|
Tzav (parsha)
Tzav, Tsav, Zav, Sav, or Ṣaw (—Hebrew for "command," the sixth word, and the first distinctive word, in the parashah) is the 25th weekly Torah portion (, ''parashah'') in the annual Jewish cycle of Torah reading and the second in the Book of Leviticus. The parashah teaches how the priests performed the sacrifices and describes the ordination of Aaron and his sons. The parashah constitutes Leviticus 6:1–8:36. The parashah is made up of 5,096 Hebrew letters, 1,353 Hebrew words, 97 verses, and 170 lines in a Torah scroll (, ''Sefer Torah''). Jews read it the 24th or 25th Sabbath after Simchat Torah, generally in the second half of March or the first half of April. Readings In traditional Shabbat Torah reading, the parashah is divided into seven readings called '' aliyot'' (). First reading—Leviticus 6:1–11 In the first reading, God told Moses to command Aaron and the priests about the rituals of the sacrifices (, ''qārbānoṯ''). The burnt offering (, ''ʿolā'') w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabernacle Camp
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle (), also known as the Tent of the Congregation (, also Tent of Meeting), was the portable earthly dwelling of God used by the Israelites from the Exodus until the conquest of Canaan. Moses was instructed at Mount Sinai to construct and transport the tabernacle with the Israelites on their journey through the wilderness and their subsequent conquest of the Promised Land. After 440 years, Solomon's Temple in Jerusalem superseded it as the dwelling-place of God. The main source describing the tabernacle is the biblical Book of Exodus, specifically Exodus 25–31 and 35–40. Those passages describe an inner sanctuary, the Holy of Holies, created by the veil suspended by four pillars. This sanctuary contained the Ark of the Covenant, with its cherubim-covered mercy seat. An outer sanctuary (the "Holy Place") contained a gold lamp-stand or candlestick. On the north side stood a table, on which lay the showbread. On the south side was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
God In Judaism
In Judaism, God has been conceived in a variety of ways. Traditionally, Judaism holds that Yahweh—that is, the God in Abrahamic religions#Judaism, god of Abraham, Isaac and Jacob, and the national god of the Israelites—delivered them from The Exodus, slavery in Egypt, and gave them the Law of Moses at Mount Sinai (Bible), Mount Sinai as described in the Torah. Jews traditionally believe in a Monotheism, monotheistic conception of God ("Shema Yisrael, God is one"), characterized by both Transcendence (religion), transcendence (independence from, and separation from, the material universe) and immanence (active involvement in the material universe). God is seen as unique and perfect, free from all faults, and is believed to be omnipotent, omnipresent, omniscient, and Absolute infinite, infinite in all attributes, with no partner or equal, serving as the sole Creator deity, creator of everything in existence. In Judaism, Aniconism in Judaism, God is never portrayed in any ima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kidney
In humans, the kidneys are two reddish-brown bean-shaped blood-filtering organ (anatomy), organs that are a multilobar, multipapillary form of mammalian kidneys, usually without signs of external lobulation. They are located on the left and right in the retroperitoneal space, and in adult humans are about in length. They receive blood from the paired renal artery, renal arteries; blood exits into the paired renal veins. Each kidney is attached to a ureter, a tube that carries excreted urine to the urinary bladder, bladder. The kidney participates in the control of the volume of various body fluids, fluid osmolality, Acid-base homeostasis, acid-base balance, various electrolyte concentrations, and removal of toxins. Filtration occurs in the glomerulus (kidney), glomerulus: one-fifth of the blood volume that enters the kidneys is filtered. Examples of substances reabsorbed are solute-free water, sodium, bicarbonate, glucose, and amino acids. Examples of substances secreted are hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guilt Offering
A guilt offering (; plural ), also referred to as a trespass offering (KJV, 1611), was a type of Biblical sacrifice, specifically a sacrifice made as a compensation payment for unintentional and certain intentional transgressions. It was distinct from the Biblical sin offering. Hebrew Bible Guilt offerings or trespass offerings were mandated in Leviticus, chapters 5 to 7, where references are made to the offering "for sin" or "for sins". In the Greek Septuagint, the phrase used is the offering ''peri tes plemmeleias'' (περὶ τῆς πλημμελείας). The transgressor furnished an unblemished ram for sacrifice at the Temple in Jerusalem, as well as (in cases of sins against holy items, theft, commission of fraud or false oaths) monetary compensation to the victim for their loss, plus a mark-up of 20% of the value to cover the priest's earnings. Monetary restitution had to be given in the pre-exile version of the currency (the ''shekel of the sanctuary''), rather tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle (), also known as the Tent of the Congregation (, also Tent of Meeting), was the portable earthly dwelling of God used by the Israelites from the Exodus until the conquest of Canaan. Moses was instructed at biblical Mount Sinai, Mount Sinai to construct and transport the tabernacle with the Israelites on their journey through the wilderness and their subsequent conquest of the Promised Land. After 440 years, Solomon's Temple in Jerusalem superseded it as the dwelling-place of God. The main source describing the tabernacle is the biblical Book of Exodus, specifically Exodus 25–31 and 35–40. Those passages describe an inner sanctuary, the Holy of Holies, created by the veil suspended by four pillars. This sanctuary contained the Ark of the Covenant, with its cherubim-covered mercy seat. An outer sanctuary (the "Holy Place") contained a gold lamp-stand or candlestick. On the north side stood a table, on which lay the showbread. On th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood is composed of blood cells suspended in blood plasma. Plasma, which constitutes 55% of blood fluid, is mostly water (92% by volume), and contains proteins, glucose, mineral ions, and hormones. The blood cells are mainly red blood cells (erythrocytes), white blood cells (leukocytes), and (in mammals) platelets (thrombocytes). The most abundant cells are red blood cells. These contain hemoglobin, which facilitates oxygen transport by reversibly binding to it, increasing its solubility. Jawed vertebrates have an adaptive immune system, based largely on white blood cells. White blood cells help to resist infections and parasites. Platelets are important in the clotting of blood. Blood is circulated around the body through blood vessels by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sin Offering
A sin offering (, ''korban ḥatat'', , lit: "purification offering") is a sacrificial offering described and commanded in the Torah (Lev. 4.1-35); it could be fine flour or a proper animal.Leviticus 5:11 A sin offering also occurs in 2 Chronicles 29:21 where seven bulls, seven rams, seven lambs and seven he-goats were sacrificed on the command of King Hezekiah for the kingdom, for the sanctuary, and for Judah. Like all types of sacrifices offered on the altar, the flour had to be unscented and the animal had to be completely unblemished. This offered sacrifice accompanied the important required core means of atonement for the committing of an ''unintentional'' transgression of a prohibition, that either has brought guilt upon the 'community of Israel' or the individual.''Jewish Encyclopedia'' This offering is brought during or after atonement for those transgressions that had been committed inadvertently, or in ignorance: intentional transgressions could only be absolved by othe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
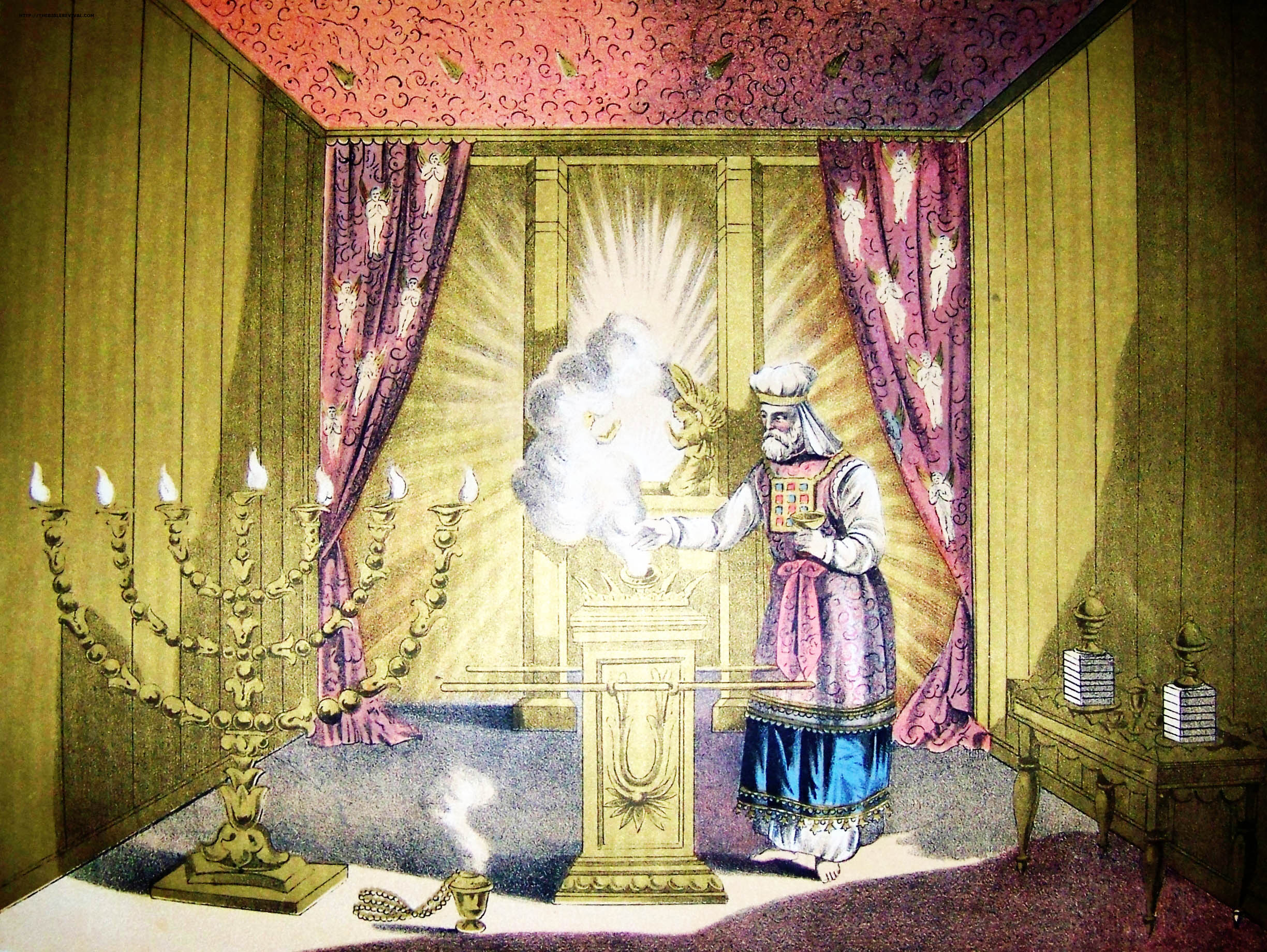
High Priest (Judaism)
In Judaism, the High Priest of Israel (, lit. ‘great priest’; Aramaic: ''Kahana Rabba'') was the head of the Israelite priesthood. He played a unique role in the worship conducted in the Tabernacle and later in the Temple in Jerusalem, as well as in some non-ritual matters. Like all priests, he was required to be descended from Aaron (the first biblical priest). But unlike other priests, the high priest followed more restrictive laws, wore unique priestly garments, and was the only priest allowed to perform certain ceremonies. Titles The high priest is referred to by a number of titles in the Hebrew Bible; the title ''kohen gadol'' did not become dominant until well into the Second Temple period. In addition to the title of "great priest" (''kohen gadol'') which later became the standard Hebrew title, the term "head priest" (''kohen harosh''; ) was used, as was "anointed priest" (''kohen mashiach''; )., , The Torah sometimes uses longer descriptions: "the great priest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leavening Agent
In cooking, a leavening agent () or raising agent, also called a leaven () or leavener, is any one of a number of substances used in doughs and batters that cause a foaming action (gas bubbles) that lightens and softens the mixture. An alternative or supplement to leavening agents is mechanical action by which air is incorporated (i.e. kneading). Leavening agents can be biological or synthetic chemical compounds. The gas produced is often carbon dioxide, or occasionally hydrogen. When a dough or batter is mixed, the starch in the flour and the water in the dough form a matrix (often supported further by proteins like gluten or polysaccharides, such as pentosans or xanthan gum). The starch then gelatinizes and sets, leaving gas bubbles that remain. Biological leavening agents * ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' producing carbon dioxide found in: ** baker's yeast ** Beer barm (unpasteurised—live yeast) ** ginger beer ** kefir ** sourdough starter * '' Clostridium perfring ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gift Offering
A meal offering, grain offering, or gift offering (, ), is a type of Biblical sacrifice, specifically a sacrifice that did not include sacrificial animals. In older English it is sometimes called an oblation, from Latin. The Hebrew noun () is used 211 times in the Masoretic Text of the Hebrew Bible with the first instances being the offered by both Cain and Abel in Genesis 4:3-5. It is also used of Jacob's "present" to Esau in Genesis 32 and again of the "present" to the Egyptian ruler (who was in fact Joseph, his own son) in Genesis 43. In the King James Version of 1611 this was rendered as "", e.g. in Exodus 29:41, since at the time the King James Version was written, referred to food in general rather than the flesh of animals in particular. In the Hebrew Bible Gift offerings were often made on their own, but also accompanied the burnt offering. Scholars believe that the term "gift offering" originally referred to all voluntary sacrifices, but that it later came to j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wood
Wood is a structural tissue/material found as xylem in the stems and roots of trees and other woody plants. It is an organic materiala natural composite of cellulosic fibers that are strong in tension and embedded in a matrix of lignin that resists compression. Wood is sometimes defined as only the secondary xylem in the stems of trees, or more broadly to include the same type of tissue elsewhere, such as in the roots of trees or shrubs. In a living tree, it performs a mechanical-support function, enabling woody plants to grow large or to stand up by themselves. It also conveys water and nutrients among the leaves, other growing tissues, and the roots. Wood may also refer to other plant materials with comparable properties, and to material engineered from wood, woodchips, or fibers. Wood has been used for thousands of years for fuel, as a construction material, for making tools and weapons, furniture and paper. More recently it emerged as a feedstock for the production ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fire
Fire is the rapid oxidation of a fuel in the exothermic chemical process of combustion, releasing heat, light, and various reaction Product (chemistry), products. Flames, the most visible portion of the fire, are produced in the combustion reaction when the fuel reaches its ignition point temperature. Flames from hydrocarbon fuels consist primarily of carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen, and nitrogen. If hot enough, the gases may become ionized to produce Plasma (physics), plasma. The color and Intensity (heat transfer), intensity of the flame depend on the type of fuel and composition of the surrounding gases. Fire, in its most common form, has the potential to result in conflagration, which can lead to permanent physical damage. It directly impacts land-based ecological systems worldwide. The positive effects of fire include stimulating plant growth and maintaining ecological balance. Its negative effects include hazards to life and property, atmospheric pollution, and water ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |