble in carbon tetrachloride (). It is a multi-luminescent dark green or black solid with a vapor pressure between 1-3 mmHg at 373.15 K. Structure and bonding Uranium hexachloride has an octahedral geometry, with point group Oh. Its lattice (dimensions: 10.95 ± 0.02 Å x 6.03 ± 0.01 Å) is hexagonal in shape with three molecules per cell; the average theoretical U-Cl bond is 2.472 Å long (the experimental U-Cl length found by X-ray diffraction is 2.42 Å), and the distance between two adjacent chlorine atoms is 3.65 Å. Chemical properties is stable up to temperatures between 120 °C and 150 °C. The decomposition of results in a solid phase transition from one crystal form of to another more stable form. It decomposes as follows: : The activation energy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Chloroform was once used as an inhalational anesthetic between the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century. It is miscible with many solvents but it is only very slightly soluble in water (only 8 g/L at 20°C). Structure and name The molecule adopts a tetrahedral molecular geometry with C3v symmetry. The chloroform molecule can be viewed as a methane molecule with three hydrogen atoms replaced with three chlorine atoms, leaving a single hydrogen atom. The name "chloroform" is a portmanteau of ''terchloride'' (tertiary chloride, a trichloride) and ''formyle'', an obsolete name for the methylylidene radical (CH) derived from formic acid. Natural occurrence Many kinds of seaweed produce chlor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium(V) Fluoride
Uranium pentafluoride is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula UF5. It is a pale yellow paramagnetic solid. The compound has attracted interest because it is related to uranium hexafluoride, which is widely used to produce uranium fuel. It crystallizes in two polymorphs, called α- and β-UF5. Synthesis and structure Uranium pentafluoride is an intermediate in the conversion of uranium tetrafluoride to volatile UF6: :2UF4 + F2 → 2UF5 :2UF5 + F2 → 2UF6 It can be produced by reduction of the hexafluoride with carbon monoxide at elevated temperatures. : 2UF6 + CO → 2UF5 + COF2 Other reducing agents have been examined. The α form is a linear coordination polymer consisting of chains of octahedral uranium centers in which one of the five fluoride anion forms a bridge to the next uranium atom. The structure is reminiscent of that for vanadium pentafluoride. In the β form, the uranium centers adopt a square antiprismatic structure. The β polymorph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neutron Diffraction
Neutron diffraction or elastic neutron scattering is the application of neutron scattering to the determination of the atomic and/or magnetic structure of a material. A sample to be examined is placed in a beam of Neutron temperature, thermal or cold neutron radiation, neutrons to obtain a diffraction pattern that provides information of the structure of the material. The technique is similar to X-ray diffraction but due to their different scattering properties, neutrons and X-rays provide complementary information: X-Rays are suited for superficial analysis, strong x-rays from synchrotron radiation are suited for shallow depths or thin specimens, while neutrons having high penetration depth are suited for bulk samples.Measurement of residual stress in materials using neutrons IAEA, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
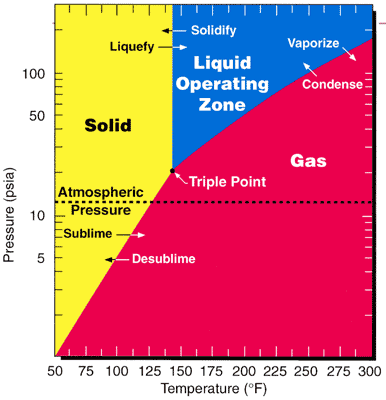
Sublimation (phase Transition)
Sublimation is the Phase transition, transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas state, without passing through the liquid state. The verb form of sublimation is ''sublime'', or less preferably, ''sublimate''. ''Sublimate'' also refers to the product obtained by sublimation. The point at which sublimation occurs rapidly (for further details, see #False correspondence with vaporization, below) is called critical sublimation point, or simply sublimation point. Notable examples include sublimation of dry ice at room temperature and atmospheric pressure, and that of solid iodine with heating. The reverse process of sublimation is deposition (phase transition), ''deposition'' (also called ''desublimation''), in which a substance passes directly from a gas to a solid phase, without passing through the liquid state. Technically, all solids may sublime, though most sublime at extremely low rates that are hardly detectable under usual conditions. At standard condi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as air pressure or barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1,013.25 millibars, 760 mm Hg, 29.9212 inchesHg, or 14.696 psi.International Civil Aviation Organization. ''Manual of the ICAO Standard Atmosphere'', Doc 7488-CD, Third Edition, 1993. . The atm unit is roughly equivalent to the mean sea-level atmospheric pressure on Earth; that is, the Earth's atmospheric pressure at sea level is approximately 1 atm. In most circumstances, atmospheric pressure is closely approximated by the hydrostatic pressure caused by the weight of air above the measurement point. As elevation increases, there is less overlying atmospheric mass, so atmospheric pressure decreases with increasing elevation. Because the atmosphere is thin relative to the Earth's radius—especially the dense atmospheric layer at low altitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxyfluoride
In chemistry, oxohalides or oxyhalides are a group of chemical compounds with the chemical formula , where X is a halogen, and A is an element different than O and X. Known oxohalides have fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), and/or iodine (I). The element A may be a main group element, a transition element, a rare earth element or an actinide. Molecular oxohalides are a group of chemical compounds in which both oxygen and halogen atoms are attached to another chemical element A in a single molecule. The term ''oxohalide'', or ''oxyhalide'', also refers to ionic oxohalides with the same overall chemical formula, but having an ionic structure. There are minerals that are ionic oxohalides. Synthesis Oxohalides can be seen as compounds intermediate between oxides and halides. There are three general methods of synthesis: *Partial oxidation of a halide: *: **In this example, the oxidation state increases by two and the electrical charge is unchanged. *Partial halogenation of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Trioxide
Uranium trioxide (UO3), also called uranyl oxide, uranium(VI) oxide, and uranic oxide, is the hexavalent oxide of uranium. The solid may be obtained by heating uranyl nitrate to 400 °C. Its most commonly encountered polymorph is amorphous UO3. Production and use There are three methods to generate uranium trioxide. As noted below, two are used industrially in the reprocessing of nuclear fuel and uranium enrichment. # U3O8 can be oxidized at 500 °C with oxygen. Note that above 750 °C even in 5 atm O2 UO3 decomposes into U3O8. # Uranyl nitrate, UO2(NO3)2·6H2O can be heated to yield UO3. This occurs during the reprocessing of nuclear fuel. Fuel rods are dissolved in HNO3 to separate uranyl nitrate from plutonium and the fission products (the PUREX method). The pure uranyl nitrate is converted to solid UO3 by heating at 400 °C. After reduction with hydrogen (with other inert gas present) to uranium dioxide, the uranium can be used in new MOX fuel rod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluorine
Fluorine is a chemical element; it has Chemical symbol, symbol F and atomic number 9. It is the lightest halogen and exists at Standard temperature and pressure, standard conditions as pale yellow Diatomic molecule, diatomic gas. Fluorine is extremely Reactivity (chemistry), reactive as it reacts with all other Periodic table, elements except for the light Noble gas, noble gases. It is highly toxicity, toxic. Among the elements, fluorine ranks Abundance of the chemical elements, 24th in cosmic abundance and 13th in crustal abundance. Fluorite, the primary mineral source of fluorine, which gave the element its name, was first described in 1529; as it was added to metal ores to lower their melting points for smelting, the Latin verb meaning gave the mineral its name. Proposed as an element in 1810, fluorine proved difficult and dangerous to separate from its compounds, and several early experimenters died or sustained injuries from their attempts. Only in 1886 did French chemist He ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uranium Tetrafluoride
Uranium tetrafluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula UF4. It is a green solid with an insignificant vapor pressure and low solubility in water. Uranium in its tetravalent ( uranous) state is important in various technological processes. In the uranium refining industry it is known as green salt. Production UF4 is prepared from UO2 in a fluidized bed by reaction with Hydrogen fluoride. The UO2 is derived from mining operations. Around 60,000 tonnes are prepared in this way annually. A common impurity is UO2F2. UF4 is susceptible to hydrolysis as well. UF4 is formed by the reaction of UF6 with hydrogen gas in a vertical tube-type reactor. The bulk density of UF4 varies from about 2.0 g/cm3 to about 4.5 g/cm3 depending on the production process and the properties of the starting uranium compounds. A molten salt reactor design, a type of nuclear reactor where the working fluid is a molten salt, would use UF4 as the core material. UF4 is generally chosen over relate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrofluoric Acid
Hydrofluoric acid is a solution of hydrogen fluoride (HF) in water. Solutions of HF are colorless, acidic and highly corrosive. A common concentration is 49% (48–52%) but there are also stronger solutions (e.g. 70%) and pure HF has a boiling point near room temperature. It is used to make most organofluorine compounds; examples include the commonly used pharmaceutical antidepressant medication fluoxetine (Prozac) and the material PTFE (Teflon). Elemental fluorine is produced from it. It is commonly used to etch glass and silicon wafers. Uses Production of organofluorine compounds The principal use of hydrofluoric acid is in organofluorine chemistry. Many organofluorine compounds are prepared using HF as the fluorine source, including Teflon, fluoropolymers, fluorocarbons, and refrigerants such as freon. Many pharmaceuticals contain fluorine. Production of inorganic fluorides Most high-volume inorganic fluoride compounds are prepared from hydrofluoric acid. Foremost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |