|
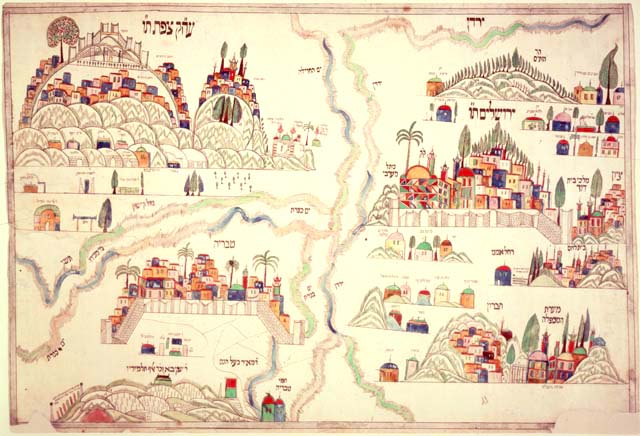
Tzfat
Safed (), also known as Tzfat (), is a city in the Northern District of Israel. Located at an elevation of up to , Safed is the highest city in the Galilee and in Israel. Safed has been identified with (), a fortified town in the Upper Galilee mentioned in the writings of the Roman Jewish historian Josephus. The Jerusalem Talmud mentions Safed as one of five elevated spots where fires were lit to announce the New Moon and festivals during the Second Temple period. Safed attained local prominence under the Crusaders, who built a large fortress there in 1168. It was conquered by Saladin 20 years later, and demolished by his grandnephew al-Mu'azzam Isa in 1219. After reverting to the Crusaders in a treaty in 1240, a larger fortress was erected, which was expanded and reinforced in 1268 by the Mamluk sultan Baybars, who developed Safed into a major town and the capital of a new province spanning the Galilee. After a century of general decline, the stability brought by the Ottoma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
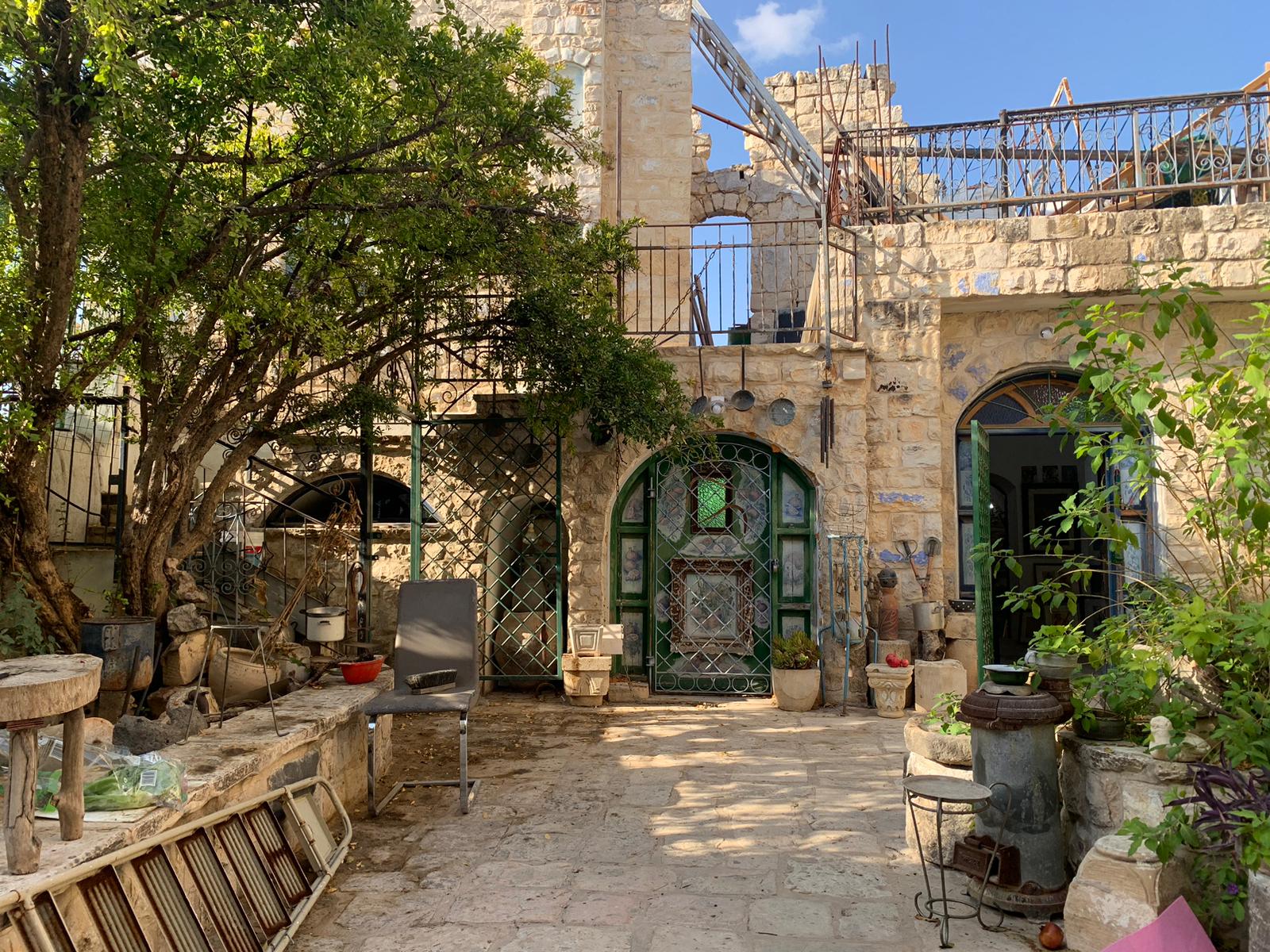
Artists' Quarter Of Safed
The Artists' Quarter in Safed, also known as the Artists' Colony, was officially founded after the capture of Safed, in the 1948 Arab–Israeli War. With the encouragement of the Safed municipality, a group of artists began to restore ruins in the Mamluk neighborhood of Harat al-Wata, on the border of the historic Jewish quarter, to build galleries and open exhibitions. However, artists had begun to settle in Safed prior to this. The first to discover Safed's artistic aura was Isaac Frenkel Frenel in 1920, followed by Moshe Castel and Mordechai Levanon in the 1930s. This attracted dozens of other artists to the Quarter. Safed's mystic aura attracted a wide range of Israeli artists affiliated with different art movements, perhaps most notably the Jewish School of Paris spearheaded by Frenkel. From the 1970s and onward, the Artists' Quarter began to lose its cachet. The founding generation died and those that remained refused to change with the times. Neglected infrastructure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Districts Of Israel
There are six main administrative districts of Israel, known in Hebrew as (; sing. , ) and in Arabic as . There are also 15 subdistricts of Israel, known in Hebrew (; sing. , ) and in Arabic as . Each subdistrict is further divided into natural regions,Key to the Codes in the Maps - Districts, Sub-Districts and Natural Regions 2018 Israel Central Bureau of Statistics, 2021 which in turn are further divided into council-level divisions: whether they might be , |
List Of Cities In Israel
This article lists the 73 localities in Israel that the Ministry of Interior (Israel), Israeli Ministry of Interior has designated as a City council (Israel), city council. It excludes the 4 List of Israeli settlements with city status in the West Bank, Israeli settlements in the West Bank designated as cities, but Israeli occupation of the West Bank, occupied East Jerusalem is included within Jerusalem. The list is based on the current index of the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS). Within Local government in Israel, Israel's system of local government, an urban municipality can be granted a city council by the Interior Ministry when its population exceeds 20,000. The term "city" does not generally refer to Local council (Israel), local councils or urban agglomerations, even though a defined city often contains only a small portion of an urban area or metropolitan area's population. List As for 2022, Israel has 18 cities with populations over 100,000, including Jeru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding territories from Muslim rule. Beginning with the First Crusade, which culminated in the capture of Jerusalem in 1099, these expeditions spanned centuries and became a central aspect of European political, religious, and military history. In 1095, after a Byzantine request for aid,Helen J. Nicholson, ''The Crusades'', (Greenwood Publishing, 2004), 6. Pope Urban II proclaimed the first expedition at the Council of Clermont. He encouraged military support for Byzantine emperor AlexiosI Komnenos and called for an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Across all social strata in Western Europe, there was an enthusiastic response. Participants came from all over Europe and had a variety of motivations. These included religious salvation, satisfying ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1838 Druze Attack On Safed
The 1838 Druze attack on Safed began on July 5, 1838, during the Druze revolt against the rule of Ibrahim Pasha of Egypt. Tensions had mounted as the Druze captured an Egyptian garrison outside of Safed.Rossoff, David. ''Safed: the mystical city''. p.162-165. The local Safed militia of several hundred was heavily outnumbered by the Druze, and the city was gripped in despair as the militia eventually abandoned the city and the Druze rebels entered the city on July 5. The Druze rebels and a Muslim mob descended on the Jewish quarter of Safed and, in scenes reminiscent of the Safed plunder four years earlier, spent three days attacking Jews, plundering their homes and desecrating their synagogues. Besides religious and sectarian tensions, the Jewish community in Safed was seen as being favorable toward Ibrahim Pasha and the Egyptian Eyalet. Some Jews ended up leaving the town, moving south to Jerusalem and Acre. Among them was Yisrael Bak, whose printing press had been destroyed a se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acre, Israel
Acre ( ), known in Hebrew as Akko (, ) and in Arabic as Akka (, ), is a List of cities in Israel, city in the coastal plain region of the Northern District (Israel), Northern District of Israel. The city occupies a strategic location, sitting in a natural harbour at the extremity of Haifa Bay on the coast of the Mediterranean's Levantine Sea. In the Village Statistics, 1945, 1945 census Acre's population numbered 12,360; 9,890 Muslims, 2,330 Christians, 50 Jews and 90 classified as "other".Department of Statistics, 1945, p4Government of Palestine, Department of Statistics. ''Village Statistics, April, 1945.'' Quoted in Hadawi, 1970, p40 Acre Prison, Acre's fort was converted into a jail, where members of the Jewish underground were held during their struggle against the Mandate authorities, among them Ze'ev Jabotinsky, Shlomo Ben-Yosef, and Dov Gruner. Gruner and Ben-Yosef were executed there. Other Jewish inmates were freed by members of the Irgun, who Acre Prison break, brok ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fakhr Al-Din II
Fakhr al-Din Ma'n (; 6 August 1572 13 April 1635), commonly known as Fakhr al-Din II or Fakhreddine II (), was the paramount Druze emir of Mount Lebanon from the Ma'n dynasty, an Ottoman Empire, Ottoman sanjak-bey, governor of Sidon-Beirut Sanjak, Sidon-Beirut and Safed Sanjak, Safed, and the strongman over much of the Ottoman Syria, Levant from the 1620s to 1633. For uniting modern Lebanon's constituent parts and communities, especially the Druze and the Maronites, under a single authority for the first time in history, he is generally regarded as the country's founder. Although he ruled in the name of the Ottomans, he acted with considerable autonomy and developed close ties with European balance of power#Crusades to Westphalia, European powers in defiance of the Sublime Porte, Ottoman imperial government. Fakhr al-Din succeeded his father as the emir of the Chouf mountains in 1591. He was appointed over the sanjaks (districts) of Sidon-Beirut in 1593 and Safed in 1602. Despit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safad Sanjak
Safed Sanjak (; ) was a '' sanjak'' (district) of Damascus Eyalet ( Ottoman province of Damascus) in 1517–1660, after which it became part of the Sidon Eyalet (Ottoman province of Sidon). The sanjak was centered in Safed and spanned the Galilee, Jabal Amil and the coastal cities of Acre and Tyre. The city of Safed was made up of Muslim and Jewish townspeople. At the same time the rest of the sanjak was populated by Sunni Muslims, Bedouins, Metouali Twelver Muslims, and Jewish and Druze peasants. Territory and demographics The territory of Safed Sanjak consisted of the area between the Zahrani River in the north to Mount Carmel (near Haifa) in the south, and the area between the Sea of Galilee in the east and the Mediterranean Sea in the west. Besides Safed, it included the port cities of Acre and Tyre and the entire Galilee and Jabal Amil area. The district had a mixed population of peasants and Bedouin. The inhabitants of the Jabal Amil region were predominantly Shia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Four Holy Cities
In Judaism, the "Four Holy Cities" are Jerusalem, Hebron, Tiberias, and Safed. Revered for their significance to Jewish history, they began to again serve as major centres of Jewish life after the Ottoman conquest of the Levant. According to '' The Jewish Encyclopedia'' in 1906: "Since the sixteenth century the Holiness of Palestine, especially for burial, has been almost wholly transferred to four cities—Jerusalem, Hebron, Tiberias, and Safed." List of the cities and significance Jerusalem Jerusalem has had the highest significance for Jews since the 11th century BCE, when David led the Israelites to conquer it from the Jebusites and established it as the capital city of the Kingdom of Israel and Judah. There, his son and successor Solomon constructed the Temple in Jerusalem, which held the Ark of the Covenant after the Holy of Holies of the Tabernacle. Though the First Temple and the Second Temple were both destroyed in antiquity, the Temple Mount, on which they sto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabbalah
Kabbalah or Qabalah ( ; , ; ) is an esoteric method, discipline and school of thought in Jewish mysticism. It forms the foundation of Mysticism, mystical religious interpretations within Judaism. A traditional Kabbalist is called a Mekubbal (). List of Jewish Kabbalists, Jewish Kabbalists originally developed transmissions of the primary texts of Kabbalah within the realm of Jewish tradition and often use classical Jewish scriptures to explain and demonstrate its mystical teachings. Kabbalists hold these teachings to define the inner meaning of both the Hebrew Bible and traditional rabbinic literature and their formerly concealed transmitted dimension, as well as to explain the significance of Jewish religious observances. Historically, Kabbalah emerged from earlier forms of Jewish mysticism, in 12th- to 13th-century Golden age of Jewish culture in Spain, al-Andalus (Spain) and in Hakhmei Provence, and was reinterpreted during the Jewish mystical renaissance in 16th-century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jewish Textile Industry In 16th-century Safed
The textile industry became an important feature of 16th-century Safed, Ottoman Galilee (at the time within Damascus Eyalet of the Ottoman Empire), following an influx of Jewish immigration in late 15th and early 16th centuries. Run as a Jewish monopoly, textile manufacturing became the community's main source of income. The industry declined toward the end of the century. Jewish refugees settle in Safed After the Alhambra Decree, expulsion of the Jews from Spain in 1492, many sought refuge in Ottoman-controlled lands. They used the opportunity to introduce the production of high-quality wool which they had manufactured in Spain and soon Jewish merchants became significantly involved in the wool trade in nearly all parts of the Ottoman Empire. Many made their way to Safed, which with its numerous springs and nearby streams, had the perfect geological conditions for the manufacture of wool-cloth. In 1522, Safed's Jewish population stood at three hundred families. The influx of Spa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |