|
Tutira Mai Nga Iwi
Tutira () is a village to the north of Napier and is part of the Hawke's Bay Region in New Zealand's North Island. It is located on State Highway 2 between Wairoa and Napier. Much of the area was surveyed by Herbert Guthrie-Smith, who farmed 60,000 acres (240 km²) surrounding Lake Tūtira. Guthrie-Smith, a naturalist, published the popular ''Tutira: the story of a New Zealand sheep station'' in 1921. Today, a camp is run at the site of his homestead. Demographics Puketitiri-Tutira statistical area, which includes Waipātiki Beach, Tangoio and Te Haroto, covers and had an estimated population of as of with a population density of people per km2. Before the 2023 census, the statistical area had a larger boundary, covering . Using that boundary, Puketitiri-Tutira had a population of 1,839 at the 2018 New Zealand census, an increase of 87 people (5.0%) since the 2013 census, and an increase of 96 people (5.5%) since the 2006 census. There were 708 households, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of New Zealand
New Zealand is divided into sixteen regions for local government in New Zealand, local government purposes. Eleven are administered by regional councils, and five are administered by Unitary authority#New Zealand, unitary authorities, which are territorial authorities of New Zealand, territorial authorities that also perform the functions of regional councils. Although technically a district but classed as a territory, The Chatham Islands Territory is outside the regions and is administered by the Chatham Islands Council, which is similar to a unitary authority, authorised under its own legislation. Current regions History and statutory basis The regional councils are listed in Part 1 of Schedule 2 of the Local Government Act 2002, along with reference to the ''New Zealand Gazette, Gazette'' notices that established them in 1989. The act requires regional councils to promote sustainable developmentthe social, economic, environmental and cultural well-being of their communitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naturalist
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is called a naturalist or natural historian. Natural history encompasses scientific research but is not limited to it. It involves the systematic study of any category of natural objects or organisms, so while it dates from studies in the ancient Greco-Roman world and the mediaeval Arabic world, through to European Renaissance naturalists working in near isolation, today's natural history is a cross-discipline umbrella of many specialty sciences; e.g., geobiology has a strong multidisciplinary nature. Definitions Before 1900 The meaning of the English term "natural history" (a calque of the Latin ''historia naturalis'') has narrowed progressively with time, while, by contrast, the meaning of the related term "nature" has widened (see also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion Of Māori People
The Māori people, Māori people have a Polynesian mythology, Polynesian religion that, prior to the introduction of Christianity in New Zealand, Christianity to New Zealand was the main religious belief for Māori. By 1845, more than half of the Māori population attended church and Christianity remains the largest religion for Māori. Very few Māori still follow traditional Māori religion, although many elements of it are still observed. Several Māori religious movements have been born out of Christianity, such as the Ratana movement. Traditional Māori religion Traditional Māori religion, that is, the pre-European belief-system of the Māori people , Māori, differed little from that of their perceived homeland, Hawaiki, Hawaiki Nui, aka Raʻiātea or Raiatea, conceiving of everything – including natural elements and all living things – as connected by common descent through whakapapa or genealogy. Accordingly, Māori regarded all things as possessing a life force ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity In New Zealand
Christianity in New Zealand dates to the arrival of missionary, missionaries from the Church Missionary Society who were welcomed onto the beach at Rangihoua Bay in December 1814. It soon became the predominant belief amongst the indigenous people, with over half of Māori people, Māori regularly attending church services within the first 30 years. Christianity remains New Zealand's largest religious group, but no one denomination is dominant and there is no official state church. According to the 2018 New Zealand census, 2018 census 38.17% of the population identified as Christians, Christian. The largest Christian groups are Anglican Church in New Zealand, Anglican, Catholic Church in New Zealand, Catholic and Presbyterian Church in New Zealand, Presbyterian. Christian organisations are the leading non-government providers of social services in New Zealand. History The first Christian church service, service conducted in New Zealand waters was probably to be carried out by F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asian New Zealanders
Asian New Zealanders are New Zealanders of Asian ancestry (including naturalised New Zealanders who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). At the 2023 census, 861,573 New Zealanders identified as being of Asian ethnicity, making up 17.3% of New Zealand's population. The first Asians in New Zealand were Chinese workers who migrated to New Zealand to work in the gold mines in the 1860s. The modern period of Asian immigration began in the 1970s when New Zealand relaxed its restrictive policies to attract migrants from Asia. Terminology Under Statistics New Zealand classification, the term refers to a pan-ethnic group that includes diverse populations who have ancestral origins in East Asia (e.g. Chinese, Korean, Japanese), Southeast Asia (e.g. Filipino, Vietnamese, Malaysian), and South Asia (e.g. Nepalese, Indian (incl. Indo-Fijians), Sri Lankan, Bangladeshi, Pakistani). New Zealanders of West Asian and Central Asi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
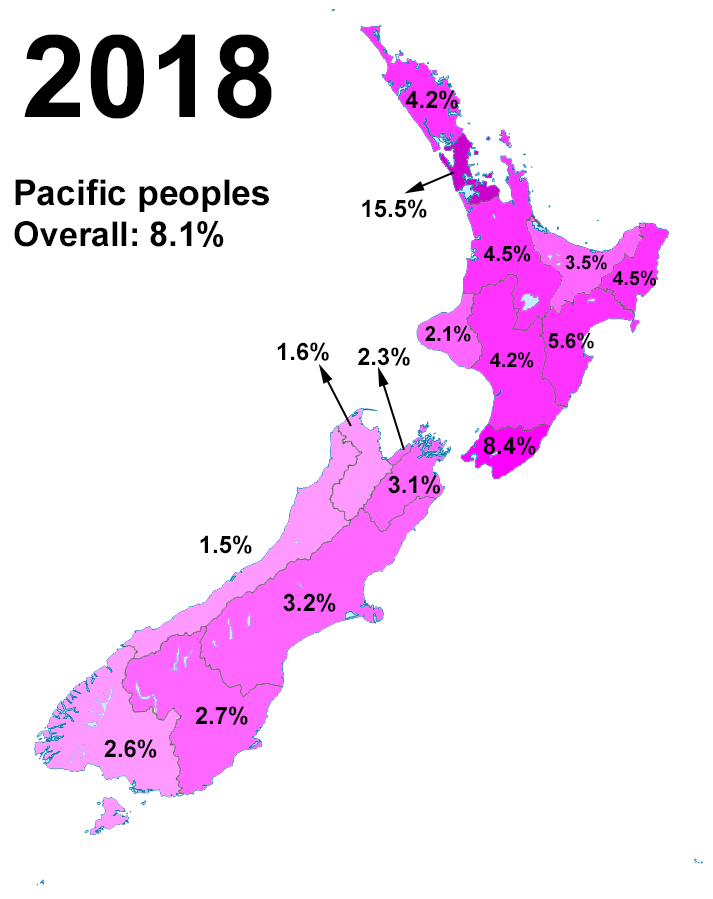
Pasifika New Zealanders
Pasifika New Zealanders (also called Pacific Peoples) are a pan-ethnic group of New Zealanders associated with, and descended from, the indigenous peoples of the Pacific Islands (also known as Pacific Islander#New Zealand, Pacific Islanders) outside New Zealand itself. They form the fourth-largest ethnic grouping in the country, after European New Zealanders, European descendants, indigenous Māori people, Māori, and Asian New Zealanders. Over 380,000 people identify as being of Pacific origin, representing 8% of the country's population, with the majority residing in Auckland. History Prior to the Second World War Pasifika in New Zealand numbered only a few hundred. Wide-scale Pasifika migration to New Zealand began in the 1950s and 1960s, typically from countries associated with the Commonwealth and the Realm of New Zealand, including Western Samoa (modern-day Samoa), the Cook Islands and Niue. In the 1970s, governments (both New Zealand Labour Party, Labour and New Zealand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Māori People
Māori () are the Indigenous peoples of Oceania, indigenous Polynesians, Polynesian people of mainland New Zealand. Māori originated with settlers from East Polynesia, who arrived in New Zealand in several waves of Māori migration canoes, canoe voyages between roughly 1320 and 1350. Over several centuries in isolation, these settlers developed Māori culture, a distinct culture, whose language, mythology, crafts, and performing arts evolved independently from those of other eastern Polynesian cultures. Some early Māori moved to the Chatham Islands, where their descendants became New Zealand's other indigenous Polynesian ethnic group, the Moriori. Early contact between Māori and Europeans, starting in the 18th century, ranged from beneficial trade to lethal violence; Māori actively adopted many technologies from the newcomers. With the signing of the Treaty of Waitangi, Treaty of Waitangi/Te Tiriti o Waitangi in 1840, the two cultures coexisted for a generation. Rising ten ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pākehā
''Pākehā'' (or ''Pakeha''; ; ) is a Māori language, Māori-language word used in English, particularly in New Zealand. It generally means a non-Polynesians, Polynesian New Zealanders, New Zealander or more specifically a European New Zealanders, European New Zealander. It is not a legal term and has no definition under New Zealand law. ''Papa'a'' has a similar meaning in Cook Islands Māori. Etymology and history The etymology of is uncertain. The most likely sources are the Māori words or , which refer to an oral tale of a "mythical, human like being, with fair skin and hair who possessed canoes made of reeds which changed magically into sailing vessels". When Europeans first arrived they rowed to shore in longboats, facing backwards: In traditional Māori canoes or , paddlers face the direction of travel. This is supposed to have led to the belief by some, that the sailors were ''patupaiarehe'' (supernatural beings). There have been several dubious interpretati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |