|
Tyrannoneustes
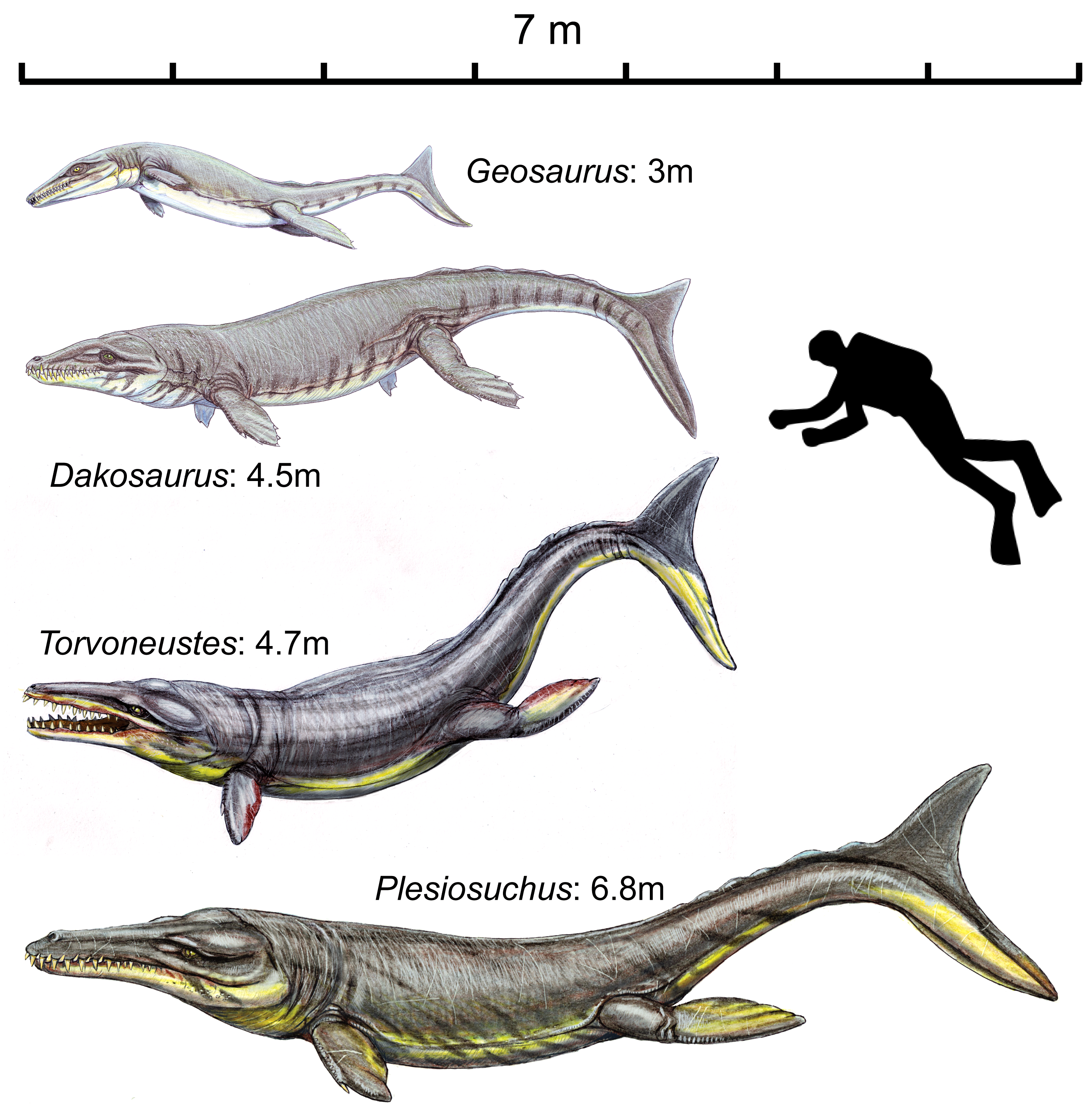
''Tyrannoneustes'' is an extinct genus of geosaurine metriorhynchid crocodyliform from the Callovian stage Oxford Clay Formation of England and the Marnes de Dives of France. It contains a single species, ''Tyrannoneustes lythrodectikos'', meaning "blood-biting tyrant swimmer". History and description The genus was rediscovered after a century of storage in a museum basement after being unearthed by fossil hunter Alfred Nicholson Leeds between the years of 1907 and 1909. Its lower jaw measured about 26 inches long and its teeth were blade-like, likely built to attack prey as large or larger than itself, similar to the Late Jurassic ''Dakosaurus'', ''Torvoneustes'', and ''Plesiosuchus ''Plesiosuchus'' is an extinct genus of geosaurine metriorhynchid crocodyliform known from the Late Jurassic (late Kimmeridgian to early Tithonian stage) of Dorset, England and possibly also Spain. It contains a single species, ''Plesiosuchus ...''. The holotype specimen was estimated to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geosaurine
Geosaurinae is a subfamily of metriorhynchid crocodyliforms from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous (Bathonian - Aptian) of Europe, North America and South America. Named by Richard Lydekker, in 1889, it contains the metriorhynchids ''Suchodus'', ''Purranisaurus'', ''Neptunidraco'', '' Tyrannoneustes'', ''Torvoneustes'', ''Dakosaurus'', ''Geosaurus'' and ''Plesiosuchus''. The last four taxa form a tribe within Geosaurinae, the Geosaurini. Geosaurinae is one of two subfamilies of Metriorhynchidae, the other being Metriorhynchinae. These marine reptiles were widespread during the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous, their fossilized remains are being frequently found on various places around the world.Daniel Madzia, Sven Sachs, Mark T. Young, Alexander Lukeneder and Petr Skupien (2021)Evidence of two lineages of metriorhynchid crocodylomorphs in the Lower Cretaceous of the Czech Republic ''Acta Palaeontologica Polonica''. doi: https://doi.org/10.4202/app.00801.2020 Phylo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford Clay
The Oxford Clay (or Oxford Clay Formation) is a Jurassic marine sedimentary rock formation underlying much of southeast England, from as far west as Dorset and as far north as Yorkshire. The Oxford Clay Formation dates to the Jurassic, specifically, the Callovian and Oxfordian ages, and comprises two main facies. The lower facies comprises the Peterborough Member, a fossiliferous organic-rich mudstone. This facies and its rocks are commonly known as lower Oxford Clay. The upper facies comprises the middle Oxford Clay, the Stewartby Member, and the upper Oxford Clay, the Weymouth Member. The upper facies is a fossil poor assemblage of calcareous mudstones. Oxford Clay appears at the surface around Oxford, Peterborough and Weymouth and is exposed in many quarries around these areas. The top of the Lower Oxford Clay shows a lithological change, where fissile shale changes to grey mudstone. The Middle and Upper Oxford Clays differ slightly, as they are separated by an argillaceo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metriorhynchid
Metriorhynchidae is an extinct family of specialized, aquatic metriorhynchoid crocodyliforms from the Middle Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous period (Bajocian to early Aptian) of Europe, North America and South America. The name Metriorhynchidae was coined by the Austrian zoologist Leopold Fitzinger in 1843.Fitzinger LJFJ. 1843. ''Systema Reptilium''. Wien: Braumüller et Seidel, 106 pp. The group contains two subfamilies, the Metriorhynchinae and the Geosaurinae. They represent the most marine adapted of all archosaurs. Description Metriorhynchids are fully aquatic crocodyliforms. Their forelimbs were small and paddle-like, and unlike living crocodylians, they lost their osteoderms ("armour scutes"). Their body shape maximised hydrodynamy (swimming efficiency), as they did have a shark-like tail fluke. Like ichthyosaurs and plesiosaurs, metriorhynchids developed smooth, scaleless skin. Metriorhynchids were the only group of archosaurs to become fully adapted to the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marnes De Dives
The Marnes de Dives is a geological formation in Normandy, France. It dates back to the upper part of the Callovian stage of the Middle Jurassic.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Middle Jurassic, Europe)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 538–541. . And is partially equivalent to the Oxford Clay in England. It predominantly consists of ooidal marl, rich in pyrite and lignite, interbedded with thin limestone horizons. It is best exposed at the base of the Falaises des Vaches Noires (Cliffs of Black Cows) as well as the foreshore at low tide. It is known for its fossils, notably those of ammonites, marine crocodiles and fragmentary remains of dinosaurs, mostly theropods. Vertebrate fauna See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations This list of dinosaur-bearing rock formations is a list of geologic formations in which dinosaur fossils h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alfred Nicholson Leeds
Alfred Nicholson Leeds (9 March 184725 August 1917) was an English amateur palaeontologist. Biography Leeds was born at Eyebury, Peterborough, the youngest of the eight children of Edward Thurlow Leeds (180251) and Eliza Mary Leeds (née Nicholson). He was educated at Warwick School. He had wanted to become a doctor, but circumstances meant that from 1868 he had to take on the management of Eyebury Farm (in The Fens, and historically attached to Peterborough Abbey) as a gentleman farmer. His elder brother Charles, a student at the University of Oxford, had been encouraged by Professor John Phillips to persevere in collecting fossils from near his home. Alfred joined him in these searches, and between them they developed better methods of disinterring, and of scientifically recording, fossils in soft clay than had been used before. (They rewarded the workmen at the clay pits (which served a brickworks in Fletton, Peterborough) for not doing so themselves, but instead sending no ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Callovian
In the geologic timescale, the Callovian is an age and stage in the Middle Jurassic, lasting between 166.1 ± 4.0 Ma (million years ago) and 163.5 ± 4.0 Ma. It is the last stage of the Middle Jurassic, following the Bathonian and preceding the Oxfordian. Stratigraphic definitions The Callovian Stage was first described by French palaeontologist Alcide d'Orbigny in 1852. Its name derives from the latinized name for Kellaways Bridge, a small hamlet 3 km north-east of Chippenham, Wiltshire, England. The base of the Callovian is defined as the place in the stratigraphic column where the ammonite genus '' Kepplerites'' first appears, which is the base of the biozone of '' Macrocephalites herveyi''. A global reference profile (a GSSP) for the base had in 2009 not yet been assigned. The top of the Callovian (the base of the Oxfordian) is at the first appearance of ammonite species '' Brightia thuouxensis''. Subdivision The Callovian is often subdivided into three substages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prehistoric Marine Crocodylomorphs
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The use of symbols, marks, and images appears very early among humans, but the earliest known writing systems appeared 5000 years ago. It took thousands of years for writing systems to be widely adopted, with writing spreading to almost all cultures by the 19th century. The end of prehistory therefore came at very different times in different places, and the term is less often used in discussing societies where prehistory ended relatively recently. In the early Bronze Age, Sumer in Mesopotamia, the Indus Valley Civilisation, and ancient Egypt were the first civilizations to develop their own scripts and to keep historical records, with their neighbors following. Most other civilizations reached the end of prehistory during the following Iron Age. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic France
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and is the only boundary between geological periods to remain formally undefined. By the beginning of the Jurassic, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossils Of England
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitatively measure the absolu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic England
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and is the only boundary between geological periods to remain formally undefined. By the beginning of the Jurassic, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |