|
Tēlpochcalli
Tēlpochcalli (, Nahuatl: ''house of the young men''), were centers where Aztec youth were educated, from age 15, to serve their community and for war. These youth schools were located in each district or ''calpulli''. Life in the telpochcalli Life in the ''telpochcalli'' was tough. From early morning strenuous activities began. The day began with a cold bath, followed by a controlled and extremely frugal meal. They had to memorize the songs which they offered as praises of their gods and practiced in the use of weapons such as the sling, and the ''macuahuitl''. Students had other obligations, such as carrying the necessary materials to repair the temples (''teocalli''), and collectively working the fields for their livelihood. The Aztec world was characterized by the care the rulers put into the education system. Tenochtitlan schools were of two types, generally depending on the boys' social background: the sons of nobles attended the ''calmecac'', an institution that was located ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calpulli
In pre-Columbian Aztec society, calpulli (from Classical Nahuatl '' calpōlli'', , meaning "large houses", singular calpul) were units of commoner housing that had been split into kin-based or other land holding groups within Nahua city-states or altepetls. In Spanish sources, calpulli are termed ''parcialidades'' or ''barrios.'' The inhabitants of a calpul were collectively responsible for different organizational and religious tasks in relation to the larger altepetl. A calpul could be created based on an extended family, being part of a similar ethnic or national background, or having similar skills and tribute demands. The misunderstanding that calpulli were family units can be blamed on the fact that the word "family" refers to blood relations in English, while in Nahuatl it refers to the people whom you live with. The primary functions of the calpulli were to coordinate land use for growing crops, food production, and manufacturing tribute. Tribute was owed by each tributary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macuahuitl
A macuahuitl () is a weapon, a wooden sword with several embedded obsidian blades. The name is derived from the Nahuatl language and means "hand-wood". Its sides are embedded with prismatic blades traditionally made from obsidian, which is capable of producing an edge sharper than high quality steel razor blades. The macuahuitl was a standard close combat weapon. Use of the macuahuitl as a weapon is attested from the first millennium CE, although specimens can be found in art dating to at least pre-classic times. By the time of the Spanish conquest the macuahuitl was widely distributed in Mesoamerica. The weapon was used by different civilisations including the Aztec (Mexicas), Olmec, Maya, Mixtec, Toltec, and Tarascans. One example of this weapon survived the Conquest of the Aztec Empire; it was part of the Royal Armoury of Madrid until it was destroyed by a fire in 1884. Images of the original designs survive in diverse catalogues. The oldest replica is the macuahuitl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calmecac
The calmecac (, from ''calmecatl'' meaning "line/grouping of houses/buildings" and by extension a scholarly campus) was a school for the sons of Aztec nobility ('' pīpiltin'' ) in the Late Postclassic period of Mesoamerican history, where they would receive rigorous training in history, calendars, astronomy, religion, economy, law, ethics and warfare. The two main primary sources for information on the ''calmecac'' and ''telpochcalli'' are in Bernardino de Sahagún's Florentine Codex of the ''General History of the Things of New Spain'' (Books III, VI, and VIII) and part 3 of the Codex Mendoza. Telpcatli ''Calmecac'' The ''calmecac'' of the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan, was located in the ceremonial centre of the city and was dedicated to Quetzalcoatl.Hassig (1988), p. 34. It was situated conveniently close to the Templo Mayor, where ''calmecac'' graduates destined for priesthood would perform the rituals they had been trained in. The main shrine was judged to be 150 feet t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macehualtin
The mācēhualtin ( IPA: , singular ''mācēhualli'' ) were the commoner social class in Aztec society. The Aztec social class of the ''mācēhualtin'' were rural farmers, forming the majority of the commoners in the Aztec Empire. The ''mācēhualtin'' worked lands that belonged to the social unit of the calpolli called chinampas, with each family maintaining rights to the land so long as it did not lie fallow for more than two years. Within these lands, the rural ''mācēhualtin'' constructed small dams and terraces to increase their agricultural yield. Crops common to Mexican agriculture were grown on these plots, including maize, beans and squash. These projects were probably organized by the local communities and were not state led. From their produce and productivity, the corn were required to pay tribute to the Aztec nobility. During the reign of Moctezuma II (1502–1520), they were banned from serving in the royal palaces, as this monarch widened the divide between ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calmecac
The calmecac (, from ''calmecatl'' meaning "line/grouping of houses/buildings" and by extension a scholarly campus) was a school for the sons of Aztec nobility ('' pīpiltin'' ) in the Late Postclassic period of Mesoamerican history, where they would receive rigorous training in history, calendars, astronomy, religion, economy, law, ethics and warfare. The two main primary sources for information on the ''calmecac'' and ''telpochcalli'' are in Bernardino de Sahagún's Florentine Codex of the ''General History of the Things of New Spain'' (Books III, VI, and VIII) and part 3 of the Codex Mendoza. Telpcatli ''Calmecac'' The ''calmecac'' of the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan, was located in the ceremonial centre of the city and was dedicated to Quetzalcoatl.Hassig (1988), p. 34. It was situated conveniently close to the Templo Mayor, where ''calmecac'' graduates destined for priesthood would perform the rituals they had been trained in. The main shrine was judged to be 150 feet t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aztec Society
Aztec society was a highly complex and stratified society that developed among the Aztecs of central Mexico in the centuries prior to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, and which was built on the cultural foundations of the larger region of Mesoamerica. Politically, the society was organized into independent city-states, called altepetls, composed of smaller divisions ( calpulli), which were again usually composed of one or more extended kinship groups. Socially, the society depended on a rather strict division between nobles and free commoners, both of which were themselves divided into elaborate hierarchies of social status, responsibilities, and power. Economically the society was dependent on agriculture, and also to a large extent on warfare. Other economically important factors were commerce, long-distance and local, and a high degree of trade specialization. Overview Aztec society can trace its roots to Mesoamerican Origins. Their language, lifestyle, and technolo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
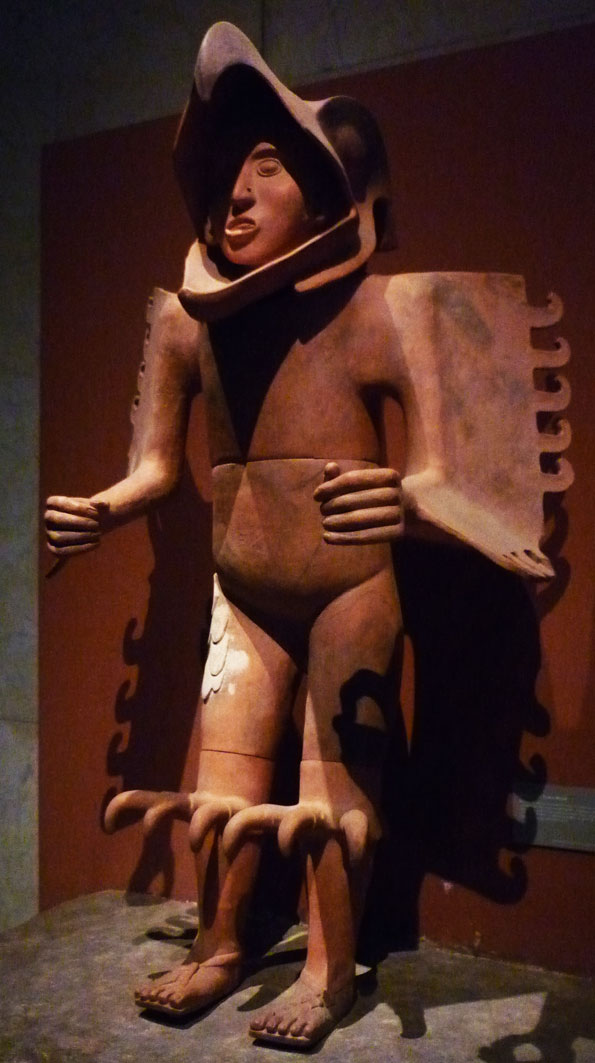
Aztec Warfare
Aztec warfare concerns the aspects associated with the military conventions, forces, weaponry and strategic expansions conducted by the Mesoamerican chronology, Late Postclassic Aztec civilizations of Mesoamerica, including particularly the military history of the Aztec Triple Alliance involving the city-states of Tenochtitlan, Texcoco (Aztec site), Texcoco, Tlacopan and other allied polity, polities of the central Mexican region. This united the Mexica, Apulteca, and Chichimeca people through marriages. The Aztec armed forces were typically made up of a large number of commoners (''yāōquīzqueh'' , "those who have gone to war") who possessed extensive military training, and a smaller but still considerable number of highly professional warriors belonging to the nobility (''Pipiltin, pīpiltin'' ) and who were organized into warrior societies and ranked according to their achievements. The Aztec state's primary purpose was political expansion and dominance of and exaction of tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahuatl
Nahuatl ( ; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahuas, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have smaller populations Nahuatl language in the United States, in the United States. Nahuatl has been spoken in central Mexico since at least the seventh century CE. It was the language of the Mexica, who dominated what is now central Mexico during the Late Postclassic period of Mesoamerican chronology, Mesoamerican history. During the centuries preceding the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, the Aztecs had expanded to incorporate a large part of central Mexico. Their influence caused the variety of Nahuatl spoken by the residents of Tenochtitlan to become a prestige language in Mesoamerica. Following the Spanish conquest, Spanish colonists and missionaries introduced the Latin script, and Nahuatl became a literary language. Many chronicles, gram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
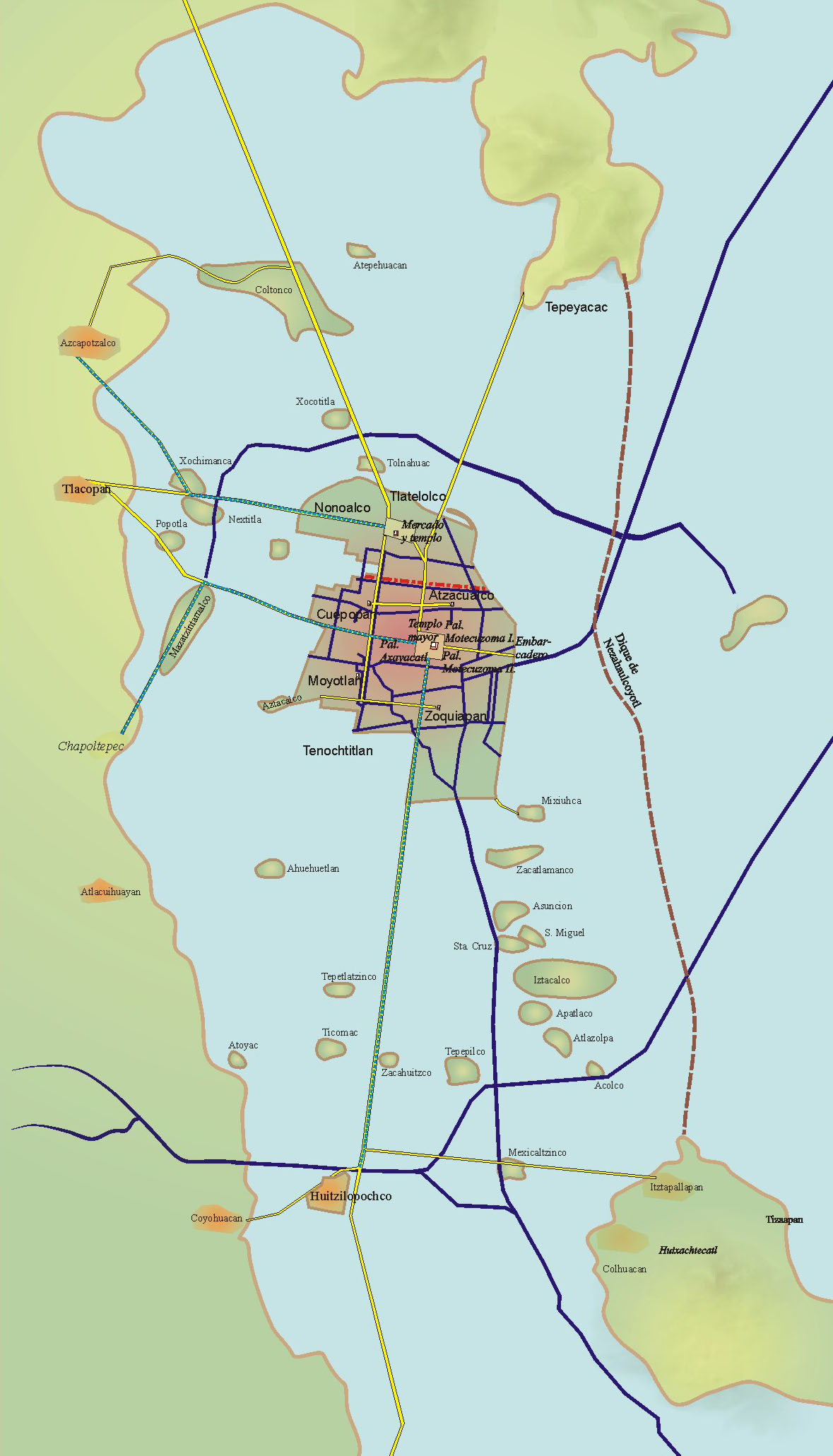
Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th anniversary of the city. The city was built on an island in what was then Lake Texcoco in the Valley of Mexico. The city was the capital of the expanding Aztec Empire in the 15th century until it was Fall of Tenochtitlan, captured by the Tlaxcaltec and the Spanish in 1521. At its peak, it was the largest city-state, city in the pre-Columbian Americas. It subsequently became a ''Municipalities of Mexico, cabecera'' of the Viceroyalty of New Spain. Today, the ruins of are in the historic center of the Mexican capital. The World Heritage Site of contains what remains of the geography (water, boats, Chinampa, floating gardens) of the Mexica capital. was one of two Mexica (city-states or Polity, polities) on the island, the other being . Etymol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chillies
Chili peppers, also spelled chile or chilli ( ), are varieties of fruit#Berries, berry-fruit plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for their pungency. They are used as a spice to add pungency (spicy heat) in many cuisines. Capsaicin and the related Capsaicin#Capsaicinoids, capsaicinoids give chili peppers their intensity when ingested or topical application, applied topically. Chili peppers exhibit a range of heat and flavors. This diversity is the reason behind the availability of different types of chili powder, each offering its own taste and heat level. Chili peppers originated in Central or South America and were first cultivated in Mexico. European explorers brought chili peppers back to the Old World in the late 16th century as part of the Columbian Exchange, which led to the cultivation of List of Capsicum cultivars, multiple varieties across the world for food and traditional medicine. Five ''Capsicum'' sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Autonomous University Of Mexico
The National Autonomous University of Mexico (, UNAM) is a public university, public research university in Mexico. It has several campuses in Mexico City, and many others in various locations across Mexico, as well as a presence in nine countries. It also has 34 research institutes, 26 museums, and 18 historic sites. A portion of (University City), UNAM's main campus in Mexico City, is a UNESCO World Heritage site that was designed and decorated by some of Mexico's best-known architects and painters. The campus hosted the main events of the 1968 Summer Olympics, and was the birthplace of the Mexican Movement of 1968, student movement of 1968. All Mexican Nobel laureates have been alumni of UNAM. In 2009, the university was awarded the Princess of Asturias Awards, Prince of Asturias Award for Communication and Humanities. More than 25% of the total scientific papers published by Mexican academics come from researchers at UNAM. UNAM was founded in its modern form, on 22 Septemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jorge Klor De Alva
Jose Jorge Klor de Alva, is a Mexican-born anthropologist, the president of Nexus Research and Policy Center, an independent research and policy advocacy organization for the improvement of college education of nontraditional and underserved students. He is also chairman of 3DMX, Inc., a technology company in Silicon Valley that focuses, through its Mexico-based University of Advanced Technologies, on education and training programs in digital and advanced manufacturing technologies. He was previously the Class of 1940 Professor at UC-Berkeley and Professor of Anthropology at Princeton University. Childhood and education J. Jorge Klor de Alva, was born May 28, 1948, in Mexico City. His parents were Maria de los Angeles de Alva, born in San Luis Potosi, and Charles W. Klor, who emigrated with his family to California from Russia in 1915. After WWII his father continued to Mexico, but returned to the U.S. when Klor de Alva was four years old. By 1957 Klor de Alva migrated to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |