|
Turtle Graphics
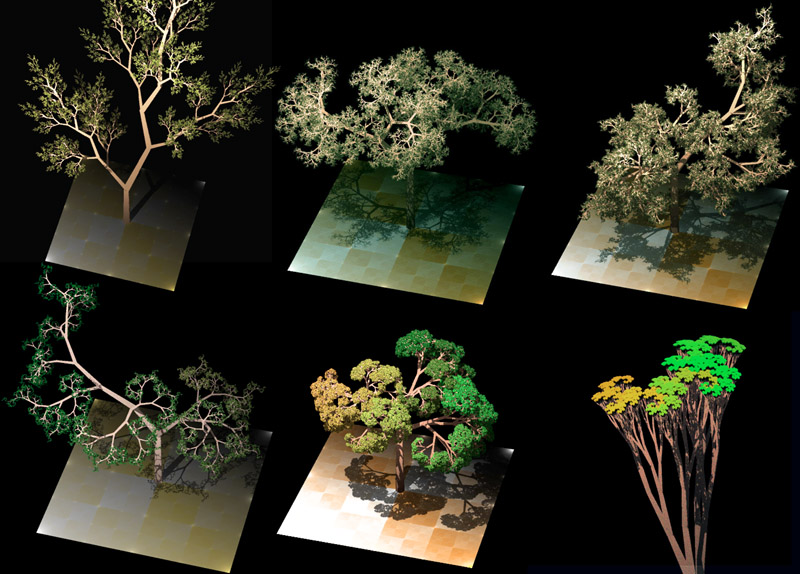
In computer graphics, turtle graphics are vector graphics using a relative cursor (the "turtle") upon a Cartesian plane (x and y axis). Turtle graphics is a key feature of the Logo programming language. It is also a simple and didactic way of dealing with moving frames. Overview The turtle has three attributes: a location, an orientation (or direction), and a pen. The pen, too, has attributes: color, width, and on/off state (also called ''down'' and ''up''). The turtle moves with commands that are relative to its own position, such as "move forward 10 spaces" and "turn left 90 degrees". The pen carried by the turtle can also be controlled, by enabling it, setting its color, or setting its width. A student could understand (and predict and reason about) the turtle's motion by imagining what they would do if they were the turtle. Seymour Papert called this "body syntonic" reasoning. A full turtle graphics system requires control flow, procedures, and recursion: many turtl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images and art with the aid of computers. Computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, digital art, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by graphics hardware, computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as Computer-generated imagery, computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of Computer graphics (computer science), computer science research. Some topics in computer graphics include user interface design, Sprite (computer graphics), sprite graphics, raster graphics, Rendering (computer graph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Python (programming Language)
Python is a high-level programming language, high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design philosophy emphasizes code readability with the use of significant indentation. Python is type system#DYNAMIC, dynamically type-checked and garbage collection (computer science), garbage-collected. It supports multiple programming paradigms, including structured programming, structured (particularly procedural programming, procedural), object-oriented and functional programming. It is often described as a "batteries included" language due to its comprehensive standard library. Guido van Rossum began working on Python in the late 1980s as a successor to the ABC (programming language), ABC programming language, and he first released it in 1991 as Python 0.9.0. Python 2.0 was released in 2000. Python 3.0, released in 2008, was a major revision not completely backward-compatible with earlier versions. Python 2.7.18, released in 2020, was the last release of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joy (programming Language)
The Joy programming language in computer science is a purely functional programming language that was produced by Manfred von Thun of La Trobe University in Melbourne, Australia. Joy is based on composition of functions rather than lambda calculus. It was inspired by the Function-level programming, function-level programming style of John Backus's FP (programming language), FP. It has turned out to have many similarities to Forth (programming language), Forth, due not to design but to an independent evolution and convergence. Overview Functions in Joy lack Parameter (computer science), formal parameters. For example, a function that squares a numeric input can be expressed as follows: DEFINE square dup * . In Joy, everything is a function that takes a stack (data structure), stack as an argument and returns a stack as a result. For instance, the numeral '5' does not represent an integer constant, but instead a short program that pushes the number 5 onto the stack. * The d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MSWLogo
MSWLogo is a programming language which is interpreted language, interpreted, based on the computer language Logo (programming language), Logo, with a graphical user interface (GUI) front end. George Mills developed it at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Its core is the same as UCBLogo by Brian Harvey (lecturer), Brian Harvey. It is free and open-source software, with source code available, in Borland C++. MSWLogo supports multiple turtle graphics, 3D computer graphics, and allows input from ports COM (hardware interface), COM and Parallel port, LPT. It also supports a Windows interface, so input/output (I/O) is available through this GUI, and keyboard and mouse events can trigger interrupts. Simple GIF animations may also be produced on MSWLogo version 6.5 with the command gifsave. The program is also used as educational software. Jim Muller wrote ''The Great Logo Adventure'', a complete Logo manual using MSWLogo as the demonstration language. MSWLogo has evolved ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FMSLogo
''FMSLogo'' is a free implementation of a computing environment called Logo, which is an educational interpreter language. GUI and Extensions were developed by George Mills at MIT. Its core is the same as UCBLogo by Brian Harvey. It is free software, with source available, written with Borland C++ and WxWidgets. FMSLogo supports multiple turtles, and 3D Graphics. FMSLogo allows input from COM ports and LPT ports. FMSLogo also supports a windows interface thus I/O is available through this GUI- and keyboard and mouse events can trigger interrupts. Simple GIF animations may also be produced with the GIFSAVE command. Jim Muller wrote ''The Great Logo Adventure'', a complete Logo manual using MSWLogo as the demonstration language. FMSLogo evolved from MSWLogo: An Educational Programming Environment, a free, open source implementation of the Logo programming language for Microsoft Windows Windows is a Product lining, product line of Proprietary software, proprietary graphical u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NetLogo
NetLogo is a programming language and integrated development environment An integrated development environment (IDE) is a Application software, software application that provides comprehensive facilities for software development. An IDE normally consists of at least a source-code editor, build automation tools, an ... (IDE) for agent-based modeling. About NetLogo was designed by Uri Wilensky, in the spirit of the programming language Logo (programming language), Logo, to be "low threshold and no ceiling". It teaches programming concepts using Agent-based model, agents in the form of ''turtles'', ''patches'', ''links'' and the ''observer''. NetLogo was designed with multiple audiences in mind, in particular: teaching children in the education community, and for Subject-matter expert, domain experts without a programming background to model related phenomena. Thousands of scientific articles have been published using NetLogo. The NetLogo environment enables exploration of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UCBLogo
UCBLogo, also termed Berkeley Logo, is a programming language, a dialect of Logo, which derived from Lisp. It is a dialect of Logo intended to be a "minimum Logo standard". It has the best facilities for handling lists, files, input/output (I/O), and recursion. It can be used to teach most computer science concepts, as University of California, Berkeley lecturer Brian Harvey did in his ''Computer Science Logo Style'' trilogy. It is free and open-source software released under a GNU General Public License (GPL). Design Logo was designed in spirit of low threshold and no ceiling, which enables easy entry by novices and yet meet the needs of high-powered users. UCBLogo has a rudimentary graphical user interface (GUI), so several projects exist that provide a better interface. ''MSWLogo'' and its successor ''FMSLogo'', for Microsoft Windows, are commonly used in schools in the United Kingdom and Australia. For input/output (I/O), text may be written to the command window (output ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L-system
An L-system or Lindenmayer system is a parallel rewriting system and a type of formal grammar. An L-system consists of an alphabet of symbols that can be used to make strings, a collection of production rules that expand each symbol into some larger string of symbols, an initial "axiom" string from which to begin construction, and a mechanism for translating the generated strings into geometric structures. L-systems were introduced and developed in 1968 by Aristid Lindenmayer, a Hungarian theoretical biologist and botanist at the University of Utrecht. Lindenmayer used L-systems to describe the behaviour of plant cells and to model the growth processes of plant development. L-systems have also been used to model the morphology of a variety of organisms and can be used to generate self-similar fractals. Origins As a biologist, Lindenmayer worked with yeast and filamentous fungi and studied the growth patterns of various types of bacteria, such as the cyanobacteria '' Anabaena ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moving Frame
In mathematics, a moving frame is a flexible generalization of the notion of a coordinate frame (an ordered basis of a vector space, in conjunction with an origin) often used to study the extrinsic differential geometry of smooth manifolds embedded in a homogeneous space. Introduction In lay terms, a ''frame of reference'' is a system of measuring rods used by an observer to measure the surrounding space by providing coordinates. A moving frame is then a frame of reference which moves with the observer along a trajectory (a curve). The method of the moving frame, in this simple example, seeks to produce a "preferred" moving frame out of the kinematic properties of the observer. In a geometrical setting, this problem was solved in the mid 19th century by Jean Frédéric Frenet and Joseph Alfred Serret. The Frenet–Serret frame is a moving frame defined on a curve which can be constructed purely from the velocity and acceleration of the curve. The Frenet–Serret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Java (programming Language)
Java is a High-level programming language, high-level, General-purpose programming language, general-purpose, Memory safety, memory-safe, object-oriented programming, object-oriented programming language. It is intended to let programmers ''write once, run anywhere'' (Write once, run anywhere, WORA), meaning that compiler, compiled Java code can run on all platforms that support Java without the need to recompile. Java applications are typically compiled to Java bytecode, bytecode that can run on any Java virtual machine (JVM) regardless of the underlying computer architecture. The syntax (programming languages), syntax of Java is similar to C (programming language), C and C++, but has fewer low-level programming language, low-level facilities than either of them. The Java runtime provides dynamic capabilities (such as Reflective programming, reflection and runtime code modification) that are typically not available in traditional compiled languages. Java gained popularity sh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |